
Original Article - Year 2011 - Volume 26 -
Study of patients with hyperhidrosis treated with botulinum toxin: a 10-year retrospective analysis
Estudo de pacientes com hiperidrose, tratados com toxina botulínica: análise retrospectiva de 10 anos
ABSTRACT
BACKGROUND: Hyperhidrosis is characterized by excessive sweating of the forehead, hands, feet, and armpits, either alone or in combination. It affects about 1% of the population. This study aimed to observe the effects of botulinum toxin in patients with hyperhidrosis and demonstrates the application technique of botulinum toxin, the areas of incidence of the disease, and the duration of the results.
METHODS: A retrospective analysis of 39 patients with primary hyperhidrosis treated between July 2000 and July 2010 and followed up for 12 months was carried out. Of these patients, 36% were male and 64% were female. Patient ages ranged from 16 to 41 years. A total of 135 areas were treated. Treatment consisted of intradermal injections of botulinum toxin. The total dose applied ranged from 37.5 U to 150 U, with an average dose of 75 U for each treated area.
RESULTS: The therapeutic effect of botulinum toxin was observed from the third day after treatment, with a 50% reduction in symptoms within the first week of treatment and up to 94% reduction in the number of hyperhidrosis events after the second week. The reduction of symptoms lasted, on average, for 7 months. No cases of compensatory hyperhidrosis or mortality were observed.
CONCLUSIONS: The treatment of primary hyperhidrosis with type A botulinum toxin, although temporary, is an effective, safe, and minimally invasive treatment option. It has a high degree of satisfaction and allows patients to return to their professional activities on the same day. Side effects and complications are temporary, infrequent, and regress without sequelae.
Keywords: Botulinum toxins. Hyperhidrosis. Sweating.
RESUMO
INTRODUÇÃO: A hiperidrose caracteriza-se por sudorese excessiva, isolada ou associada, da testa, das mãos, dos pés e das axilas. Atinge cerca de 1% da população. O objetivo deste estudo foi observar os efeitos da toxina botulínica nos pacientes com hiperidrose, demonstrando a técnica, as áreas de incidência e a duração dos resultados obtidos.
MÉTODO: Foi realizada análise retrospectiva de 39 pacientes com hiperidrose primária tratados no período de julho de 2000 a julho de 2010, acompanhados durante 12 meses. Desses pacientes, 36% eram do sexo masculino e 64%, do sexo feminino. A idade variou de 16 anos a 41 anos. No total, foram tratadas 135 áreas. Realizou-se tratamento com injeções intradérmicas de toxina botulínica. A dose total aplicada variou entre 37,5 U e 150 U, com dose média de 75 U para cada região tratada.
RESULTADOS: O efeito terapêutico foi observado a partir do terceiro dia, com redução de 50% dos sintomas na primeira semana do tratamento e de até 94% do quadro de hiperidrose após a segunda semana de tratamento. A redução dos sintomas durou, em média, 7 meses. Nenhum caso de hiperidrose compensatória foi observado. A mortalidade foi nula.
CONCLUSÕES: O tratamento da hiperidrose primária com toxina botulínica tipo A, embora temporário, é uma opção de tratamento eficaz, segura, pouco invasiva e com alto grau de satisfação, permitindo aos doentes o retorno às atividades profissionais no mesmo dia. Os efeitos colaterais e as complicações são temporários, pouco frequentes e regridem sem deixar sequelas.
Palavras-chave: Toxinas botulínicas. Hiperidrose. Sudorese.
Hyperhidrosis is characterized by excessive and uncontrollable sweating, which may occur without any apparent triggering factor. It affects men and women, and is manifested at different ages. Although it is essential to control body temperature, especially during exercise, excessive sweating causes a significant impact on the professional and emotional life of people with hyperhidrosis. The symptoms stop during sleep. Embarrassment, isolation, physical discomfort, psychological alterations, low self-esteem, and other problems related to social life are examples of the consequences of this illness among those who have it.
