ABSTRACT
INTRODUCTION: Placement of breast implants is the most commonly used form of breast reconstruction. Despite its advantages, infection of the implant, either in the tissue expander or mammary prosthesis, can be a significant problem, including the need to remove it. The objective of this work is to evaluate the infection rate of breast implants used for breast reconstruction in patients submitted to surgery at the Cancer Institute of the State of São Paulo (ICESP), as well as its correlation with clinical, oncological, and surgical factors.
PATIENTS AND METHODS: This is a retrospective study on 120 patients submitted to breast reconstruction with breast implants at the ICESP from February 2009 to March 2010.
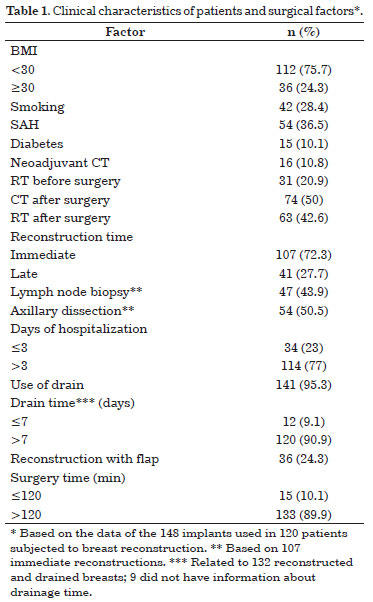
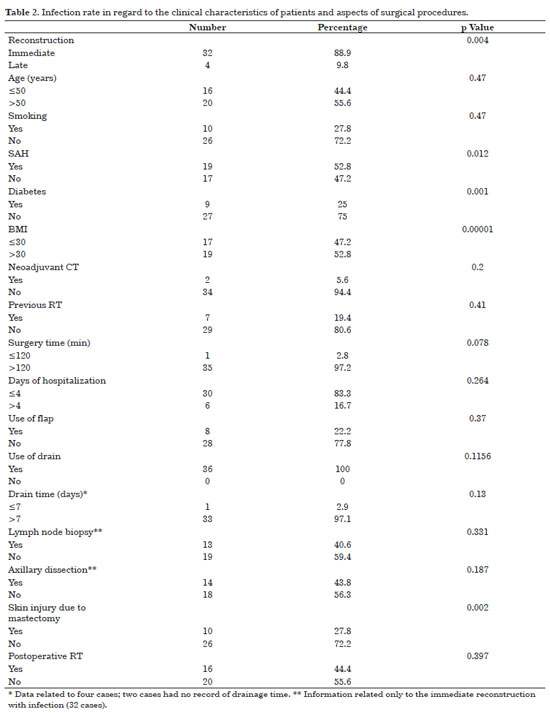
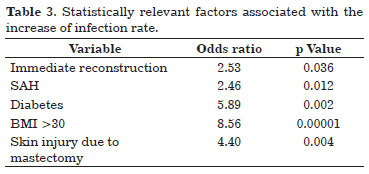
RESULTS: The infection rate (24.3%) was statistically related to immediate reconstruction (88.9%), diabetes mellitus (25%), body mass index >30 (52.8%), systemic arterial hypertension (52.8%), and skin injury due to mastectomy (27.8%). Of the infected implants, 44% were removed, most of which were expanders placed during immediate reconstruction.
CONCLUSIONS: Breast reconstruction with implants is the safest and most effective form of treatment. However, consideration should be given to patients who are prone to the development of infection, in order to optimize its prevention and attempt to perform its treatment at an early stage.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Expander/Breast implant; Infection.