
Original Article - Year 2017 - Volume 32 -
Comparison of the rate of seroma between conventional and inverted T abdominoplasty in post-bariatric patients
Comparação da ocorrência de seroma entre as técnicas de abdominoplastia convencional e em âncora nos pacientes pós-bariátricos
ABSTRACT
INTRODUCTION: The earliest descriptions of abdominoplasties date back to the early 20th century and have been unchanged over time. However, only within the last three decades have there been major advances and innovations in the technique, largely because of the rising popularity of bariatric surgery. In certain patients, we observed a higher incidence of complications, including seroma development. The objective is to evaluate and compare the incidence of seroma between two abdominoplasty techniques, conventional and inverted T, in post-bariatric patients.
METHODS: We retrospectively analyzed the records of 30 patients with a history of bariatric surgery and body mass index (BMI) less than 30 who underwent abdominoplasty by a single surgeon between February 2009 and March 2015. Of these, 15 patients were treated by the conventional technique (conventional group), while the other 15 patients were treated by the inverted T technique (Inverted T group). During the postoperative clinical follow-up, the occurrence of seroma and other complications was assessed.
RESULTS: Thirty female patients with a mean age of 36 years, mean weight of 70 kg and a mean BMI of 25 kg/m2, without significant differences between groups, were studied. The overall occurrence of seroma in the study was 23%. A statistically significant difference (p = 0.04) was observed between the conventional group, in which six patients (40%) developed seroma, compared to the anchor group, in which one patient (6.7%) developed seroma. Dehiscence was observed, with no significant difference in occurrence between the two groups.
CONCLUSION: The incidence of seroma was higher in patients who underwent conventional abdominoplasty compared to those who underwent inverted T abdominoplasty.
Keywords: Seroma; Abdominoplasty; Abdominoplasty/adverse effects; Bariatric surgery.
RESUMO
INTRODUÇÃO: As primeiras descrições de abdominoplastias remontam do início do século XX, sendo pouco modificadas no decorrer do tempo. Porém, somente nas últimas três décadas, devido à popularidade da cirurgia bariátrica, houve grandes avanços e inovações na técnica. Com esse paciente peculiar, notamos uma maior incidência de complicações, dentre elas o seroma. O objetivo é avaliar e comparar a ocorrência de seroma entre duas técnicas de abdominoplastia, convencional e em âncora, nos pacientes pós-bariátricos.
MÉTODOS: Estudo retrospectivo, de um único cirurgião, na qual 30 pacientes com história de cirurgia bariátrica e IMC (Índice de Massa Corporal) menor que 30 foram submetidas à abdominoplastia, entre o período de fevereiro de 2009 a março de 2015, sendo 15 pacientes operadas pela técnica convencional (Grupo convencional) e 15 pela técnica em âncora (Grupo em âncora). No seguimento clínico pós-operatório, foi investigada a ocorrência de seroma e outras complicações.
RESULTADO: Foram estudadas 30 pacientes do sexo feminino com idade média de 36 anos, peso médio de 70 Kg e IMC médio de 25 Kg/m2, sem diferenças significativas entre os grupos. A ocorrência global de seroma no estudo foi de 23%. Foi observado uma diferença estatisticamente significante (p = 0,04) entre os grupos convencional, seis pacientes (40%), em relação ao grupo em âncora, um paciente (6,7%). Foi observada a ocorrência de deiscência, sem diferença significativa entre os grupos.
CONCLUSÃO: A incidência de seroma foi maior naquelas pacientes submetidas à abdominoplastia convencional em relação à abdominoplastia em âncora.
Palavras-chave: Seroma; Abdominoplastia; Abdominoplastia/efeitos adversos; Cirurgia bariátrica.
The procedures used to improve body contour of the abdomen can be traced back to the early 20th century, consisting of dermolipectomy of the abdominal apron fat tissue. These surgeries were performed only to remove excess skin and the underlying fat, with little regard for aesthetic principles.
In the middle of the century, advances in abdominoplasty techniques consisted of improving the positioning of the scar, plication of the abdominal wall, and the transposition of the navel.
