
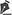
Ideas and Innovation - Year 2021 - Volume 36 -
Nanofat injector: a low-cost disposable device for standardization and optimization of grafting time
Nanofat injector: dispositivo descartável de baixo custo para padronização e otimização do tempo de enxertia
ABSTRACT
Introduction: Nanofat graft improves skin quality in damage secondary to aging and scar sequelae. We present the initial results of the nanofat graft using a low-cost disposable device, proposing a standardization of its use according to the area to be treated.
Methods: A prospective cohort was conducted from July 2019 to March 2020. The inclusion criterion was patients who underwent nanofat grafting for skin treatment. The exclusion criterion was the previous performance of some invasive treatment of the skin. Twenty consecutive patients who met the prerequisites were analyzed. The results were evaluated in the 6th postoperative month. The patients answered a questionnaire, classifying from 1 - very bad to 10 - excellent, changes in skin quality.
Results: The twenty patients followed did not present any postoperative complications. Edema after the application was reduced between three and seven days. There was no hematoma or infection. Patients who underwent only nanofat grafting without another associated surgery could return to their activities after 24 hours. The scores reported by patients at 6 months were between 7 and 10, with a mean of 8.
Conclusion: The use of the SmartneedleTM system for nanofat grafting presents patient satisfaction similar to other application methods and allows a uniform and standardized distribution of the graft according to the anatomical region and optimizing surgical time
Keywords: Fats; Face; Skin; Skin abnormalities; Facial expression.
RESUMO
Introdução: O enxerto de gordura nano melhora a qualidade da pele nos danos secundários ao envelhecimento e nas sequelas cicatriciais. Apresentamos resultados iniciais do enxerto de gordura nano com o uso de um dispositivo descartável de baixo custo propondo uma padronização da sua utilização conforme a área a ser tratada.
Métodos: Foi realizada uma coorte prospectiva de julho de 2019 a março de 2020. O critério de inclusão foi pacientes que realizaram enxerto de gordura nano para tratamento da pele. Já o critério de exclusão foi a realização prévia de algum tratamento invasivo da pele. Foram analisadas 20 pacientes consecutivas que preencheram os pré-requisitos. Os resultados foram avaliados no 6º mês de pós-operatório. As pacientes responderam um questionário, classificando de 1 - muito ruim a 10 - excelente, as alterações na qualidade da pele.
Resultados: As vinte pacientes acompanhadas não apresentaram nenhuma complicação pós-operatória. O edema após aplicação reduziu entre três e sete dias. Não houve hematoma nem infecção. As pacientes que realizaram somente enxerto de gordura nano, sem outra cirurgia associada, conseguiram voltar às suas atividades após 24 horas. Os escores relatados pelas pacientes com 6 meses foram entre 7 e 10, com média de 8.
Conclusão: A utilização do sistema SmartneedleT para a enxertia de gordura nano apresenta resultados na satisfação das pacientes semelhante aos outros métodos de aplicação e permite uma distribuição uniforme e padronizada do enxerto conforme a região anatômica, além de otimizar o tempo cirúrgico.
Palavras-chave: Gorduras; Face; Pele; Anormalidades da pele; Expressão facial
INTRODUCTION
Tonnard et al., in 20131, described the nanofat graft. The intradermal injection of the graft with 27 gauge needles became viable through the emulsification and filtering of the liposuctioned fat. The laboratory analysis showed complete destruction of the adipocytes and a total loss of the volumization capacity; however, it allows the isolation of the stromal vascular fraction of the fat, maintaining its regenerative potential intact2. The nanofat graft improves the quality of the skin in damages secondary to aging and in the healing sequelae3-5. This work aims to present the initial results of the nanofat graft with the use of a low-cost disposable device, proposing a standardization of its use according to the area to be treated.
METHODS
A prospective cohort was conducted from July 2019 to March 2020. The approval of the institutional review board of the Hospital de Clínicas de Porto Alegre was granted, project number 2008-0058, and this research-based study was conducted following the provisions of the Declaration of Helsinki. The inclusion criterion was patients who underwent nanofat grafting for skin treatment. The exclusion criterion was the previous performance of some invasive treatment of the skin. Twenty consecutive patients who met the prerequisites were analyzed.
The results were evaluated in the 6th postoperative month. The patients answered a questionnaire, classifying from 1 - very bad to 10 - excellent, changes in skin quality.