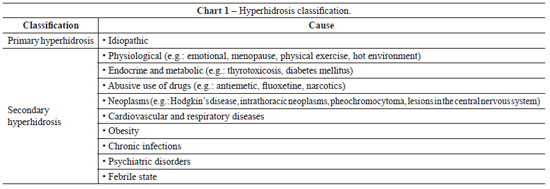
Primary hyperhidrosis is the most common form of hyperhidrosis and constitutes an idiopathic, chronic, focal, bilateral, and symmetrical alteration in sweating. In 30% to 50% of cases, there is a family history of the illness. When unilateral, it affects the armpits (21%) and hands (6%). Primary hyperhidrosis is commonly associated with hyperactivity of the sympathetic autonomous nervous system, which generates glandular hypertrophy and hypersecretion of the eccrine sweat glands in certain anatomical areas. It affects about 1% of the population, impairing both their professional performance and social relations. Secondary hyperhidrosis is related to an underlying disease. In Chart 1, hyperhidrosis classification is presented1.
Hyperhidrosis can be considered a benign disease characterized by excessive sweating of the forehead (frontal hyperhidrosis), hands (palmar hyperhidrosis), feet (plantar hyperhidrosis), and armpit (axillary hyperhidrosis). It may occur in an isolated manner, affecting only a specific anatomical area (i.e., hands, armpits, feet, or forehead). When it affects more than one anatomical region, it is called associated hyperhidrosis (e.g., palmar + axillary, palmar + plantar, etc.)2. When hyperhidrosis symptoms are severe, spontaneous dripping occurs in the affected region, leaving the skin macerated. Intense sweating may lead to the presence of a fetid odor, caused by decomposition of the sweat and bacterial and fungal cell remnants, a phenomenon called bromhidrosis3.
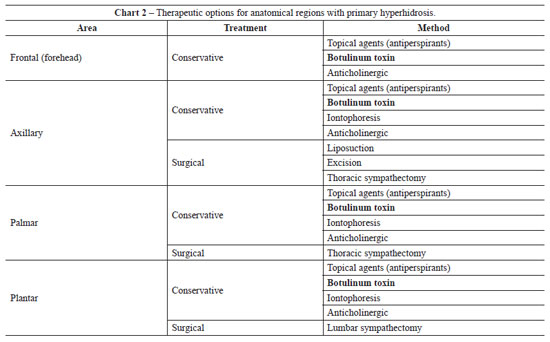
Considering that the history and clinical signs of excessive production of sweat normally begin in adolescence, the diagnosis is essentially clinical. The illness mainly affects adults and young people, and family history is present in 30% to 50% of patients. The presence of hyperhidrosis over a period of years generates emotional tension in patients, triggering repetitive processes that lead to the worsening of symptoms, making it even more difficult to live with the disease. The set of psychosomatic reactions that trigger the illness and the worsening of symptoms via a vicious circle have been described as the "syndrome of hyperhidrosis trigger"4,5. Two main types of treatment have been reported for primary hyperhidrosis6: conservative and surgical (Chart 2).
- Conservative treatment:
Topical agents (aluminum hydrochloride-based antiperspirants): the treatment of choice. This treatment promotes the blockage of excreting ducts from eccrine glands. It has the advantage of being very accessible, with a low cost and easy application, and can be used in association with other treatments. Among the undesired effects that may arise are dermatitis, skin spots, spots on clothes, and the need for daily use of the treatment. Anticholinergic and sedative agents: anticholinergic drugs (e.g., oxybutynin at a dose of 5-15 mg/day) are rarely used because of their side effects (dry mouth; vertigo; palpitation; urinary retention; and disorders of speech, taste, chewing, and swallowing). In addition, they do not promote the desired reduction in excessive sweating. The use of sedative agents and psychological assistance help to reduce secretions and social anxieties; however, they have little effect on hyperhidrosis. Iontophoresis: although its mechanism of action is not fully understood, this treatment may cause temporary blockage of the sweat duct in the stratum corneum, which reduces sweating. This treatment is not very practical, is painful (it involves administration of small electric shocks), and may generate skin lesions. The effect can last from 15 to 30 days. Sweat may be reduced in specific areas; however, the treatment has to be administered in a continuous and repetitive manner. Botulinum toxin: this treatment blocks the release of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine, i.e., it blocks synaptic transmission, producing efficient chemical denervation of the gland and temporary cessation of excessive sweating. It is an easy treatment, which can be administered under topical anesthesia, local or locoregional anesthesia, or even sedation. It has the disadvantages of a temporary therapeutic effect (4 to 12 months, with an average duration of 7 months), elevated cost, and discomfort associated with multiple injections7-9.
- Surgical treatment:
Excision of the axillary tissue: excision of the subcutaneous tissue, or excision of the skin and subcutaneous tissue en bloc, as well as excision of the skin and underlying subcutaneous tissue. This technique is not recommended because it may cause unsightly scars and scar retraction, with possible limitation of articular mobility. Subdermal axillary liposuction: this treatment causes rupture of the nervous supply to the sweat glands and removal or destruction of some of the sweat glands. It does not have the expected therapeutic effect because a great number of the sweat glands that cause hyperhidrosis maintain their function, as they are located in the dermis. It may cause hematoma, seroma, infections, asymmetries, skin retractions, and articular mobility alterations10. Thoracic sympathectomy (video assisted): this technique is the only definitive surgical treatment for hyperhidrosis, of both palmar and axillary forms. It promotes the interruption of ganglia T2, T3, and T4 of the upper dorsal sympathetic chain, leading to definitive cessation of sweating in the area of nerve distribution. This treatment requires hospitalization and is carried out under general anesthesia. The complications and side effects are very significant, such as irreversible compensatory sweating (20% to 50%), low satisfaction with results, Claude-Bernard-Horner syndrome, pneumothorax, hemothorax, asymmetry of results, intercostal neuralgia, causalgia, incomplete results, and anesthetic complications11-13. Retroperitoneoscopic lumbar sympathectomy (video-assisted): this technique is effective in the treatment of isolated or persistent plantar hyperhidrosis (compensatory after thoracic sympathectomy). The treatment consists of removing the nerves of the sympathetic chain located in the abdomen, in the anterolateral portion of the lumbar vertebrae. It requires hospitalization and is carried out under general anesthesia. It may lead to complications such as lesions of structures adjacent to the sympathetic chain, light abdominal distension, neuralgia, and causalgia as well as hypoesthesia in the thighs and groin, limitation of leg movement, paresthesia in the anterolateral abdominal wall, change in libido, dyspareunia, pulmonary thromboembolism, hemorrhages, arrhythmias, and cardiac decompensation, amongst others. It definitively eliminates plantar hyperhidrosis14,15.
The objective of this study was to observe the effects of type A botulinum toxin in patients with primary hyperhidrosis and demonstrate the technique of application used, the areas of incidence of the disease, and the duration of the results obtained with the treatment.
METHODS
A retrospective analysis of 10 years' experience of using botulinum toxin for hyperhidrosis treatment was carried out. Exclusion criteria for the study were as follows: presence of severe systemic disease; sensitivity to botulinum toxin; neuromuscular diseases (such as severe myasthenia and syndrome of Eaton-Lambert); use of antibiotics of the aminoglycoside group; pregnancy or breastfeeding; use of calcium channel blockers, muscle relaxation drugs, or acetylsalicylic acid; history of recent operation; and inflammatory or infectious signs in the skin or areas of botulinum toxin application. All patients had undergone previous treatments, such as use of topical agents (antiperspirants), without achieving the expected result. To provide a therapeutic option for these patients, we used the conservative treatment of intradermal injections of type A botulinum toxin.
