
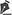
Articles - Year 2002 - Volume 17 -
Effect of Autonomization Surgical Techniques on Transverse Rectus Abdominis Myocutaneous Flaps - Experimental Study in Female Rats
Efeito das Técnicas Operatórias de Autonomização no Retalho Musculocutâneo Transverso do Músculo Reto do Abdome. Estudo Experimental em Ratas
ABSTRACT
A study was conducted on the effect of autonomization surgical techniques on monopediculated transverse rectus abdominis mycutaneous flaps in female rats. Animals in Group A (control) were submitted to the flap procedure proposed for the study, consisting of an incision, removal of the fragment in area 3 and detachment of the flap up to the lower abdomen, followed by on site suture. Animals in groups B, C, D, E, F, G, and H were submitted to different autonomization surnical techniques, seven days before the flap procedure proposed for the study. The area of necrosis in relation to the total flap healing area was assessed by using a sheet of standard graph paper, a fine point Pilot® pen and a transparent cast. A light microscopy histological study was performed on the fragments removed from the contra lateral end of the vascular pedicle of the flap. The autonomization surgical technique that divided the cranial portion of rectus abdominis muscles bilaterally and cauterized both upper deep epigastric vessels used on group C animals was more effective in reducing the area of necrosis of the flap studied, and did not result in histological changes in the fragments examined.
Keywords: Autonomization; flap; skin necrosis; histology.
RESUMO
Estudou-se o efeito das técnicas operatórias de autonomização utilizadas no retalho musculocutâneo transverso do músculo reto do abdome monopediculado de ratas. Os animais do grupo A (controle) foram submetidos à operação do retalho proposto para o estudo, que consistiu na incisão, remoção do fragmento na área 3 e descolamento do retalho até o abdome inferior, seguido de sutura no próprio leito. Os animais dos grupos B, C, D, E, F, G e H foram submetidos a diferentes técnicas operatórias de autonomização, sete dias antes da operação do retalho proposto para o estudo. Avaliou-se a porcentagem de área de necrose em relação à área total do retalho em cicatrização, utilizando-se uma folha milimetrada padronizada, uma caneta Pilot® de ponta fina e um molde transparente. Um estudo histológico, por microscopia de luz, foi realizado nos fragmentos removidos da extremidade contralateral ao pedículo vascular do retalho. A técnica operatória de autonomização que realizou divisão bilateral cranial dos músculos retos do abdome e cauterização de ambos os vasos epigástricos superiores profundos utilizada nos animais do grupo C foi a mais eficaz na redução da área de necrose do retalho estudado, não determinando alterações histológicas nos fragmentos examinados.
Palavras-chave: Autonomização; retalho; necrose de pele; histologia
The transverse rectus abdominis mycutaneous flap was described bv Hartrampf et al. (1982)(1) and Gandolfo (1982)(2), and is considered an excellent flap for breast reconstruction alter mastectomy.
Risk factors(3) included vascular involvement and necrosis of the transverse rectus abdominis mycutaneous flap with a non-dominating vascular pedicle, which were more frequent in obese patients or those who smoked or had abdominal scars, chronic lung conditions, severe cardiovascular conditions, psychological problems or an inexperienced surgeon.
Surgical autonomization led ro an intentional and scheduled ischemia, resulting in an increase in internal vascularization and a reduction in the area of necrosis of cutaneous(4) and myocutaneous flaps with a deficient blood flow, according to previous studies performed in animals(5, 6, 7, 8, 9).
The transverse rectus abdominis mycutaneous flap model in rats was choscn for thc study. This experimental flap model proposed by ögzentas et al. (1994)(6)greatly resembles the transverse rectus abdominis mycutaneous flap in humans, in regard to myocutaneous perforans and nutrition from the nondominating vascular pedicle.
MATERIAL AND METHOD
We used eiiihtv Wistar female rats, weighiny: between 250 g and 300 g, kept under the same conditions at the experimental laboratory of the graduate course on surgerv at the Minas Gerais Federal University Medical School.
Anesthesia was given by the intramuscular route, associating 10 mg/kg of Ketamine Hydrochloride (Ketalar®) and 0.1 mg/kg of 2-(2,6-xilidine)-5,6-dihvdro-4H-l,3Tiazine Hydrochloride (Rompun®).
The 4.2 cm x 2.1cm rectangular transverse rectus abdominis mvcutancous flap model used was divided into areas 1, 2, and 3 (Fig. 1).

Fig. 1- Drawing of the transverse rectus abdominis mycutancous flap with areas 1, 2, and 3. Projection of the rectus abdominis muscle in red. The arrow shows the segment to be sent for histological exam.
The flap procedure consisted of incision, fragment removal in area 3 and detachment of the flap up to the lower abdomen (Figs. 2 and 3). After complete detachment of the flap, nourished by deep lower epigastric vessels and of the rectus abdominis, the flap was sutured with monofilament 4-0 nylon on site.
