
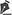
Reviw Article - Year 2011 - Volume 26 -
Biomaterials for orbital reconstruction: literature review
Biomateriais para reconstrução da órbita: revisão da literatura
ABSTRACT
The treatment of traumatic lesions of the orbit remains a challenge for the maxillofacial surgeon. When surgical correction is not performed or is performed incorrectly, may occur enophthalmos, diplopia, ocular dystopia, restriction of ocular movements and dysfunction of the infraorbital nerve. The importance of surgery is to release the herniated orbital tissue at the fracture site, restoring the normal architecture of the orbit, aiming at an adequate functional and aesthetic results. In recent decades, many advances have occurred in the surgical treatment of these fractures, as well as in diagnostic methods. With the development of multislice CT, it became possible to analyze three-dimensional orbit, as well as its volumetric evaluation, which revolutionized the surgical management of these fractures. Another factor with direct impact on the reconstruction of the orbits, is the availability of various biomaterials for the restoration of the orbital walls. The objective of this paper is to review the materials available for reconstruction in cases of fractures of the orbital floor, its applicability to compare practices and highlight those most used in the Plastic Surgery Service, Hospital de Clinicas, Unicamp, in recent years. Among the materials of choice in our service, we highlight the autogenous skull bone, cartilage of ear shell, the titanium mesh and porous high density polyethylene. Each biomaterial has specific indications, according to the characteristics of orbital fracture, being considered for choosing the material, the long-term results and experience of surgeon.
Keywords: Orbit/injuries. Orbit/surgery. Biocompatible Materials. Facial Injuries.
RESUMO
O tratamento de lesões traumáticas da órbita permanece um desafio para o cirurgião maxilofacial. Quando a correção cirúrgica não é realizada ou é feita de maneira inadequada, pode ocorrer enoftalmia, diplopia, distopia ocular, restrição da movimentação ocular e disfunção do nervo infraorbital. A importância da cirurgia consiste em liberar o tecido orbitário herniado pelo foco de fratura, restaurar a arquitetura normal da órbita, objetivando um resultado estético e funcional adequado. Nas últimas décadas, vários avanços ocorreram no tratamento cirúrgico destas fraturas, bem como nos métodos diagnósticos. Com o desenvolvimento de tomografias computadorizadas de múltiplos detectores, tornou-se possível a análise tridimensional da órbita, assim como sua avaliação volumétrica, o que revolucionou o manejo cirúrgico destas fraturas. Outro fator com impacto direto nas reconstruções das órbitas é a disponibilidade de diversos biomateriais, para restauração das paredes orbitárias. Assim, o objetivo desse artigo é revisar os materiais disponíveis para reconstrução nos casos de fraturas do assoalho da órbita, comparar suas aplicabilidades práticas e destacar aqueles mais utilizados no Serviço de Cirurgia Plástica do Hospital de Clínicas da Unicamp, nos últimos anos. Dentre os materiais de escolha, em nosso Serviço, destacamos o osso autógeno de calota craniana, a cartilagem de concha auricular, a tela de titânio e o polietileno poroso de alta densidade. Cada biomaterial apresenta indicações específicas, de acordo com as características da fratura orbitária, sendo considerados, para a escolha do material, os resultados a longo prazo e a experiência do cirurgião.
Palavras-chave: Órbita/lesões. Órbita/cirurgia. Materiais Biocompatíveis. Traumatismos Faciais.
Considerações Gerais
O trauma é uma das principais causas de morbidade e mortalidade nos dias atuais. Entre os diversos tipos de trauma, destaca-se o trauma de face, pelas repercussões físicas, emocionais e possibilidade de lesões permanentes. Há elevado índice de lesões traumáticas da face se comparado a outras áreas do corpo. Tal fato se deve à grande exposição e pouca proteção da região facial1.
A ocorrência do trauma orbitário está relacionada a condições socioeconômicas, acometendo, mais frequentemente, indivíduos do gênero masculino, jovens, de baixa renda ou economicamente inativos. Entre as principais causas de fraturas orbitárias, destacam-se os acidentes com veículos, quedas, práticas esportivas, violência interpessoal e acidentes de trabalho2,3. O tratamento visa à recuperação da função do esqueleto orbitário, evitar a desfiguração e alteração da simetria facial, além de devolver, precocemente, o paciente às suas atividades habituais.
A órbita é composta por sete ossos que formam uma pirâmide, que tem a função de proteger o olho e suas estruturas anexas. Esses ossos se articulam em 4 paredes: lateral (zigomático, esfenoide e frontal); medial (maxilar, lacrimal, etmoide e esfenoide); superior ou teto (frontal e esfenoide) e inferior ou assoalho (zigomático, maxilar e palatino). Esta forma piramidal da cavidade orbital tem uma base anterior, circunscrita pelo rebordo e, um ápice posterior. As principais relações da órbita incluem a fossa craniana anterior, acima, e o seio maxilar, abaixo. Medialmente, o seio etmoidal e o osso lacrimal separam a órbita da cavidade nasal. Mais posteriormente, as cavidades orbitais são separadas entre si pelo osso esfenoide. Lateralmente, a órbita se relaciona com a fossa temporal e com a fossa craniana média. A porção superior da órbita é composta por estruturas ósseas rígidas, em contraste com a parede medial e com o assoalho, que são áreas de fragilidade, compostas por ossos extremamente delgados.
O assoalho da órbita quase sempre sofre uma lesão cominutiva na parte côncava central, cuja gravidade varia com a intensidade da força de impacto. A posição do globo ocular é determinada pela integridade destas paredes e pelos ligamentos que o suspendem. Lesões nas paredes orbitárias e no sistema de ligamentos suspensórios causam deslocamento nos tecidos moles, pelas forças da gravidade e retração cicatricial. Estes processos alteram o formato dos tecidos moles da órbita de um cone para uma esfera e o globo sofre recuo e depressão, levando à enoftalmia4 (Figura 1).
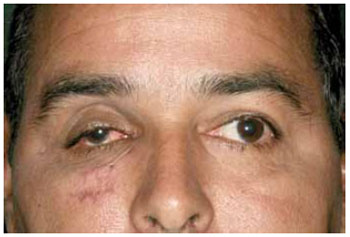
Figura 1 - Enoftalmia. Sequela de fratura orbitária direita, por coice de animal.
Nos pacientes portadores de fraturas de órbita, pode ocorrer edema, equimose periorbitária, equimose no sulco bucal vestibular superior no lado afetado, afundamento da proeminência zigomática, deformidade do processo zigomático da maxila, da margem orbitária e do arco zigomático, enoftalmia ou exoftalmia e proptose ocular, deslocamento da fenda palpebral, nível e reflexo pupilar alterado, oftalmoplegia e distopia ocular vertical, epistaxe no lado afetado, equimose subconjuntival, enfisema, crepitação, trismo, dor, alteração sensibilidade na região afetada e parestesia no trajeto no nervo infraorbitário, diplopia5.
A enoftalmia, assim como o relato de diplopia, é indicativa da necessidade de intervenção cirúrgica. Outra indicação é a herniação de tecidos periorbitários, através de defeitos no assoalho e a presença de fragmentos ósseos no interior da órbita evidenciados pelos exames de imagem. Porém, a falta de maiores evidências pode tornar a indicação e a época ideal cirurgia em temas controversos e variáveis.
Alguns desses sinais e sintomas, citados acima, são observados em pacientes com fraturas tipo blowout. Estas fraturas acometem, exclusivamente, o assoalho e/ou a parede medial orbitária, nos pontos mais fracos destas paredes, que são a porção situada medialmente ao canal infraorbitário no assoalho e a lâmina papirácea do etmoide na parede medial (Figura 2). A fisiopatologia destas fraturas é explicada por duas teorias. A primeira chamada de teoria hidráulica relata que a força é transmitida por meio do impacto no globo ocular, o qual sofre retropropulsão e eleva a pressão intraorbital. Esta pressão é transmitida à parede medial ou inferior, enquanto a borda orbitária permanece intacta. A segunda teoria é explicada pelo impacto direto da força na borda orbitária, onde a força é transmitida para a parede de menor espessura, causando a fratura6.
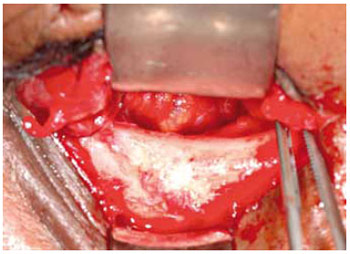
Figura 2 - Defeito ósseo em assoalho de órbita.
Biomateriais para Reconstrução Orbitária
Nos últimos anos, houve um avanço considerável dos biomateriais disponíveis para reconstrução do assoalho da órbita e, ao mesmo tempo, a experiência cirúrgica e a observação clínica tornaram possível selecionar os materiais mais confiáveis e de aplicação clínica adequada.
O material ideal deve ser inerte, biocompatível, não alergênico, não carcinogênico, resistente à infecção, esterilizável, radiopaco, de fácil manuseio, moldável, permitir a estabilização e fixação, de custo viável, facilmente disponível e possível de ser removido sem danos às estruturas adjacentes.