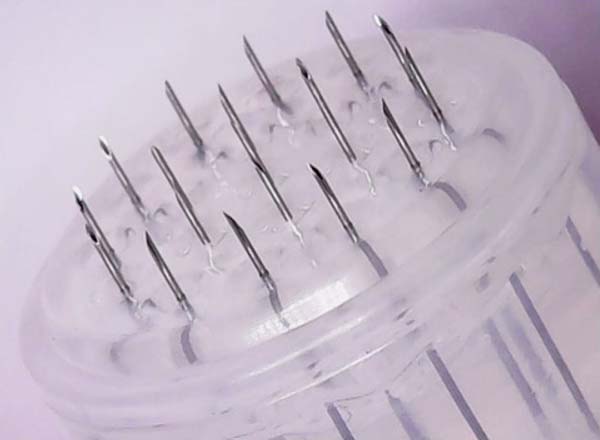
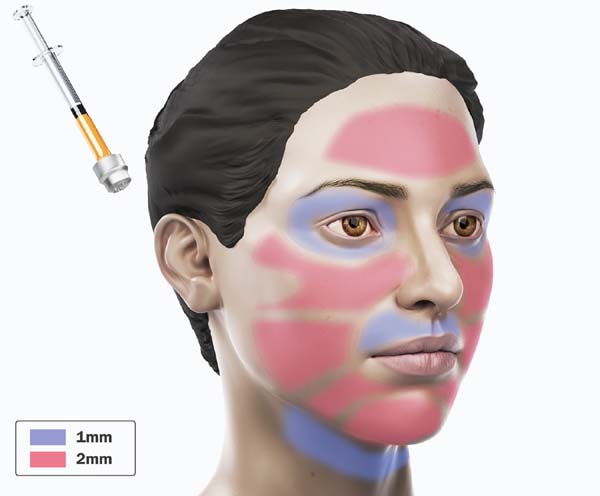
To remove the graft, we chose between the infraumbilical region or the inner thigh6. Infiltration is performed with saline solution and adrenaline at a concentration of 1:300,000. Liposuction is performed with a 3mm cannula, with 1mm holes and rough surface(1, FAGA).
The collected fat is washed and decanted7. The first part is the micrograft and is ready for use; the second is transferred 30 times by each of the three 2.4mm, 1.8mm and 1.4mm(FAGA)protractors. After transfers, the emulsified graft will be ready1. According to the need for nano graft volume, a percentage of the emulsified graft can go to the third stage. This step consists of passing once in each of the threefilters(1, FAGA): 0.5mm, 0.3mm and 0.15mm (Figures 1 and 2).
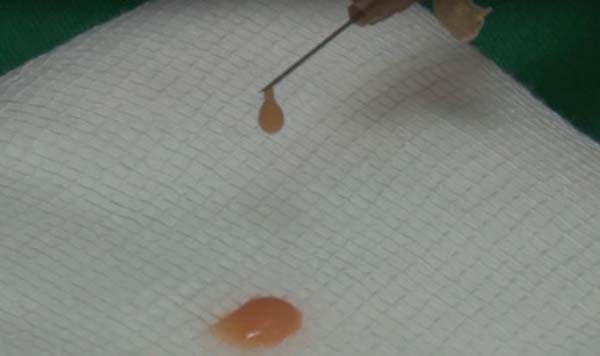
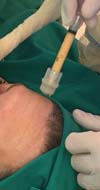
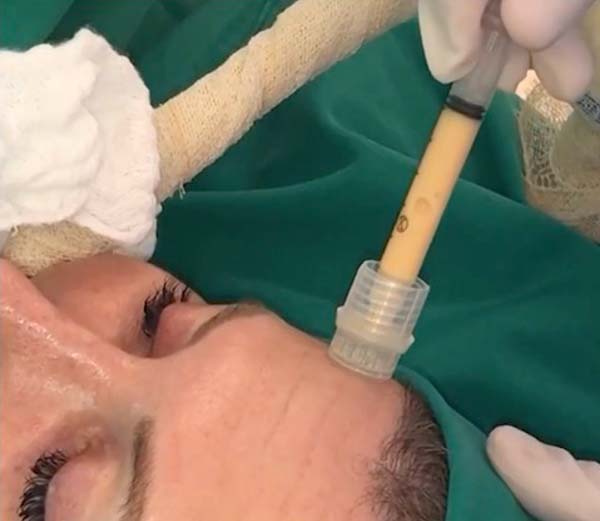
For application, the fat is transferred from the 20ml syringe to the 3ml syringe and coupled to the Multineedle 19 Needles System (JM Biotech Co. Ltd., Daegu, South Korea) (Figures 3 and 4). The depth to be grafted is standardized by anatomical region (Table 1 and Figure 5). The system is applied to 90 degrees concerning the skin for complete penetration of all needles. An application of 0.3ml of nano graft per stitch is performed (0.016ml injected by each needle) (Figure 6). After finishing the grafting, skin massage is performed with the nano graft.