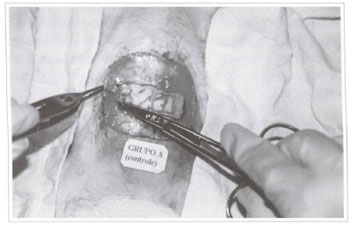
fig. 2 - Fragment of area 3 being removed during the surgical procedure.
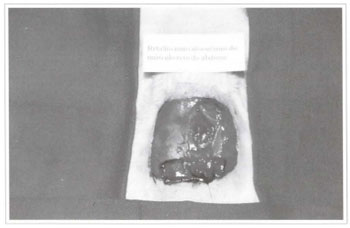
Fig. 3 - Transverse rectus abdominis mycutaneous flap detached and flipped up to the lower abdomen.
The animals in group A (control) were submitted only to the flap procedure proposed for the srudy. The animals in groups B, C, D, E, F, G and H were submitted to different autonomization surgical techniques (Table I) (Figs. 4 and 5). After the seven-day autonomization period, animals were submitted to a flap procedure, similar to the one performed on the animals in group A (control).

Fig. 4 - Autonomization surgical techniques used on the animals in groups B, C, D, and E.
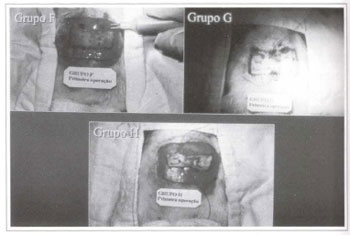
Fig. 5 - Autonomization surgical techniques used on the animals in groups E, G, and H.
The area of necrosis of flaps was measured on the fifth post-surgical dav, using a transparent cast, a fine point Pilot® pen and a sheet of standardized graph paper. Then, the percentage of the area of necrosis in relation to the total flap healing area was calculated.
Fragments removed from flap area 3 were embedded in paraffin blocks, and cut into five micra thick histological slices on a manual microtome, then stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H.E.) for light microscopy studies.
RESULTS
MACROSCOPIC CHANGES
The areas of necrosis began after approximately 48 hours and were defined on the fourth post-surgical day (Fig. 6).
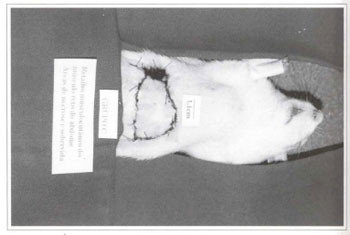
Fig. 6 - Area of necrosis in the transverse rectus abdominis mycutaneous flap.
The animals in group A (control) had necrosis in areas 2, 3 and the lateral part of area 1.
The animals in group B had necrosis in area 3 and part of area 2.
The animals in group C had necrosis only on the lateral part of area 3. There was total flap survival in six female rats.
The animals in group D had necrosis in area 3 and on the lateral part of area 2. There was total flap survival in three female rats.
The animals in group K had necrosis in area 3 and part of area 2. There was total flap survival in six female rats.
The animals in group F had necrosis in area 3 and part of area 2. There was total flap survival in three female rats.
The animals in group G had necrosis in area 3 and part of area 2. There was total flap survival in one female rat.
The animals in group H had necrosis in area 3 and part of area 2. There was total flap survival in one female rat.
STATISTICAL ANALYSIS
The F test indicated a significant difference among groups and the test for minimum significant differences (MSD) allowed tor multiple comparisons between each group (Table II). The graph of percentage of necrosis area in each group was plotted as a histogram (Fig. 7).


Fig. 7 - Percentage of area of necrosis in each group.
MICROSCOPIC CHANGES
Tile fragments removed from the animals in groups A, B, C and G showed no histological changes (Fig. 8).
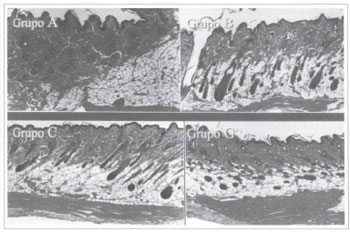
Fig. 8 - Histological slices of groups A, B, C, and G, stained by H. E. (40x).
The tissues in die fragments removed from die animals in groups D, E, F and H presented stcatoneerosis, granulation tissue, abundant inflammatory infiltrate, fascia neovascularization and abscesses (Fig. 9).
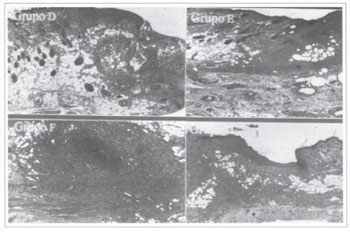
Fig. 9 - Histological slices of groups D, E, F, and H, stained by H. E. (40x).