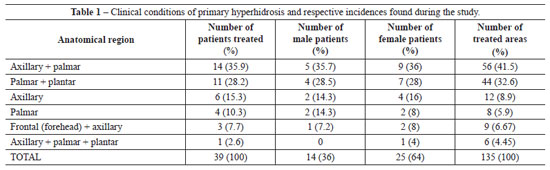
Thirty-nine patients with primary hyperhidrosis were treated between July 2000 and July 2010. The patients were aged between 16 and 41 years (mean age, 29 years), and 14 (36%) were male while 25 (64%) were female. Of these patients, 32 (82%) were white and 7 (18%) were brown. All patients were followed up during the 12 months after intradermal injections of botulinum toxin. The patients returned for observation after the first and second weeks, and then after 2 months, 6 months, and 12 months. A total of 135 areas were treated. For statistical purposes, we considered the frontal region (forehead) one area, right and left axillary regions two areas, right and left palmar region two areas, and the right and left plantar region two areas. Throughout the study period, 10 (25.6%) patients had hyperhidrosis in 2 areas, 3 (7.7%) had hyperhidrosis in 3 areas, 25 (64.1%) had hyperhidrosis in 4 areas, and only 1 (2.6%) patient had hyperhidrosis in more than 4 areas (Table 1). Each anatomical region received multiple intradermal injections (multi-points) of botulinum toxin in a single session conducted every 7 months on average.
The iodine-starch test (Minor test) was performed in all patients to determine the intensity of hyperhidrosis and the most affected locations. During the Minor test, frontal, axillary, palmar, and plantar hyperhidrosis was determined by positioning the patient in a supine position, with their arms in an abduction position at 90 degrees. A gauze wetted with 10% povidone iodine was applied over the cutaneous surface of the regions with hyperhidrosis. Then, a thin layer of maize starch was applied and left for 5 to 10 minutes. In this test, the impaired areas have different intensities of reaction. Areas with excessive sweating react with the iodine and starch, generating multiple regions of a dark violet color, which may be coalescent or form in multiple points.
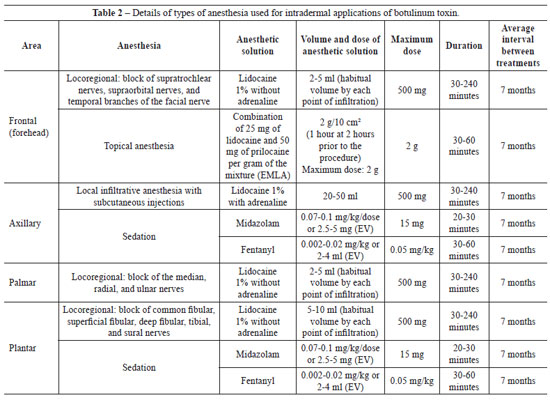
In this study, intradermal injections of type A botulinum toxin were performed under topical anesthesia, local infiltrative anesthesia, locoregional anesthesia, or sedation, depending on the clinical case, as demonstrated in Table 2.
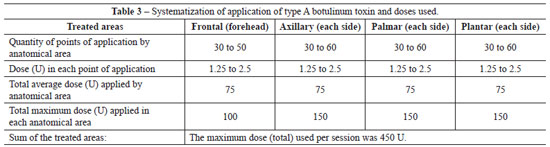
In order to ensure good coverage and efficient action of the botulinum toxin, multiple points were marked, with a distance of 1 cm to 2 cm between each point. As illustrated in Table 3, the sum of the multiple points marked in each region ranged from 30 to 50 points in the frontal region, from 30 to 60 points on each side of the armpit, from 30 to 60 points on each palmar side, and from 30 to 60 points on each plantar side. The content of one flask containing 100 U of type A botulinum toxin was diluted in 4 ml of 0.9% physiological saline solution, providing a concentration of 2.5 U in every 0.1 ml.
Intradermal injections of the diluted solution of botulinum toxin were applied in areas previously anesthetized. Whenever possible, a 0.5 ml or 1 ml syringe with a block system (Luer Lock) and a 4 mm 30 G needle was used, to avoid wasting the drug and reduce the risk of injections in undesired regions or structures located in deeper planes. The total dose applied in each anatomical region with hyperhidrosis ranged from 37.5 U to 150 U, with an average dose of 75 U for every treated region, i.e., palmar, axillary, plantar, and frontal (forehead). The maximum applied dose (total) in each session was 450 U (Table 3). The time of the procedure ranged from 20 to 80 minutes, with an average of 35 minutes per session.