With the introduction of bariatric surgery between the 1970s and 1980s by the Brazilian surgeon Salomão Chaib and the American Edward Mason1, a new avenue was opened in plastic surgery: the surgical treatment of patients with significant flaccidity due to large weight losses. The inverted T abdominoplasty procedure for post-bariatric patients was described by Joffe, which was followed by Matory and Soundararajan2.
In the 1980s, liposuction was described by Illouz. For a long time, the combination of abdominoplasty with liposuction was prohibitive or indicated with caution, due to the high risk of abdominal flap necrosis. From 2000 onward, a new concept of abdominoplasty developed due to a better understanding of the neurovascular anatomy, with preservation of the perforating bundles of the rectus abdominis muscle, and improvements in the surgical technique, with supra-umbilical tunneled detachment and use of smaller diameter cannulae. This has made lipoabdominoplasty an excellent technique for remodeling and improving body contour3,4.
Obesity and Bariatric Surgery
Obesity is currently considered a public health problem. It is a multifactorial disease of epidemic proportions: 52.5% of Brazilians are overweight, according to data from the Ministry of Health5. There are about 30 million obese individuals worldwide, and 10% are considered morbidly obese1. With the increase in this number, the number of bariatric surgeries has also risen.
In 2014 alone, 88,000 procedures were performed and, consequently, there was an increase in demand for plastic surgery to treat the skin excesses resulting from the laxity of large weight loss. Hence, it is of utmost importance that plastic surgeons be familiar and recognize all biopsychosocial problems that this process involves. As Dr. Alfredo Donnabella, regent of the chapter of Post-Bariatric Plastic Surgery of the SBCP, stated:
"The post-bariatric patient is a constant challenge. Knowing the behavior of this patient's body and its limitations is very important to create real expectations as to the possible outcomes. It is important to point out that the ex-obese patient suffered a lot before reaching the plastic surgeon's clinic, was discriminated against, was charged as "shameless" because he had difficulty in losing weight and struggled with his self-esteem. The Plastic Surgeon should receive this patient as someone who asks for help to finish the process of building a new body, and why not, a new soul, that started with bariatric surgery"5.
It should be recognized that individuals who have undergone gastroplasty and present with flaccidity due to weight loss are peculiar patients, who are accompanied by a degree of anemia and malnutrition and often have excess skin, all of which are surgically challenging. Thus, new techniques and innovations have been developed to improve the performance of abdominoplasty.
Current Trends in Abdominoplasty
According to a global survey conducted by the International Society of Aesthetic Plastic Surgery, abdominoplasty was found to be the 6th most common surgical procedure worldwide, with a total of 682,568 (7.1% in total) surgeries having been performed in 2014. In Brazil, it is the 4th most common procedure, with 121,884 surgeries having been performed, only after liposuction, breast augmentation and eyelid surgery6.
However, if we consider only post-bariatric patients, abdominal dermolipectomy is the most common procedure, being performed in almost all cases involving female patients. The prevalence of men who undergo bariatric surgery and who apply for abdominoplasty is around 20%7.
Abdominoplasties can be divided into four basic groups:
1. Low transverse pubic abdominoplasty, known as standard, conventional or classic abdominoplasty;
2. Xiphopubic abdominoplasty with transverse pubic compensation, which results in a scar in inverted T cases, also known as fleur-de-lis or anchor;
3. Enlarged and non-enlarged mini-abdominoplasty, with elongated Pfannenstiel incision;
4. Reverse abdominoplasty 8.
Complications of Abdominoplasty
Significant complications still occur in abdominoplasties, and develop at a rate that varies between 4% and 80%. This is due to the large variation in techniques, associated procedures, patient biotypes, and associated diseases.
The most frequent complications, according to a review of 354 articles, included seroma, necrosis, hematoma, infection, and venous thromboembolism. The occurrence of seroma, which ranges in incidence from 1% to 57%, is one of the most frequent complications, with most authors believing that 10% of patients develop the condition. Approximately one third of the articles addressing complications in abdominoplasties classify seroma as a single theme9.
Seroma
Seroma is a collection of fluid, formed by an exudate, in areas of large detachment and "dead" space, which can be detected clinically or through imaging tests, such as ultrasonography. It is predominantly composed of neutrophils and a high concentration of proteins10. Its pathophysiology is still uncertain, with several theories postulating, among others, that vessels and lymphatic channels rupture and create dead space wherein shear forces develop between the flap and the muscular fascia, and induce the release of inflammatory mediators.
The predisposing factors include a high body mass index (BMI), the detachment plan of the flap, and the combination of treatment with liposuction or other procedures. Usually, it is a self-limited phenomenon; however, it can be persistent and sometimes leads to encapsulation of the collection. The clinical picture is manifested by pain and fluid bulging, commonly observed in the lower segments of the abdomen.
In general, the formation of seroma is related to the lack of adherence between the flap and the underlying tissue, which is worsened by shear forces. During traditional abdominoplasty, the flap is elevated juxta-aponeurotically, thereby sectioning many lymphatic vessels. It is proposed that, in this type of technique, the fat behind the abdominal flap does not adhere well to the surface of the aponeurosis, which leads to the formation of the seroma. To circumvent this problem, many authors have proposed the use of adhesive sutures (Baroudi sutures)11, progressive tension sutures (Pollock sutures)12, and/or preservation of the Scarpa's fascia (Saldanha technique)4.
Notably, any factor that increases the inflammatory process after surgery may increase the chance of seroma, and minimizing each of these processes is an important foundation in its prevention. Therefore, seroma risk is reduced with the sparing use of electrocautery, the avoidance of thermal damage, a meticulous hemostasis, the careful handling of the flap, and a decreased surgical time.9
OBJECTIVE
To evaluate and compare the incidence of seroma between two abdominoplasty techniques, conventional and inverted T, in post-bariatric patients.
METHODS
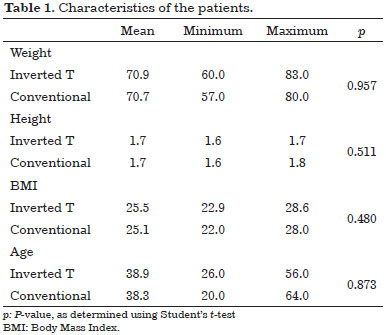
Between February 2009 and March 2015, consecutive patients who had undergone treatment at the Brazilian Red Cross Hospital, in São Paulo, SP, were retrospectively selected for this study. In total, 30 patients were included in the study, of which 15 were treated with conventional abdominoplasty and 15 were treated with inverted T abdominoplasty. The patients signed an informed consent form and the study protocol followed the principles outlined in the Declaration of Helsinki. Table 1 describes the characteristics of the patients.
All data were collected and all surgical procedures as well as postoperative care were performed by the same surgeon (L.S.S.).
Written informed consent was obtained from all patients prior to their inclusion in this study, and their anonymity was assured. The information collected from the patients included age, weight, height and BMI, associated diseases, history of smoking, time of drain, follow-up time, occurrence of seroma, dehiscence, and the development of other complications.
The inclusion criteria were: patients who sought our service to improve abdominal body contour, a BMI less than or equal to 30 kg/m2, and previous laparoscopy or open bariatric surgery. The exclusion criteria were: presence of comorbidities, such as diabetes, malnutrition and anemia; a BMI greater than 30 kg/m2; previous liposuction or abdominal surgery, with the exception of bariatric surgery and cesarean deliveries; smoking habit; associated surgical procedures, such as liposuction; and refusal to participate in the study. Fifty-eight patients were excluded. The inclusion rate was 34%.
The patients were divided into two groups: the Conventional Group, in which conventional abdominoplasty was performed, and the Inverted T Group, in which inverted T abdominoplasty was performed.
The decision to use each technique was individualized according to the commitment of each patient's body contour. Patients who presented with infraumbilical abdominal flaccidity underwent conventional abdominoplasty. Those with an important surplus of dermal adipose tissue, including in the lateral vector, underwent inverted T abdominoplasty.
Statistical Analysis
This was a retrospective, analytical, descriptive study with a convenience sample validated to achieve statistical significance.
Initially, the data were analyzed descriptively. The categorical variables are presented as absolute and relative frequencies, and numeric variables are presented as summary measures (mean, quartiles, minimum, maximum and standard deviations).
The mean comparisons between the two groups were performed using Student's t-test, which assumes normality of the data, and was verified using the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test.
The presence of associations between the type of surgery and adverse events were recorded using the Fisher's exact test due to the size of the sample*. Considering that the inverted T surgery produces superior results, unilateral tests were adopted.
For all statistical tests, a significance level of 5% was used. The statistical software SPSS 20.0 was used in the analysis.
Pre-operative
Patients who were admitted to the outpatient clinic underwent a thorough anamnesis and physical examination to evaluate the surgical indication. A minimum of 6 months of weight stabilization and discharge from the bariatric surgery team was required. The patient was examined for hernias or other scars that could compromise surgical procedures and outcomes.
Routine laboratory examinations included complete blood count, renal function, electrolyte levels, fasting glucose level and total protein and fraction levels. The presence of anemia, malnutrition, or other changes contraindicated surgery at that time and the patient was forwarded to the respective specialties.
Resting electrocardiogram and routine chest x-ray were requested, as well as Doppler echocardiography, in patients over 60 years of age.
The evaluation of the abdominal wall in search of hernias was complemented with ultrasonography.
The patient was informed about the surgical procedure, as well as the possible complications, the use of anesthesia, and the nature of postoperative care. An informed consent form was read and signed by all patients.
On the day of the surgery, frontal, profile, and semi-profile photographs of patients were obtained.
The patient was marked in an orthostatic position. The marking of the horizontal incision was positioned at 6 to 7 cm of the rima vulvae, with a 12-cm suprapubic transverse line, and oblique extensions following the natural fold to the anterior axillary line. In the inverted T technique, the vertical triangle has its vertex marked 2 cm below the xiphoid process and the width of the triangle was determined by bimanual palpation throughout the vertical segment. The base of the lateral flaps did not exceed the height of the umbilical scar.
In all patients, antibiotic prophylaxis was performed on anesthetic induction with 2 g of cefazolin. Prophylaxis of venous thrombosis was achieved using anti-thrombotic stockings, intermittent pneumatic compressors, early ambulation, and Enoxaparin (40 mg/day) treatment for 5 days.
In all cases, epidural anesthesia was used with sedation.
Operative technique: conventional (Figure 1)
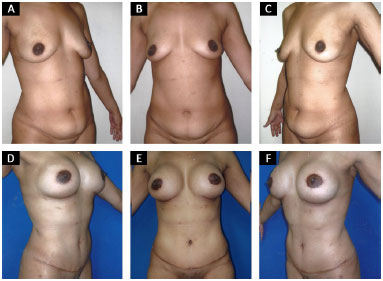
Figure 1. Conventional abdominoplasty. A, B and C: Preoperative; D, E and F: Post-operative period of 6 months.
Detachment of the flap was performed in a supra-aponeurotic plane with electrocautery and supraumbilical epigastric tunneling. Plication of the diastasis of the rectus abdominis muscle was performed in a single plane using an interrupted and inverted "X" suture made with a nylon 2-0 nonabsorbable suture.
After the patient was placed in a semi-flected position, the excess of the dermofat flap was excised. Adhesive sutures (three supraumbilical and four infraumbilical (two on each side)) between the fascia of the flap and the aponeurosis were created. Two 4.8 mm suction drains were placed with output in the pubis and connected to a single reservoir. Sutures were made by planes: subcutaneous, subdermal and intradermal. Then, the navel transposition was performed.
Operative technique: inverted T (Figures 2 and 7)
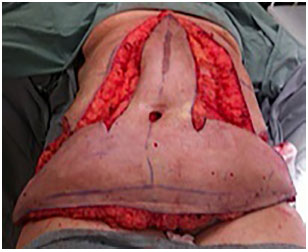
Figure 2. Intraoperative aspect inverted T abdominoplasty.
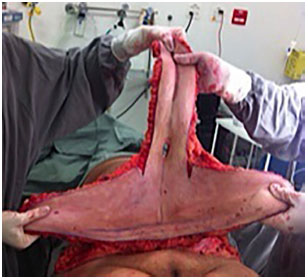
Figure 3. