
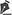
Case Reports - Year 2012 - Volume 27 -
Surgical correction of a giant neurofibroma
Abordagem cirúrgica de neurofibroma gigante
ABSTRACT
Neurofibromatosis is a disease of genetic origin with autosomal dominant inheritance that is classified into 3 types: neurofibromatosis type I (NF1), neurofibromatosis type 2 (NF2), and schwannomatosis. The main characteristics of NF1 are caféaulait spots, dermal and plexiform neurofibromas, false dermal and plexiform neurofibromas, false axillary or inguinal ephelides, and Lisch nodules. This study describes the case of a 26year-old man who presented with small cutaneous nodules, present since he was 3 years old, and caféaulait spots of different sizes distributed diffusely. At the age of 13, the patient developed a mass in the back and abdomen that subsequently developed into a rapidly growing voluminous mass, which hindered walking and caused social isolation. The surgical treatment consisted of the excision of the tumor in 2 phases, with a 2month interval between procedures. Although a cure for neurofibromatosis has not been discovered, surgical removal is indicated in cases of neurological involvement, pain, disfigurement, possible involvement of adjacent structures, and suspicion of malignancy. Partial resection is acceptable if total removal is not possible. In the present case, surgical treatment was an excellent choice because it enabled the complete excision of the lesion, with satisfactory wound healing and aesthetic results, as well as the improvement of the quality of life of the patient.
Keywords: Neurofibromatoses. Neurofibroma. Cafeaulait spots.
RESUMO
Neurofibromatose é uma doença de origem genética autossômica dominante composta por três tipos: neurofibromatose tipo 1 (NF1), neurofibromatose tipo 2 (NF2) e schwannomatose. As principais características da NF1 são mancha café com leite, neurofibromas dérmicos e plexiformes, falsas efélides axilares ou inguinais e nódulos de Lisch. Neste trabalho é apresentado o caso de um paciente do sexo masculino, 26 anos de idade, com relato de aparecimento de pequenos nódulos cutâneos desde os 3 anos de idade e manchas café com leite disseminadas e de diferentes dimensões. Após os 13 anos de idade, o paciente apresentou crescimento acelerado de volumosa massa em dorso e abdome, impossibilitando a deambulação e causando afastamento do convívio social. O tratamento cirúrgico foi constituído de exérese do tumor em duas etapas, com intervalo de 2 meses. Não existe cura para a neurofibromatose, porém a remoção cirúrgica está indicada nos casos em que há dor, déficit neurológico, desfiguramento, comprometimento de estruturas adjacentes e suspeita de malignidade. São aceitáveis ressecções parciais, quando não houver possibilidade de exérese total. O tratamento cirúrgico realizado constituiu ótima opção para o tratamento do presente caso, uma vez que permitiu a exérese da lesão, com cicatrização satisfatória de ótimo aspecto estético e melhora da qualidade de vida do paciente.
Palavras-chave: Neurofibromatoses. Neurofibroma. Manchas cafécomleite.
Neurofibromatosis is a generic denomination for 3 diseases of genetic origin with autosomal dominant inheritance: neurofibromatosis type I (NF1), neurofibromatosis type 2 (NF2), and schwannomatosis1. The main characteristics of NF1, also known as cutaneous disease of Von Recklinghausen or peripheral neurofibromatosis, are café au lait spots, dermal and plexiform neurofibromas, false axillary or inguinal ephelides, and Lisch nodules2. However, it is a multisystemic disease with potential for ophthalmologic, osteomuscular, cardiovascular, endocrine, and central and peripheral nervous system involvement, as well as the involvement of the learning systems3.
NF1 is characterized by genetic mutations in chromosome 17. It is the most common human disease caused by a defect in only 1 gene, but the phenotypic expression is extremely varied, even among identical twins1. NF1 has an incidence of 1:30001 to 1:40004 newborns. It is inherited from one of the parents in approximately 50% of the cases5. The remaining patients do not have a family history of NF1, suggesting high incidence of new mutations5. NF1 affects male and female patients equally.
Although not all neurofibromatosis patients have serious clinical or aesthetic complications, the majority of patients with NF1 and their families are affected by the uncertain evolution of the disease, the potential appearance of new tumors, aesthetic concerns, and the possible transmission of the disease to their offspring. These issues have a significant impact on the quality of life of the patients and their families6.
This study describes the case of a patient with a giant neurofibroma and its surgical management and includes a short review of the literature on the subject.
CASE REPORT
In November 2009, a 26-year-old man was admitted to the Service of Plastic Surgery and Reconstructive Microsurgery of the Federal University of Ceará, presenting with small cutaneous nodes, which had been present since the age of 3, and café-au-lait spots of different sizes. At the age of 13, the patient developed a mass in the back and abdomen that subsequently developed into a rapidly growing voluminous mass, which hindered walking and caused social isolation.
Physical examination showed that the patient was of short stature (1.32 m), exhibited significant scoliosis, and was unable to walk. Sessile and pedunculated lesions of different sizes were observed mostly in the back and abdomen, freckles were observed in the armpits, and café-au-lait spots of different sizes were widespread (Figures 1 to 3). The patient showed normal intellect but appeared emotionally labile.