Até o presente momento, nenhum tipo de material foi capaz de reunir todas as características acima, porém, com os avanços atuais, tem se aproximado bastante disto. Devem ser lembrados, também, os diversos fatores que influenciam na escolha do material, como o tamanho do defeito, o envolvimento de múltiplas paredes orbitárias, a adaptação ao contorno orbitário, a restauração do volume apropriado, a presença de comunicação com cavidades dos seios da face, principalmente o seio maxilar, a prevenção de migração e deslocamento, através da fixação do material com suturas, parafusos ou adesivos, o risco de aderências e restrição à motilidade ocular, a prevenção de colonização bacteriana, a época da correção cirúrgica em relação ao trauma.
Ressalta-se a importância da abordagem cirúrgica precoce para prevenir o encarceramento do conteúdo orbitário, com restauração mais confiável do volume apropriado, evitando sequelas. Enfim, a experiência do cirurgião é um fator que deve ser citado, como um dos principais para definir a escolha do material7.
REVISÃO DA LITERATURA
Seleção do Material
Existem biomateriais de ocorrência natural, assim como substâncias sintéticas. Didaticamente divide-se em materiais autógenos, alógenos e aloplásticos. Dentre os materiais autógenos destacam-se os ossos (calota craniana, crista ilíaca, arcos costais, parede de seio maxilar e mandíbula) e cartilagens (concha auricular e septo nasal). Entre os alógenos, pouco usados na prática, mas que merecem citação, encontram-se a dura-máter e a fáscia lata liofilizada, além de ossos provenientes de doador cadáver. E, por fim, os materiais aloplásticos, cuja importância tem sido reconhecida e com crescente utilização, tanto de materiais inabsorvíveis, como de absorvíveis.
Materiais Autógenos
Os tecidos autógenos, ou seja, extraídos do próprio paciente, foram os primeiros a serem usados para reconstrução orbitária e permanecem como material-padrão, com o qual os outros materiais são comparados e são frequentemente utilizados ainda hoje. As maiores vantagens deste tipo de material incluem sua eficácia e confiabilidade, com uma taxa aceitável de complicações a longo prazo.
O osso e a cartilagem autólogos conferem estabilidade ao assoalho da órbita, em função de sua resistência e pelo fato de permitirem uma incorporação ao tecido adjacente e vascularização. Assim, demonstram ser adequados, anatômica e fisiologicamente, para correção de defeitos do assoalho orbitário.
Estes enxertos estão associados a baixa taxa de infecção e extrusão, e não causam rejeição ou reação de corpo estranho8. Porém, algumas desvantagens afastam estes materiais do ideal desejado. Uma taxa de reabsorção, imprevisível, pode ocorrer, variando de 20 a 75%, com potencial evolução para enoftalmia tardia, por perda de sustentação do conteúdo orbitário. Outra desvantagem é a necessidade de um segundo sítio operatório, que aumenta o tempo e a morbidade cirúrgica. Apesar disto, quando se opta pelo osso da calota craniana ou pela cartilagem auricular, temos uma área cirúrgica adjacente ao acesso original, com pouca dor pós-operatória, acrescentando muito pouca morbidade. Ainda, as cicatrizes são bem aceitáveis esteticamente ou até imperceptíveis.
Por serem tecidos de áreas sadias, do próprio paciente, estão disponíveis em quantidades limitadas, o que restringe seu uso pelo risco de causar deformidades iatrogênicas na área doadora. Isto é pouco comum para enxertos ósseos de calota craniana, mas importante no caso de cartilagens auriculares e nasais.
Osso Autógeno: Calota Craniana
As principais fontes de osso autólogo, citadas na literatura, são calota craniana, crista ilíaca, costela, parede de seio maxilar e mandíbula. O osso de calota craniana tem aplicabilidade prática efetiva, sendo o enxerto ósseo autógeno de primeira escolha em defeitos amplos (Figura 3). O fato de ser constituído, em sua maior parte, por osso cortical torna-o resistente e com baixa taxa de reabsorção, entre 20 a 30%. A proximidade com o sítio cirúrgico primário e, em algumas circunstâncias através do mesmo acesso cirúrgico, coronal, é outro fator favorável, assim como a disponibilidade de quantidade suficiente para correção de múltiplos defeitos, sem causar deformidades. A resistência óssea é um fator benéfico, mas que pode atrapalhar a capacidade de modelagem do material, dificultando a adaptação às paredes, pela sua pouca maleabilidade. Exige, como alternativa, por vezes, a fratura do fragmento ósseo de calota e fixação com placas e parafusos que funcionem como uma dobradiça, facilitando a acomodação ao defeito orbitário e sua fixação. Algumas das poucas complicações descritas são hematomas intracerebrais, hemorragia subaracnoidea e fístulas liquóricas9.
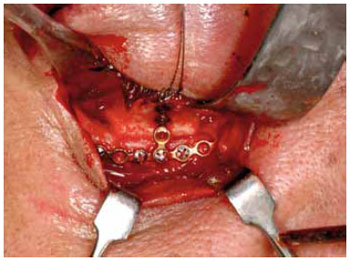
Figura 3 - Osso autógeno. Enxerto de calota craniana em assoalho de órbita.
Com relação aos enxertos de crista ilíaca e costelas, seu uso tem as desvantagens de adicionar um segundo sítio cirúrgico, distante da área abordada. Além disto, existem maiores dificuldades técnicas, risco de pneumotórax, necessidade de drenos, internação prolongada, cicatrizes indesejáveis, pós-operatório delicado devido a dor e desconforto, que acrescentam morbidade cirúrgica, praticamente, inaceitável frente aos outros materiais disponíveis. A única vantagem, quando comparados à calota craniana, é o fato de serem mais facilmente ajustáveis ao contorno orbitário por serem constituídos por menor quantidade de osso cortical, o que, por outro lado, aumenta a taxa de reabsorção óssea futura10,11.
Cartilagem Autógena: Concha Auricular
O uso de enxertos cartilaginosos autólogos foi inicialmente descrito para reconstruções nasais. Posteriormente, seu uso foi adaptado para reconstruções de assoalho de órbita (Figura 4), com resultados bem satisfatórios. As áreas doadoras incluem a concha auricular e a cartilagem quadrangular do septo nasal. Apresenta flexibilidade, facilidade de manuseio, baixas taxas de infecção e reabsorção, com discreta morbidade da área doadora.
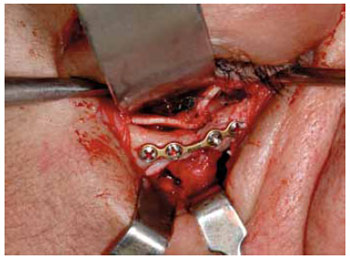
Figura 4 - Cartilagem autógena. Enxerto de cartilagem auricular em assoalho e parede medial de órbita.
Os resultados insatisfatórios estão relacionados à sua tendência a arquear, em decorrência da grande "memória", tendendo a retomar seu formato original. Neste caso, a flexibilidade deixa de ser um benefício. A cartilagem do septo nasal tende a arquear menos. Por estas razões, o uso de cartilagem torna-se limitado a pequenos defeitos da órbita, sendo incapaz de suportar o conteúdo intraorbitário, com probabilidade de complicações tardias, tais como enoftalmo e diplopia12,13.
De mesma maneira, ainda mais que os ossos autógenos, as cartilagens estão disponíveis em quantidades limitadas e a retirada excessiva pode causar alterações estéticas e funcionais, tanto da orelha, quanto do nariz. Alguns autores relatam que os resultados obtidos com o uso da cartilagem são inferiores àqueles apresentados quando do uso de osso. Outras experiências são mais favoráveis à cartilagem, devido às características histológicas, pobre vascularização, baixa taxa de reabsorção e tendência à calcificação. A indicação do uso do septo nasal é restrita, pois o paciente não pode apresentar disfunção respiratória, história prévia de cirurgia nasal e desvio de septo significativo. Conclui-se, assim, que cartilagem autógena permite correção de pequenos defeitos do assoalho da órbita, nos pacientes adequadamente selecionados14.
Materiais Alógenos
O uso de materiais orgânicos provenientes de outro indivíduo, geralmente doador cadáver, ou até mesmo de outra espécie, como porco e boi, também foi aventado como reconstrutores do assoalho da órbita. Inicialmente, utilizaram-se ossos homógenos de banco, mais comumente crista ilíaca, mas também costela, seguido por cartilagem, dura-máter e fáscia lata liofilizadas. Existem artigos descrevendo o uso de derme porcina e esclera bovina, previamente tratadas.
Os ossos homógenos e heterógenos não contêm células vivas, mas podem apresentar características ostecondutoras ou osteoindutoras na sua integração aos sítios receptores. Atuam como arcabouço para o novo osso e possuem características físicas semelhantes ao osso autógeno, embora sejam mais lentos para a revascularização e integração. Esses enxertos não são usados com tanta frequência, pois possuem taxas de reabsorção e infecção maiores do que os enxertos autógenos. Devido à possibilidade de obtenção em grande quantidade e à sua integração ao leito receptor, são considerados como materiais aceitáveis para reconstruções orbitárias. Outra vantagem é não exigirem um segundo campo operatório, e consequente redução do tempo cirúrgico. Apesar das técnicas de esterilização, o risco de transmissão de infecções, como a doença de Creutzfeld-Jakob, e o potencial antigênico, podendo desenvolver reação de corpo estranho, desencorajam sua utilização15.