All injections of botulinum toxin were applied in a hospital environment, mostly in an outpatient setting. Due to emotional lability and anxiety, treatment with sedation was performed in a surgical center with the support of an anesthesiologist in three patients: 1 female patient with axillary-palmar-plantar hyperhidrosis, 1 male patient with axillary-palmar hyperhidrosis, and 1 female patient with palmar-plantar hyperhidrosis.
Figures 1 to 9 illustrate the systematization of the intradermal injection of type A botulinum toxin, the results of the iodine-starch test (Minor test), and the incidence of this illness.
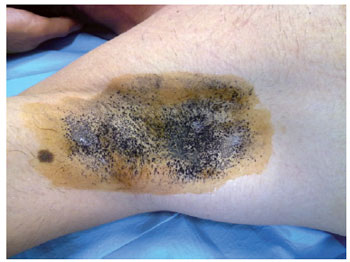
Figure 1 - Minor test for right axillary hyperhidrosis.
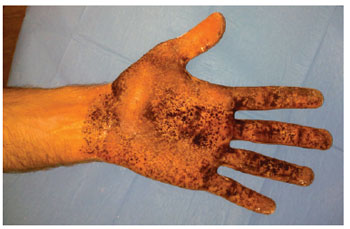
Figure 2 - Minor test for left palmar hyperhidrosis.
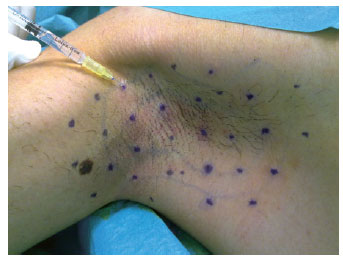
Figure 3 - Equidistant points, 1 cm to 2 cm from each other, in the axillary region for intradermal injections of type A botulinum toxin.
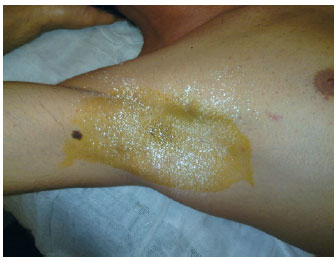
Figure 4 - Result of axillary hyperhidrosis control eight days after botulinum toxin injections.
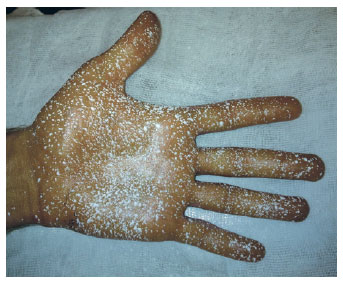
Figure 5 - Result of palmar hyperhidrosis control eight days after botulinum toxin injections.
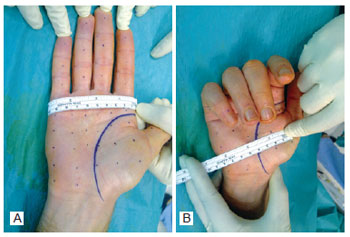
Figure 6 - Marking the injection points for type A botulinum toxin in the bilateral palmar region, 1 cm to 2 cm equidistant from one another.
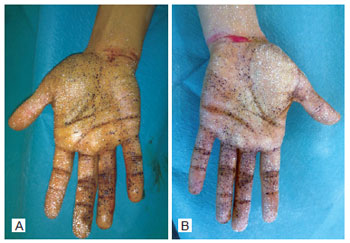
Figure 7 - Minor test prior to the performance of regional anesthetic block and administration of intradermal injections of botulinum toxin.
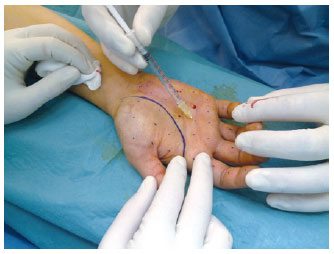
Figure 8 - Intradermal injections in the palmar region after regional anesthetic block in the fist.
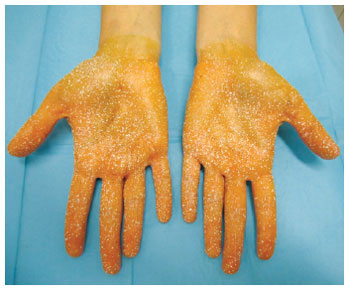
Figure 9 - Result evidencing improvement in hyperhidrosis 8 months after the intradermal injection of type A botulinum toxin.