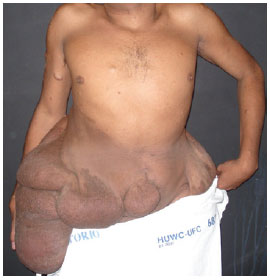
Figure 1 - Preoperative appearance, anterior view.
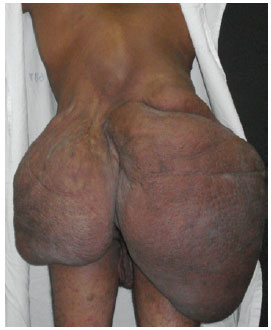
Figure 2 - Preoperative appearance, posterior view.
Figure 3 - Preoperative appearance, lateral view.
Neurofibromatosis was diagnosed on the basis of semiologic criteria and biopsy findings, which indicated multiple subcutaneous nodes and proliferation of fusiform cells with waved and irregular nuclei suggestive of plexiform neurofibroma.
In February 2010, the patient underwent the first surgical intervention (Figure 4), in which a 14.8-kg specimen was excised (Figure 5). Blood transfusion was performed to compensate for blood loss, and the patient was put on a hypercaloric, hyperprotein diet. In April 2010, the patient underwent a second surgery for the resection of a 9.9-kg mass (Figure 6). The patient had a hematoma, which was drained during the immediate postoperative period. The patient was hospitalized for 7 days for each surgery.
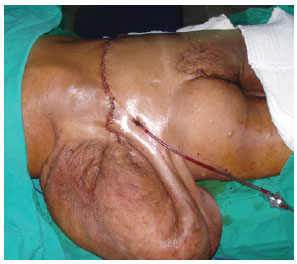
Figure 4 - Transoperative appearance, posterior view.
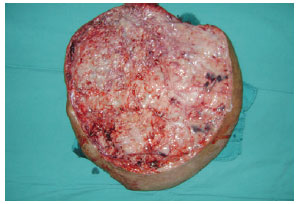
Figure 5 - Mass resected during the first surgical intervention.
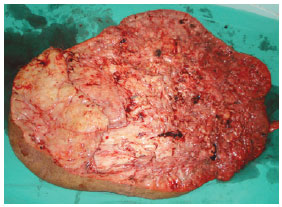
Figure 6 - Mass resected during the second surgical intervention.
DISCUSSION
According to the National Institute of Health (NIH) guidelines, the diagnosis of NF1 is based on the presence of at least 2 of the following signs: occurrence of 6 or more café-au-lait spots larger than 5 mm, 2 or more neurofibromas, axillary freckling, optic glioma, 2 or more Lisch nodules, and bone dysplasia7.
Neurofibromas most commonly present as cutaneous nodes (localized cutaneous neurofibroma). Less frequently, neurofibromas present as self-contained masses in peripheral nerves (localized intraneural neurofibroma) or as diffuse growths of larger nerve branches or of several adjacent nerves (plexiform neurofibroma). Even less frequent is the involvement of the skin and subcutaneous tissue (diffuse cutaneous neurofibroma) or the massive involvement of soft tissues in a specific area of the body (local gigantism or neuromatous elephantiasis)8.
Plexiform neurofibroma, the type of tumor resected from the patient described in this study, is characterized by elongated lesions with multiple nodes. It is classified as a benign peripheral nerve sheath tumor that affects multiple trunks of a single plexus or multiple fascicles of a large nerve. It does not show metastatic behavior; it is highly vascularized, locally invasive, slow growing, and normally appears during childhood and rarely during adolescence9.
A cure for neurofibromatosis has not been discovered; however, surgical removal is indicated in cases associated with pain, neurological deficit, disfigurement, involvement of adjacent structures, and suspicion of malignancy10.
Several possible treatment approaches are available for the correction of neurofibromas including surgical resection of tumors that compromise function or aesthetics, orthopedic surgery for correcting pseudoarthritis and scoliosis, and neurosurgery for preventing serious complications associated with brain or spinal cord tumors10.
From the perspective of plastic surgery, resection of giant neurofibromas is usually a complicated procedure, depending on the size, localization, vascularization, neurological involvement, and microscopic extension of the tumor. The complete resection of large tumor masses is difficult because of the limited space between the tumor and adjoining tissues.
Surgery of this kind is performed under conditions of controlled hypotension, with the employment of associated blood transfusion techniques11.
The assessment of the extent of vascular commitment is very important because spontaneous bleeding during surgery may be extensive and result in hemorrhagic shock and death. The blood vessels supplying the tumor must be isolated and ligated, and usually there are a large number of such vessels11.
A circumferential excision is normally performed from the periphery to the center in the plane under the fascia, which is not highly vascularized. In cases associated with skin loss, it is important to attempt reconstruction during the same hospitalization period because the procedure may result in the generation of a large wound that is difficult to manage outside the hospital environment. Back lesions pose an additional challenge because they are located in an area that is often prone to pressure, which may compromise the integration of the cutaneous graft12.