DISCUSSION
The transverse rectus abdominis mycutaneous flap with a non-dominating vascular pellicle, usually used for breast reconstruction, led to a higher incidence of complications, such as skin necrosis. Autonomization reduces flap skin necrosis according to previous studies (4, 5, 6, 7,8,9).
One disadvantage in the present study in regard to working with female rats was tissue laxity and the small size of the abdominal wall structures in these animals, which demanded greater technical care and the use of a 2.5x magnifying glass.
The anesthetic technique used proved satisfactory, by associating the analgesic effect of ketamine hydrochloride (Ketalar®) and the analgesic muscle relaxant action of 2-(2,6-xilidine)-5,6-dihydro-4H-l,3-tiazine hydrochloride (Rompun®) (lO).
The autonomization period chosen for observing the animals was seven days, which was the period responsible for significant changes leading to the reduction of the area of necrosis of the transverse rectus abdominis mycutaneous flap in the rats(8).
The F test of analysis of variance (ANOVA) showed a significant difference between groups and the test for minimum significant differences allowed for multiple comparisons between groups(ll, 12).
The autonomization procedure used in the animals in group H, the segment in which area 2 was detached and myocutaneous perforans cauterized, associated with the incision in the borders of the flap, was less effective in reducing d1e area of necrosis of d1e flap, contrary to what has been found in the literature(9).
The fragments examined from the animals in groups D, E, F, and H presented histological changes that were compatible with inflammatory process and tissue healing, according to the histological studies in rat tissue described in the literature(13, 14).
The experimental study allowed us to conclude that the autonomization procedure performed on the animals in group C was more effective in reducing the area of necrosis of the transverse rectus abdominis mycutaneous flap with a non-dominating vascular pedicle and did not lead to histological changes in the tissues of the fragments examined.
REFERENCES
1. Hartrampf CR, Sheflan M, Black PW. Breast reconstruction with a transverse abdominal island flap. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1982;69(2):216-25.
2. Gandolfo EA. Breast reconstruction with a lower abdominal myocutaneous flap. Br J Plast Surg. 1982;25:452-7.
3. Hartrampf CR Jr. The transverse abdominal island flap for breast reconstruction: A 7-year experience. Clin Plast Surg. 1988;15(4):703-16.
4. Milton SH. Experimental studies on island flaps II. Ischemia and Delay. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1972;49(4):444-7.
5. Dorion D, Boyd JB, Pang CY. Augmentation of transmidline skin perfusion and viability in transverse rectus abdominis myocutaneous (TRAM) flaps in the pig. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1991;88(4):642-9.
6. Özgzentas HE, Shenaq S, Spira M. Study of the delay phenomenon in the rat tram flap model. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1994;94(7):1018-24.
7. Hallock GG, Rice DC. Evidence for the efficacy of TRAM flap delay in rat model. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1995;96(6):1351-7.
8. Restifo RJ, Ahmed SS, Isemberg SJ, Thomson JG. Timing, magnitude, and utility of surgical delay in the TRAM flap. I: Animal studies. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1997;99(5):1211-6.
9. Restifo RJ, Ahmed SS, Rosser J, Zahir K, Zink J, Lalikos JA, Thomson JG. TRAM flap perforator ligation and delay phenomenon: development of an endoscopic / laparoscopic delay procedure. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1998;101(6):1503-11.
10. Massone F. Anestesiologia veterinária - farmacologia e técnicas. In: Técnicas anestésicas em animais de laboratório. 3. ed. Rio de Janeiro: Guanabara Koogan; 1999. Cap. 10; p. 97-102.
11. Johnson R, Bhathacharyya G. Statistics principles and methods. New York:Wiley; 1986. p. 578.
12. Montgomery DC. Design and analysis of experiments. New York:Wiley; 1991. p. 649.
13. Alfonso CG, Perez FP. Patología quirúrgica de los animales domésticos. Barcelona:Científico-médica; 1982. Cap. 3; p. 119-74.
14. Cheville NF. Introdução a Patologia Veterinária. Manole:São Paulo; 1994. Cap. 19; p. 321-42.
I. Senior Member of SBC T. Master's Degree in Medicine from the Universidade Federal de Minas Gerais.
2. Head Professor of Digestive System Surgery in the Department of Medicine of Universidade Federal de Minas Genus.
Address for correspondence:
Rui Lopes Filho, MD
R. Concgo Rocha Franco, 133 - ap. 302
30430-000 - Belo Horizontc - MG Brazil
Phone: (55 31) 3337-8597


 Read in Portuguese
Read in Portuguese
 Read in English
Read in English
 PDF PT
PDF PT
 Print
Print
 Send this article by email
Send this article by email
 How to Cite
How to Cite
 Mendeley
Mendeley
 Pocket
Pocket
 Twitter
Twitter