RESULTS
The most common clinical event was axillary-palmar hyperhidrosis (35.9%), followed by palmar-plantar (28.2%), isolated axillary (15.3%), and isolated palmar hyperhidrosis (10.3%) (Table 1 and Figure 10). Therapeutic effects were observed from the third day after treatment, with a reduction in symptoms of approximately 50% within the first week of treatment and up to 94% reduction after the second week. Only 2 (5.2%) patients, one with axillary-palmar hyperhidrosis and the other with axillary-palmar-plantar hyperhidrosis, required small reinforcement doses of intradermal botulinum toxin to treat residual areas of excessive sweat; these were administered 2 months after the first session of treatment. The length of reduction of hyperhidrosis symptoms ranged from 4 to 12 months. The average length of reduction of symptoms, based on follow-up studies and patient observation, was 7 months. With regard to the results, 95.3% of the patients declared they were very satisfied, even though botulinum injections are a temporary treatment.
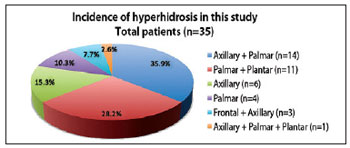
Figure 10 - Areas impaired by primary hyperhidrosis in the 39 patients of this study. n = number of patients.
In 6 (20%) patients, ecchymosis at some injection points and bilateral paresthesia of the hands and fingers occurred immediately after intradermal injections in palmar regions, with regression and spontaneous disappearance of the symptoms up to the second week.
Only 2 (6.7%) patients had ecchymosis at some injection points and bilateral paresthesia of the hands and fingers associated with neuropathic pain and reduction in the force of intrinsic movements of the hand. There was no evidence of vascular deficit of the hands and fingers. Oral ibuprofen (600 mg every 12 hours) and physiotherapy sessions were prescribed. Muscle strength returned to normal within 72 hours, and the other symptoms had completely receded by the second week. No cases of compensatory hyperhidrosis or mortality were observed.
DISCUSSION
During consultation for hyperhidrosis, the plastic surgeon should determine the best method to use in each case, choosing between conservative and surgical treatments. It is essential to clearly understand the details of each treatment, always considering the risks, complications, and permanent or temporary side effects of each treatment.
It is important to understand the patients' motivations and expectations before selecting the therapeutic option and to explain the possible complications and limitations of each treatment. The patients are not free from side effects, complications, and the need for further intervention, depending on the treatment used; therefore, careful assessment of each case is essential.
Conservative treatment with injections of type A botulinum toxin has increased the degree of satisfaction and decreased the rate of complications or side effects16,17. On the other hand, surgical treatment has high risks, permanent side effects, and complications such as compensatory hyperhidrosis, pneumothorax, hemothorax, Horner syndrome, hematomas, asymmetries of the results, and a variable degree of patient satisfaction18. Recently, Boscardim et al.19 questioned if the elimination of one disorder and the consequential creation of another is rational, as the surgical treatment of hyperhidrosis (by video-assisted sympathectomy), although definitive, safe, and efficient, causes an increase in compensatory sweating in other parts of the body in 67% to 85% of patients20.
Considering that the eccrine sweat glands are hypertrophied and hypersecreting in hyperhidrosis, specialists use botulinum toxin to achieve synaptic transmission block in the glands, interrupting hyperhidrosis symptoms. Botulinum toxin probably causes atrophy and involution of the eccrine sweat glands15.
In the present study, the average duration of the effects of botulinum toxin on hyperhidrosis was approximately 7 months, although some patients reported benefits for up to 12 months. This prolonged effect possibly results from the use of cognitive-behavioral therapy in association with botulinum toxin, which may reduce the chance of return of hyperhidrosis symptoms after the end of toxin action21.
Only two patients had temporary complaints of ecchymosis, paresthesia, pain, and decreased strength in the intrinsic muscles of the hands, which were probably related to a micro-trauma of nervous and vascular structures during anesthetic block in the fist. The possibility of complex regional pain syndrome causing neuropathic pain cannot be disregarded. This syndrome is also called reflex sympathetic dystrophy and causalgia, and it is caused by trauma to the peripheral nerves during anesthetic drug infiltration. There was complete regression of symptoms in all patients included in this study and no record of sequelae. In 2009, Baron and Zloty22 reported a clinical case with complex regional pain syndrome after infiltration in the fist for an anesthetic block of the peripheral nerves during treatment of palmar hyperhidrosis; the syndrome receded after clinical treatment and physiotherapy sessions23.
The most common clinical condition in this study was axillary-palmar hyperhidrosis (35.9%), followed by palmar-plantar (28.2%), isolated axillary (15.3%), and isolated palmar hyperhidrosis (10.3%). On the other hand, Grunfeld et al.24 reported a greater incidence of axillary hyperhidrosis (51%), followed by plantar (30%), palmar (24%), and frontal hyperhidrosis (10%).
CONCLUSIONS
The treatment of primary hyperhidrosis with intradermal injections of type A botulinum toxin is an effective, safe, and minimally invasive treatment option. It provides a high degree of satisfaction and allows patients to return to their professional activities on the same day. It is a precise and easy to implement method, after suitable training. Side effects and complications are temporary, infrequent, and regress without sequelae. However, the cost of this treatment is still very high. The synaptic block caused by botulinum toxin probably causes atrophy and involution of the sweat glands. These effects, associated with improvements in the patient's emotional state and self-esteem, delay the reappearance of the symptoms of hyperhidrosis and enhance patient quality of life.
REFERENCES
1. Haider A, Solish N. Focal hyperhidrosis: diagnosis and management. CMAJ. 2005;172(1):69-75.
2. Glaser DA, Hebert AA, Pariser DM, Solish N. Primary focal hyperhidrosis: scope of the problem. Cutis. 2007;79(5 Suppl):5-17.
3. Klein AW. Treatment of dyshidrotic hand dermatitis with intradermal botulinum toxin. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004;50(1):153-4.
4. Connor KM, Cook JL, Davidson JR. Botulinum toxin treatment of social anxiety disorder with hyperhidrosis: a placebo-controlled double-blind trial. J Clin Psychiatry. 2006;67(1):30-6.
5. Francischelli NM. A técnica de multipontos para controle da hiperidrose axilar, palmar e frontal (região frontal) com a toxina botulínica: a síndrome do gatilho da hiperidrose. In: Yamaguchi C, ed. Procedimentos estéticos minimamente invasivos II. São Paulo: Santos; 2006. p. 87-98.
6. Atkins JL, Butler PE. Hyperhidrosis: a review of current management. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2002;110(1):222-8.
7. Rohrich RJ, Janis JE, Fagien S, Stuzin JM. The cosmetic use of botulinum toxin. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2003;112(5 Suppl):177S-88S.
8. Huang W, Foster JA, Rogachefsky AS. Pharmacology of botulinum toxin. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2000;43(2 Pt 1):249-59.
9. Kinkelin I, Hund M, Naumann M, Hamm H. Effective treatment of frontal hyperhidrosis with botulinum toxin A. Br J Dermatol. 2000;143(4):824-7.
10. Dornelas M, Machado D, Gonçalves A, Maués GL, Correa MPD. Tratamento da hiperidrose axilar com lipoaspiração. Rev Bras Cir Plast. 2008;23(3):145-8.
11. Cardoso PO, Lacerda KC, Mendes CM, Petroianu A, Resende M, Alberti LR. Avaliação de pacientes submetidos a tratamento cirúrgico de hiperidrose palmar quanto à qualidade de vida e ao surgimento de hiperidrose compensatória. Rev Col Bras Cir. 2009;36(1):14-8.
12. Araújo CA, Azevedo IM, Ferreira MA, Ferreira HP, Dantas JL, Medeiros AC. Compensatory sweating after thoracoscopic sympathectomy: characteristics, prevalence and influence on patient satisfaction. J Bras Pneumol. 2009;35(3):213-20.