| Muscle | Number of a needles | Size |
|---|---|---|
| Frontal | 19 needles | 1mm |
| Orbital | 19 needles | 1mm |
| Zygomatic | 19 needles | 2mm |
| Maxillary and Mandibular | 19 needles | 2mm |
| Perioral | 19 needles | 1mm |
| Anterior cervical | 19 needles | 1mm |
| Back of hands | 19 needles | 1mm |
| Skin treatment after radiotherapy | 19 needles | 2mm |
RESULTS
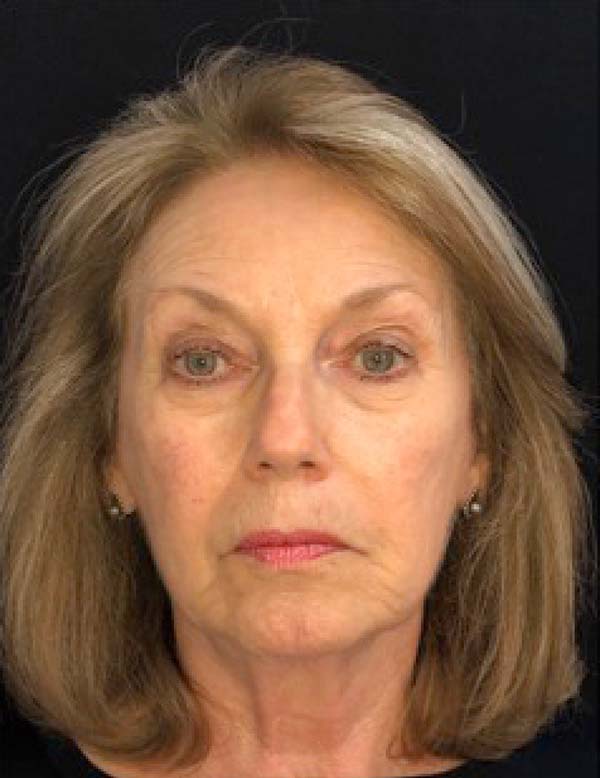
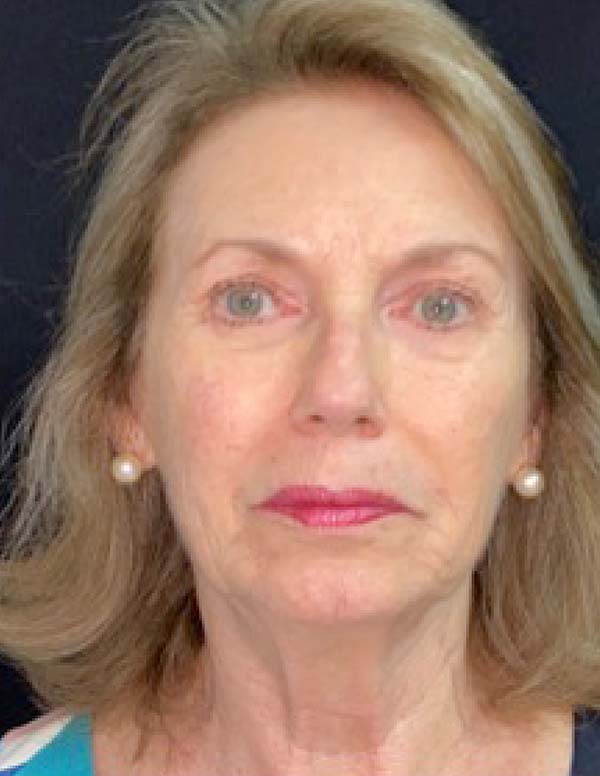
The twenty patients followed did not present any postoperative complications. Edema after application decreased between three and seven days. There was no hematoma or infection. Patients who underwent only nanofat grafting without another associated surgery could return to their activities after 24 hours (Figures 7 and 8).