Materiais Aloplásticos
Os materiais aloplásticos têm ganho popularidade para reconstrução da órbita, em razão da facilidade de uso e da eliminação de morbidade da área doadora, além da diminuição significativa do tempo cirúrgico. Outro fator atraente é a multiplicidade de formas e tamanhos disponíveis16. Até mesmo implantes pré-fabricados e individualizados, específicos para cada fratura, podem ser obtidos após estudo tomográfico, incluindo cálculos de volumetria da órbita, o que permite uma reconstrução precisa, reduzindo a taxa de complicações relacionadas à restauração da arquitetura orbitária17-19.
Estes materiais, também, podem ser absorvíveis, ampliando o interesse por materiais aloplásticos. Dentre os inabsorvíveis destacam-se a tela de titânio e o polietileno poroso de alta densidade, ficando em segundo plano o silicone, o politetrafluoretileno e a hidroxiapatita. Dentre os materiais absorvíveis temos a tela de poliglactina e as placas de polidioxanona. Estes, contudo, também não apresentam todas as características do material ideal, visto que são corpos estranhos, interpretados como antígeno pelo organismo, com potencial de reação variável pelo hospedeiro20,21. Existem outros produtos disponíveis no mercado, alguns sem avaliação a longo prazo, o que se torna uma preocupação, devido ao surgimento de complicações ainda imprevisíveis.
Inabsorvíveis
1. Tela de Titânio
Implantes metálicos revolucionaram o tratamento das fraturas de face, permitindo a fixação estável, de maneira tridimensional. As telas de titânio são amplamente aceitas e adequadas para a reconstrução do assoalho da órbita (Figuras 5 e 6). Isto levou ao desenvolvimento de múltiplas formas, tamanhos e espessuras. Esta tecnologia contribuiu para assegurar uma correção anatômica precisa, com resultados muito favoráveis a longo-prazo, com redução de complicações relacionadas à alteração de volume e conteúdo orbitário, reduzindo o risco de enoftalmia.
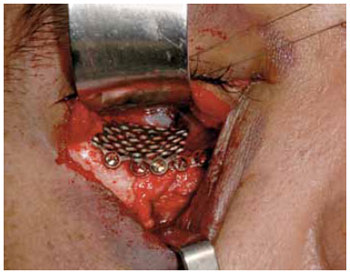
Figura 5 - Tela de titânio. Implante em assoalho de órbita.
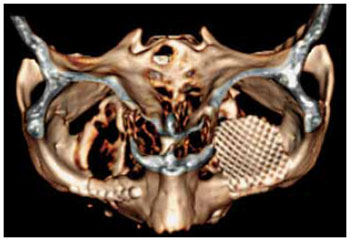
Figura 6 - Tela de titânio em assoalho de órbita esquerda. Reconstrução tridimensional de tomografia computadorizada.
A tela de titânio apresenta excelente biocompatibilidade, boa osteointegração e é completamente inerte. As telas são finas, permitindo o ajuste e a moldelagem com facilidade, para poderem ser adaptadas ao contorno do assoalho orbitário e promover sustentação eficaz de largos defeitos. Elas mantêm a forma a longo prazo, com habilidade única de compensar o volume orbitário, já que não estão sujeitas a reabsorção. Estes implantes estão disponíveis em quantidade, por apresentarem um custo viável. O fato de serem radiopacas permite controle de imagem pós-operatório. Por serem altamente resistentes à corrosão, são esterilizáveis e apresentam baixa taxa de infecção.
Estas telas podem ser fixadas por parafusos, prevenindo seu deslocamento e migração, reduzindo, assim, o risco de extrusão e a necessidade de remoção, o que é dificultado pela incorporação de tecido fibroso e ósseo ao seu redor. Umas das preocupações, inerentes ao uso deste material, é o risco de resposta inflamatória local, com formação de aderências que possam contribuir para restrição da motilidade ocular extrínseca, complicação pouco relatada15.
2. Polietileno Poroso de Alta Densidade
O polietileno poroso de alta densidade tem sido utilizado em cirurgia maxilofacial desde 1984, como um material versátil, substituindo ossos e cartilagens (Figura 7). Para o assoalho orbitário, esse material é apresentado em forma de lâminas, com espessura variando entre 0,25 a 3,0 mm (Medpor®, Porex Corporation, USA).
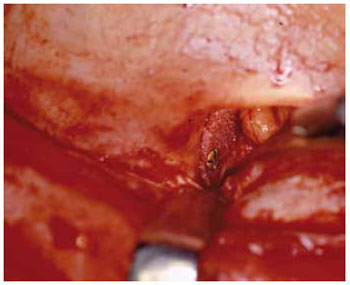
Figura 7 - Polietileno de alta densidade. Implante em parede medial de órbita.
