ABSTRACT
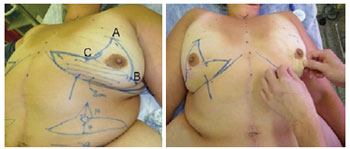
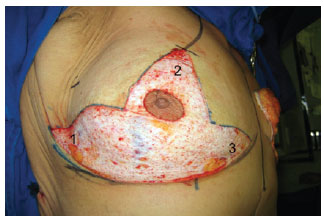
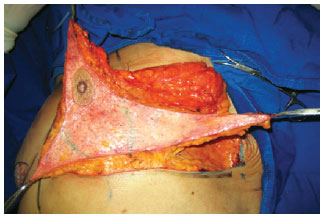
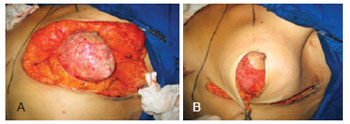
BACKGROUND: Patients who experience major weight loss may have pronounced breast ptosis, loss of projection of the higher pole, and excessive tissue in the lateral thorax. Rubin & Khachi described a mastopexy technique with dermal suspension and parenchymal remodeling associated with augmentation with autologous tissue. This technique treats the mammary deformity and the excessive tissue in the lateral thorax in a single surgery. In this study, we describe this surgical technique and demonstrate its reproducibility and the possible complications.
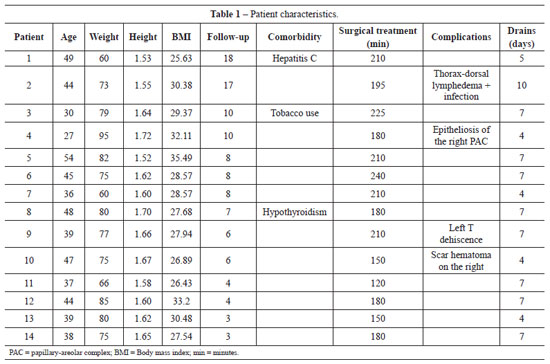
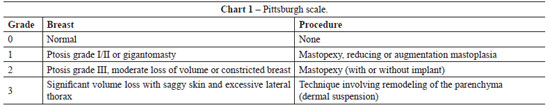
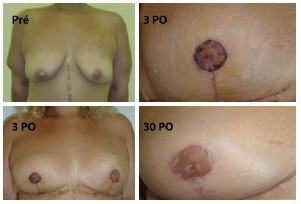
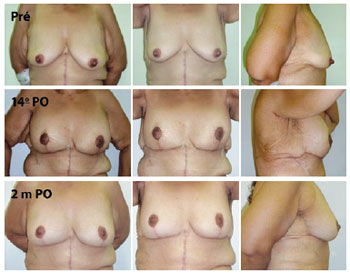
METHODS: From December 2008 to December 2009, surgery was performed using the technique described above on 14 patients with grade 2 and 3 deformities according to the Pittsburgh scale. The following data were analyzed: type of breast deformity, translocation of the papillary-areolar complex (PAC), dimension of the flaps used, surgical time, permanence time of the drain, and the incidence of complications.
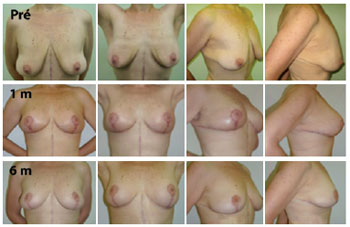
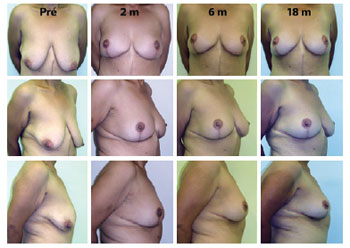
RESULTS: The mean age of the patients was 41.21 ± 7.67 years and the mean body mass index was 29.30 ± 2.77. The follow-up period ranged from 3 months to 18 months, with a mean of 8 months. Among the 14 patients that underwent surgery, 4 patients (28.6%) had grade 3 deformities and 10 patients (71.4%), had grade 2 deformities. The mean translocation of the PAC was 6.38 cm, the mean dimensions of the flap were 25.21 cm × 6.92 cm, and the mean surgical time was 188.57 minutes. The drains remained for an average of 6.21 days. The following complications were observed: PAC epitheliosis, dehiscence of the T-junction, a small hematoma, and lateral thoracic lymphedema.
CONCLUSIONS: Mastopexy with dermal suspension, parenchyma remodeling, and augmentation with autologous tissue is a reproducible technique that can be performed quickly and has a low complication rate.
Keywords: Mammaplasty. Weight loss. Postoperative complications. Breast/surgery.