The scores reported by patients at six months were between 7 and 10, with a mean of 8 (Table 2).
| Score 0-10 6 months P.O. | Age | Gender | |
|---|---|---|---|
| MEC | 7 | 54 | F |
| IT | 9 | 44 | F |
| ES | 10 | 53 | F |
| EM | 8 | 53 | F |
| JP | 8 | 50 | F |
| SM | 7 | 43 | F |
| LG | 7 | 44 | F |
| EP | 8 | 52 | F |
| LP | 9 | 67 | F |
| MG | 7 | 63 | F |
| IR | 8 | 64 | F |
| RP | 7 | 60 | F |
| FL | 7 | 61 | F |
| EB | 10 | 74 | F |
| LB | 8 | 54 | F |
| VR | 8 | 59 | F |
| LC | 9 | 58 | F |
| JM | 7 | 55 | F |
| RR | 8 | 48 | F |
| MT | 8 | 76 | F |
DISCUSSION
The indication of nanofat graft aiming at skin treatment is growing worldwide. We did not find any article described with an unfavorable conclusion to its use. The main advantages of the nano graft are the maintenance of stem cells derived from adipose tissue (ADSCs), in addition to the possibility of intradermal grafting, which was not possible before its description. The ADSCs have already been widely studied, and their regenerative potential well documented, with several applications to plastic surgery3-5,8. Sesé, in 20192, described that the isolation of ADSCs, when carried out by the mechanical emulsification system, requires a quantity of fat ten times lower than the standard method, enzymatic isolation, and produces a higher concentration of stem cells, which explains its regenerative potential2. The process of obtaining the nano graft is summarized in three stages: micrograft, emulsified fat and nanofat graft. Despite adding surgical time - due to preparation in three stages - when compared to the classic graft, all stages generate grafts with properties to treat different changes in aging, as shown in Figure 1.
In 2013, Tonnard et al. 1 described the application of the nano graft with 27 gauge needles. Still, the method requires a long time to perform, resulting in prolonged edema due to the formation of subdermal “fat lakes” and, mainly, the impossibility of standardizing the depth of application. Verpaele et al., in 20199, described a new method, where they associate micro-needling with the deposit of the nano graft; for this, 8ml and 20 minutes of micro-needling are required. The system described in this article allows standardizing the injection depth according to the different anatomical areas10. With standardized grafting, injections are uniformly intradermal, reducing the risk of perforation of subdermal vascular plexus. This explains the lower potential of ecchymosis secondary to the procedure compared to the other methods already described1.
Furthermore, the proposed technique allows the control of the injection volume of the nano graft, and with the system of 19 needles, it is possible to graft 8ml in 2 minutes. Each application of 0.3ml requires between three and five seconds, with an injection of 0.016ml per point, which reduces the risk of large deposits, as well as prolonged edema1. If the surgeon’s goal is nano graft deposition and not microneedling, we believe this is the best system currently available. It allows a fast application, low morbidity, uniform deposit and adequate depth for the selected anatomical region. Finally, state-of-the-art technologies are usually associated with high investment. Still, the described system has a cost of R$ 65 per device, so it is possible to put it on the surgical budget without derailing the surgery.
CONCLUSION
The use of the Smartneedle™ system for nanofat grafting presents results in patient satisfaction similar to other application methods. It allows a uniform and standardized distribution of the graft according to the anatomical region and optimizes surgical time.
REFERENCES
1. Tonnard P, Verpaele A, Peeters G, Hamdi M, Cornelissen M, Declercq H. Nanofat grafting: basic research and clinical applications. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2013 Oct;132(4):1017-26.
2. Sesé B, Sammartin JM, Ortega B, Matas-Palau A, Llull R. Nanofat cell aggregates: a nearly constitutive stromal cell inoculum for regenerative site-specific therapies. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2019 Nov;144(5):1079-88.
3. Oh DS, Kim DH, Roh TS, Yun IS, Kim YS. Correction of dark coloration of the lower eyelid skin with nanofat grafting. Arch Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2014;20:92-6.