Os implantes apresentam características favoráveis, não sofrem reabsorção ou degradação, induzindo mínima reação tecidual. O tamanho dos poros influencia, diretamente, a taxa de crescimento de tecido fibrovascular, o que minimiza a formação de cápsula e permite a migração de células de defesa imunológica, favorecendo a resistência à infecção. Este crescimento tecidual, ao mesmo tempo, promove estabilidade, o que evita o deslocamento e a extrusão. Outras características importantes são a boa resistência tênsil e a flexibilidade adequada, adquirindo facilmente e de maneira estável o formato desejado. Este material pode ser fixado com parafusos, garantindo sua imobilidade. Uma desvantagem é não permitir controle radiológico, por ser radiolúcido. Poucas complicações têm sido relatadas com seu uso22,23.
Este material foi aprimorado, melhorando suas características mecânicas e tornando-se radiopaco, com a incorporação, ao seu interior, de uma tela de titânio (Medpor Titan®, Porex Corporation, USA) (Figura 8).
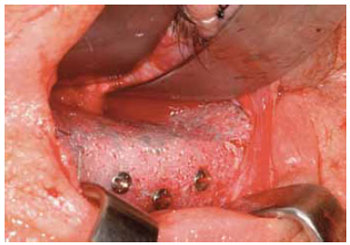
Figura 8 - Polietileno poroso de alta densidade + tela de titânio. Implante em assoalho de órbita.
DISCUSSÃO
Diferentes materiais podem ser utilizados com o intuito de reconstruir o assoalho orbitário. A escolha está associada à disponibilidade do material, ao custo-benefício de cada um e ao planejamento prévio de cada caso. Contudo, independente de qual seja o material, todos devem ser biocompatíveis, prevenindo as reações de corpo estranho e a contaminação local, o que compromete o resultado final esperado24. Em nossa experiência, são mais frequentemente utilizados o osso autógeno de calota craniana, a cartilagem autógena de concha auricular, as telas de titânio e o polietileno poroso de alta densidade. Todos estes materiais, desde que bem selecionados a cada caso, podem levar a bons resultados finais, dentro de padrões esperados de estética e função.
De modo geral, o material ideal é aquele cujas propriedades físicas se assemelhem ao tecido a ser substituído. Assim, sendo a órbita constituída por osso, parece lógico usar enxertos ósseos para substituir os segmentos ausentes. O osso autógeno é um biomaterial popular na reconstrução orbitária, particularmente o osso da calota craniana, e apresenta baixas taxas de infecção. Apesar do osso da calota estar menos sujeito à reabsorção que ossos de outras áreas doadoras, ele pode, também, apresentar taxas imprevisíveis de reabsorção, com subsequente desenvolvimento de enoftalmia ou distopia ocular. Uma dificuldade encontrada com o osso do crânio é a modelagem e adaptação ao contorno orbitário, necessitando de osteotomias e fixações para obtenção de peças curvas. A disparidade entre as capacidades físicas do osso e a anatomia da região torna difícil o posicionamento de peças ósseas extremamente finas, que geralmente fraturam na manipulação. Esse fato restringe o uso da parede do seio maxilar, além da quantidade óssea ser muitas vezes insuficiente para a reconstrução de defeitos extensos da órbita. A desvantagem cirúrgica de se utilizar o osso autógeno é a necessidade de uma área doadora, com aumento do tempo cirúrgico. Apesar do procedimento de remoção do enxerto de calota ser geralmente um procedimento benigno, há um potencial para complicações como fístula liquórica, hematoma subdural e hemorragia intracraniana. Adicionalmente, existem problemas relacionados à área doadora, como cicatriz, alopecia e lesão do ramo temporal do nervo facial. Múltiplos estudos, de várias especialidades que usam fontes ósseas para enxerto, demonstram morbidade da área doadora entra 5 a 9% 25.
Em nosso Serviço, a cartilagem de concha auricular é bastante utilizada para a reconstrução de pequenos defeitos no assoalho da órbita. Um motivo é a simplicidade e a rapidez na remoção do enxerto, com acesso anterior ou posterior, dependendo da preferência do cirurgião e do paciente, já que a cicatriz é mínima e pouco visível, com pouco acréscimo na morbidade cirúrgica. O uso desta cartilagem fica restrito à cobertura de pequenas falhas ósseas, de até 2 x 2 cm. Pode ser fixada com miniplacas e parafusos ou sutura com fio de nylon.
Outra alternativa é o uso de materiais aloplásticos. Existem muitos materiais disponíveis, cada um com diferentes propriedades biomecânicas e químicas. O problema principal com implantes aloplásticos é a tendência natural do sistema imunológico para isolar substâncias estranhas por encapsulamento, que passa a ser uma interface entre o implante e o hospedeiro. A proposta dos modernos materiais aloplásticos é a incorporação do implante ao redor dos tecidos através de osseointegração. Isto é, contato direto entre o material e o osso, sem a presença de cápsula26. As telas de titânio e o polietileno poroso de alta densidade têm propriedades químicas e físicas que os tornam biocompatíveis, com poucos efeitos colaterais.