13. Wilson MJ, Magee TR, Galland RB, Dehn TC. Results of thoracoscopic sympathectomy for the treatment of axillary and palmar hyperhidrosis with respect to compensatory hyperhidrosis and dry hands. Surg Endosc. 2005;19(2):254-6.
14. Montessi J, Almeida EP, Vieira JP, Abreu MM, Souza RLP, Montessi OVD. Simpatectomia torácica por videotoracoscopia para tratamento da hiperidrose primária: estudo retrospectivo de 521 casos comparando diferentes níveis de ablação. J Bras Pneumol. 2007;33(3):248-54.
15. Loureiro MP, Roman N, Weigmann SC, Fontana A, Boscardim PB. Simpatectomia lombar retroperitoneoscópica para tratamento de hiperidrose plantar. Rev Col Bras Cir. 2007;34(4):222-4.
16. Goldman A. Toxina botulínica na cirurgia plástica: indicações e experiências em 1200 áreas tratadas. Rev Bras Cir Plast. 1999;14(2):21-30.
17. Goldman A. Treatment of axillary and palmar hyperhidrosis with botulinum toxin. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2000;24(4):280-2.
18. Young O, Neary P, Keaveny TV, Mehigan D, Sheehan S. Evaluation of the impact of transthoracic endoscopic sympathectomy on patients with palmar hyperhydrosis. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2003;26(6):673-6.
19. Boscardim PCB, Oliveira RA, Oliveira AAFR, Souza JM, Carvalho RG. Simpatectomia torácica ao nível de 4a e 5a costelas para o tratamento de hiper-hidrose axilar. J Bras Pneumol. 2011;37(1):6-12.
20. Gemperli R, Gimenez RP, Salles AG, Ferreira MC. Análise retrospectiva das alterações das rugas faciais após aplicações seriadas de toxina botulínica tipo A. Rev Bras Cir Plast. 2010;25(2):297-303.
21. Lessa LR, Fontenelle LF. Botulinum toxin as a treatment for social phobia with hyperidrosis. Rev Psiq Clín. 2011;38(2):84-6.
22. Baron JA, Zloty DM. Bilateral type 1 complex regional pain syndrome after local nerve blocks for palmar hyperhidrosis. Dermatol Surg. 2009;35(5):885-7.
23. Stanton-Hicks M. Complex regional pain syndrome. Anesthesiol Clin North America. 2003;21(4):733-44.
24. Grunfeld A, Murray CA, Solish N. Botulinum toxin for hyperhidrosis: a review. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2009;10(2):87-102.
1. Full member of the Brazilian Society of Plastic Surgery (SBCP), Ibero Latin American Society of Plastic Surgery; Portuguese Society of Burns; Portuguese Society of Plastic Surgery, and of the Brazilian Society of Burns. Specialist member of the Association of Reconstructive and Aesthetic Plastic Surgery of the Order of Physicians of Portugal; hospital assistant of Plastic Surgery at Centro Hospitalar de Lisboa Central, Lisbon, Portugal.
2. Resident physician of the Plastic Surgery Service at Centro Hospitalar de Lisboa Central, Lisbon, Portugal.
Correspondence to:
Gilberto Marcos Dias dos Reis
Av. Placidino Brigagão, 1.040 - ap. 51 - Centro
São Sebastião do Paraíso, MG, Brazil - CEP 37950-000
E-mail: gilbertoreis25@hotmail.com
Submitted to SGP (Sistema de Gestão de Publicações/Manager Publications System) of RBCP (Revista Brasileira de Cirurgia Plástica/Brazilian Journal of Plastic Surgery).
Paper received: February 24, 2011
Paper accepted: September 8, 2011
Study conducted at the Plastic Surgery Service of Centro Hospitalar de Lisboa Central, Lisbon, Portugal.


 Read in Portuguese
Read in Portuguese
 Read in English
Read in English
 PDF PT
PDF PT
 Print
Print
 Send this article by email
Send this article by email
 How to Cite
How to Cite
 Mendeley
Mendeley
 Pocket
Pocket
 Twitter
Twitter