4. Menkes S, Luca M, Soldati G, Polla L. Subcutaneous injections of nanofat adipose-derived stem cell grafting in facial rejuvenation. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2020 Jan;8(1):e2550. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1097/GOX.0000000000002550
5. Jan SN, Bashir MM, Khan FA, Hidayat Z, Ansari HH, Sohail M, et al. Unfiltered nanofat injections rejuvenate postburn scars of face. Ann Plast Surg. 2019 Jan;82(1):28-33. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1097/SAP.0000000000001631
6. Padoin AV, Braga-Silva J, Martins P, Rezende K, Rezende AR, Grechi B, et al. Sources of processed lipoaspirate cells: influence of donor site on cell concentration. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2008 Aug;122(2):614-8. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0b013e31817d5476
7. Condé-Green A, Amorim NF, Pitanguy I. Influence of decantation, washing and centrifugation on adipocyte and mesenchymal stem cell content of aspirated adipose tissue: a comparative study. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2010 Aug;63(8):1375-81.
8. Martins JMP, Oliveira FS, Lima EOC, Dullius D, Durli ICLO, Hiraiwa E, et al. Use of derived adipose stem cells to reduce complications of cutaneous scarring in smokers. An experimental model in rats. Acta Cir Bras. 2019;34(6):e201900605. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1590/s0102-865020190060000005
9. Verpaele A, Tonnard P, Jeganathan C, Ramaut L. Nanofat needling: a novel method for uniform delivery of adipose-derived stromal vascular fraction into the skin: correction. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2019 Jul;144(1):264. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0000000000006078
10. Hausauer AK, Josnes DH. PRP e microagulhamento em medicina estética. Rio de Janeiro: Thieme Revinter Publicações; 2019.
1. Hospital de Clínicas de Porto Alegre, Serviço de Cirurgia Plástica, Porto Alegre,
RS, Brasil.
2. Clínica Privada, Clínica Privada - Porto Alegre, Porto Alegre, RS, Brasil.
Corresponding author: João Maximiliano Rua Ramiro Barcelos, 2350, Santa Cecília, Porto Alegre, RS, Brazil. Zip Code: 90035-003. E-mail: jmaximilianopm@gmail.com
Article received: May 07, 2020.
Article accepted: April 23, 2021.
Conflicts of interest: none
COLLABORATIONS
JM Analysis and/or data interpretation, Conception and design study, Conceptualization, Data Curation, Final manuscript approval, Formal Analysis, Funding Acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project Administration, Realization of operations and/or trials, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing - Original Draft Preparation, Writing - Review & Editing
MP Analysis and/or data interpretation, Conception and design study, Conceptualization, Data Curation, Final manuscript approval, Formal Analysis, Funding Acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project Administration, Realization of operations and/or trials, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing - Original Draft Preparation, Writing - Review & Editing
ACPO Analysis and/or data interpretation, Conception and design study, Conceptualization, Data Curation, Final manuscript approval, Formal Analysis, Funding Acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project Administration, Realization of operations and/or trials, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing - Original Draft Preparation, Writing - Review & Editing
EMZ Analysis and/or data interpretation, Conception and design study, Conceptualization, Data Curation, Final manuscript approval, Formal Analysis, Funding Acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project Administration, Realization of operations and/or trials, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing - Original Draft Preparation, Writing - Review & Editing
DWD Analysis and/or data interpretation, Conception and design study, Conceptualization, Data Curation, Final manuscript approval, Formal Analysis, Funding Acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project Administration, Realization of operations and/or trials, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing - Original Draft Preparation, Writing - Review & Editing
CPP Analysis and/or data interpretation, Conception and design study, Conceptualization, Data Curation, Final manuscript approval, Formal Analysis, Funding Acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project Administration, Realization of operations and/or trials, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing - Original Draft Preparation, Writing - Review & Editing
JLM Analysis and/or data interpretation, Conception and design study, Conceptualization, Data Curation, Final manuscript approval, Formal Analysis, Funding Acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project Administration, Realization of operations and/or trials, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing - Original Draft Preparation, Writing - Review & Editing
MVMC Analysis and/or data interpretation, Conception and design study, Conceptualization, Data Curation, Final manuscript approval, Formal Analysis, Funding Acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project Administration, Realization of operations and/or trials, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing - Original Draft Preparation, Writing - Review & Editing












 Read in Portuguese
Read in Portuguese
 Read in English
Read in English
 PDF PT
PDF PT
 Print
Print
 Send this article by email
Send this article by email
 How to Cite
How to Cite
 Mendeley
Mendeley
 Pocket
Pocket
 Twitter
Twitter