O uso de tela de titânio é bastante frequente, sendo o material aloplástico mais utilizado em nossa prática cirúrgica. Uma das preocupações inerentes ao uso deste material é o risco de resposta inflamatória local, com formação de aderências que possam contribuir para restrição da motilidade ocular extrínseca. Esta é uma complicação pouco relatada e que não temos visto em nosso Serviço. A grande vantagem é de estarem disponíveis em quantidades não limitadas27,28.
O polietileno poroso de alta densidade é um material biocompatível, que apresenta boa modelagem e adaptação, sendo ainda mais favorável quando apresentado em conjunto com a tela de titânio. Esta associação favorece a adaptação ao defeito ósseo, a preservação da forma estabelecida e, ainda, facilita a fixação do implante ao rebordo ósseo29. Nossa experiência tem se mostrado bastante favorável ao uso deste material, sendo fator limitante o custo.
Diferentes defeitos ósseos e situações clínicas requerem abordagens distintas. Segundo Ellis e Messo15, o tipo de material utilizado em reconstruções orbitárias primárias e secundárias não deve ser o mesmo. Nas reconstruções primárias, o material deve ter a função de dar suporte ao globo ocular e de restabelecer o contorno das paredes orbitárias. Nesta situação, o material mais indicado é a tela de titânio, uma vez que é fina e de fácil adaptação, pode ser usada como uma ponte ao reconstruir grandes defeitos ósseos. Nas reconstruções orbitárias secundárias, quando os tecidos orbitários estão numa configuração anormal, e a enoftalmia já está instalada, há necessidade de, além de restaurar as paredes orbitárias, reconstituir sua morfologia e seu volume perdido30. Nestas situações, o polietileno poroso de alta densidade tem apresentado excelentes resultados, pois é um material que não reabsorve e é estável volumetricamente.
Revendo a literatura, conclui-se que a seleção de materiais para a reconstrução de assoalho de órbita é um assunto amplo. Existe uma série de biomateriais, facilmente disponíveis, que promovem resultados confiáveis no reparo de várias lesões. O conhecimento dos materiais existentes evita a aplicação imprópria, o que pode reduzir a ocorrência de complicações.
REFERÊNCIAS
1. Kontio R, Lindqvist C. Management of orbital fractures. Oral Maxillofac Surg Clin North Am. 2009;21(2):209-20.
2. Cruz AA, Eichenberger GC. Epidemiology and management of orbital fractures. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2004;15(5):416-21.
3. Pereira MD, Kreniski T, Santos RA, Ferreira LM. Trauma craniofacial: perfil epidemiológico de 1223 fraturas atendidas entre 1999 e 2005 no Hospital São Paulo - UNIFESP-EPM. Rev Bras Cir Craniomaxilofac. 2009;11(1):47-50.
4. Chang EL, Bernardino CR. Update on orbital trauma. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2004;15(5):411-5.
5. Jank S, Schuchter B, Emshoff R, Strobl H, Koehler J, Nicasi A. Clinical signs of orbital wall fractures as a function of anatomic location. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2003;96(2):149-53.
6. Mazock JB, Schow SR, Triplett RG. Evaluation of ocular changes secondary to blowout fractures. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2004;62(10):1298-302.
7. Potter JK, Ellis E. Biomaterials for reconstruction of the internal orbit. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2004;62(10):1280-97.
8. Kontio R. Treatment of orbital fractures: the case for reconstruction with autogenous bone. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2004;62(7):863-8.
9. Al-Sukhun J, Lindqvist C. A comparative study of 2 implants used to repair inferior orbital wall bony defects: autogenous bone graft versus bioresorbable poly-L/DL-Lactide [P(L/DL)LA 70/30] plate. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2006;64(7):1038-48.
10. Cieślik T, Skowronek J, Cieślik M, Cieślik-Bielecka A. Bone graft allpication from anterior sinus maxillary wall in orbital floor reconstruction. J Craniofac Surg. 2009;20(2):512-5.
11. Cavusoglu T, Vargel I, Yazici I, Cavusoglu M, Vural AC. Reconstruction of orbital floor fractures using autologous nasal septal bone graft. Ann Plast Surg. 2010;64(1):41-6.
12. Castellani A, Negrini S., Zanetti U. Treatment of orbital floor blowout fractures with conchal auricular cartilage graft: a report on 14 cases. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2002;60(12):1413-7.
13. Ozyazgan I, Eskitascioglu T, Baykan H, Coruh A. Repair of traumatic orbital wall defects using conchal cartilage. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2006;117(4):1269-76.