Partial resections are acceptable in cases in which successful complete excision is not possible.
Giant neurofibroma may cause significant functional disability and can result in disfigurement. Surgical resection was an excellent choice for treatment in the present case, because it enabled complete excision of the mass, with satisfactory wound healing and great aesthetic appearance (Figures 7 and 8), and contributed to the improvement of the patient's quality of life.
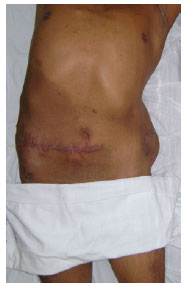
Figure 7 - Postoperative appearance, anterior view.
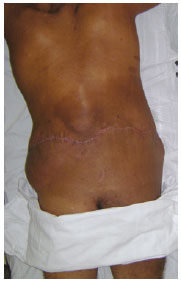
Figure 8 - Postoperative appearance, posterior view.
REFERENCES
1. Souza JF, Toledo LL, Ferreira MCM, Rodrigues LOC, Rezende NA. Neurofibromatose tipo 1: mais comum e mais grave do que se imagina. Rev Assoc Med Bras. 2009;55(4):394-9.
2. North K. Clinical aspects of neurofibromatosis 1. Eur J Paediatr Neurol. 1998;2(5):223-31.
3. Ruggieri M, Huson SM. The neurofibromatosis. An overview. Ital J Neurol Sci. 1999;20(2):89-108.
4. Neville BW, Damm DD, Allen CM, Bouquot JE. Patologia oral e maxilofacial. 2ª ed. Rio de Janeiro: Guanabara Koogan; 2004.
5. Friedman JM. Epidemiology of neurofibromatosis type 1. Am J Med Genet. 1999;89(1):1-6.
6. Riccardi VM, Eichner JE. Neurofibromatosis: phenotype, natural history and pathogenesis. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press; 1992.
7. National Institutes of Health Consensus Development Conference. Neurofibromatosis. Conference statement. Arch Neurol. 1988;45(5):575-8.
8. Kittur SD, Bagdon MM, Lubs ML, Phillips JA 3rd, Murray JC, Slaugenhaupt SA, et al. Linkage analysis of neurofibromatosis type 1, using chromosome 17 DNA markers. Am J Hum Genet. 1989;44(1):48-50.
9. Darrigo Jr LG, Geller M, Bonalumi Filho A, Azulay DR. Prevalence of plexiform neurofibroma in children and adolescents with type I neurofibromatosis. J Pediatr. 2007;83(6):571-3.
10. Beiro AC, Dantas JFC, Conte Neto N, Nasciben MB, Scarso Filho J. Neurofibromatose: uma desordem hereditária. Relato de caso de ocorrência em mãe e filha. R Ci Md Biol. 2008;7(2):193-7.
11. Lin YC, Chen HC. Rare complication of massive hemorrhage in neurofibromatosis with arteriovenous malformation. Ann Plast Surg. 2000;44(2):221-4.
12. Ritz Filho GM, Batti HTB, Vigeti NC, Roça GB, Pintarelli G. Neurofibroma plexiforme gigante de dorso: relato de caso. Rev Bras Cir Plást. 2009;24(3):381-4.
1.Preceptor physician of the Service of Plastic Surgery and Reconstructive Microsurgery of the University Hospital Walter Cantídio of the Federal University of Ceará, specialist member of the Sociedade Brasileira de Cirurgia Plástica (Brazilian Society of Plastic Surgery) (SBCP), Fortaleza, CE, Brazil.
2. Head of the Service of Plastic Surgery and Reconstructive Microsurgery of the University Hospital Walter Cantídio of the Federal University of Ceará, full member of SBCP, Fortaleza, CE, Brazil.
3. Clinical head of the Service of Plastic Surgery and Reconstructive Microsurgery of the University Hospital Walter Cantídio of the Federal University of Ceará, full member of SBCP, Fortaleza, CE, Brazil.
4. Medical student at the Federal University of Ceará, member of the League of Plastic Surgery and Reconstructive Microsurgery Dr. Germano Riquet, Fortaleza, CE, Brazil.
Correspondence to:
Iana Silva Dias
Rua Francisco Gonçalves, 1351 - ap. 1602 - Cocó
Fortaleza, CE, Brazil - CEP 60135-430
E-mail: ianasilvadias@yahoo.com.br
Article submitted to SGP (Sistema de Gestão de Publicações/ Manager Publications System) of RBCP (Revista Brasileira de Cirurgia Plástica/Brazilian Journal of Plastic Surgery).
Article received: December 9, 2010
Article accepted: April, 2011
This study was carried out at the Service of Plastic Surgery and Reconstructive Microsurgery of the University Hospital Walter Cantídio, Fortaleza, CE, Brazil.


 Read in Portuguese
Read in Portuguese
 Read in English
Read in English
 PDF PT
PDF PT
 Print
Print
 Send this article by email
Send this article by email
 How to Cite
How to Cite
 Mendeley
Mendeley
 Pocket
Pocket
 Twitter
Twitter