14. Bayat M, Momen-Heravi F, Khalilzadeh O, Mirhosseni Z, Sadeghi-Tari A. Comparison of conchal cartilage graft with nasal septal cartilage graft for reconstruction of orbital floor blowout fractures. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2010;48(8):617-20.
15. Ellis E 3rd, Messo E. Use of nonresorbable alloplastic implants for internal orbital reconstruction. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2004;62(7):873-81.
16. Metzger MC, Schön R, Zizelmann C, Weyer N, Gutwald R, Schmelzeisen R. Semiautomatic procedure for individual preforming of titanium meshes for orbital fractures. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2007;119(3):969-76.
17. Choi SH, Cheung HH. A versatile virtual prototyping system for rapid product development. Comput Ind. 2008;59:477-88.
18. Robiony M, Salvo I, Costa F, Zerman N, Bandera C, Filippi S, et al. Accuracy of virtual reality and stereolithographic models in maxillo-facial surgical planning. J Craniofac Surg. 2008;19(2):482-9.
19. Schön R, Metzger MC, Zizelmann C, Weyer N, Schmelzeisen R. Individually preformed titanium mesh implants for a true-to-original repair of orbital fractures. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2006;35(11):990-5.
20. Ng JD, Huynh TH, Burgett R. Complications of bioresorbable orbital implants and fixation plates. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg. 2004;20(1):85-6.
21. Tuncer S, Yavuzer R, Kandal S, Demir YH, Ozmen S, Latifoglu O, et al. Reconstruction of traumatic orbital floor fractures with resorbable mesh plate. J Craniofac Surg. 2007;18(3):598-605.
22. Yilmaz M, Vayvada H, Aydın E, Menderes A, Atabey A. Repair of fractures of the orbital floor with porous polyethylene implants. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2007;45(8):640-4.
23. Ozturk S, Sengezer M, Isik S, Turegun M, Deveci M, Cil Y. Long-term outcomes of ultra-thin porous polyethylene implants used for reconstruction of orbital floor defects. J Craniofac Surg. 2005;16(6):973-7.
24. Cole P, Boyd V, Banerji S, Hollier LH Jr. Comprehensive management of orbital fractures. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2007;120(7 Suppl 2):57S-63S.
25. Rinna C, Ungari C, Saltarel A, Cassoni A, Reale G. Orbital floor restoration. J Craniofac Surg. 2005;16(6):968-72.
26. Folkestad L, Granström G. A prospective study of orbital fracture sequelae after change of surgical routines. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2003;61(9):1038-44.
27. Ellis E 3rd, Tan Y. Assessment of internal orbital reconstructions for pure blowout fractures: cranial bone grafts versus titanium mesh. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2003;61(4):442-53.
28. Guo L, Tian W, Feng F, Long J, Li P, Tang W. Reconstruction of orbital floor fractures: comparison of individual prefabricated titanium implants and calvarial bone grafts. Ann Plast Surg. 2009;63(6):624-31.
29. Matteini C, Renzi G, Becelli R, Belli E, Iannetti G. Surgical timing in orbital fracture treatment: experience with 108 consecutive cases. J Craniofac Surg. 2004;15(1):145-50.
30. Jatla KK, Enzenauer RW. Orbital fractures: a review current literature. Curr Surg. 2004;61(1):25-9.
1. Médico; Residente de Cirurgia Geral do Hospital de Clínicas da Universidade Estadual de Campinas (Unicamp), Campinas, SP, Brasil.
2. Médico; Residente de Cirurgia Plástica do Hospital de Clínicas da Unicamp, Campinas, SP, Brasil.
3. Professor Titular de Cirurgia Buco-Maxilo-Facial da Área de Cirurgia Plástica da Faculdade de Ciências Médicas da Unicamp, Campinas, SP, Brasil.
Correspondência para:
Prof. Dr. Luis Augusto Passeri
Faculdade de Ciências Médicas - Unicamp
Rua Tessália Vieira de Camargo, 126 - Cidade Universitária "Zeferino Vaz"
Campinas, SP, Brasil - CEP 13083-887
E-mail: passeri@fcm.unicamp.br
Artigo submetido no SGP (Sistema de Gestão de Publicações) da RBCP.
Artigo recebido: 6/7/2010
Artigo aceito: 30/8/2010
Trabalho realizado no Serviço de Cirurgia Plástica do Hospital de Clínicas da Faculdade de Ciências Médicas da Universidade Estadual de Campinas (Unicamp), Campinas, SP, Brasil.


 Read in Portuguese
Read in Portuguese
 PDF PT
PDF PT
 Print
Print
 Send this article by email
Send this article by email
 How to Cite
How to Cite
 Mendeley
Mendeley
 Pocket
Pocket
 Twitter
Twitter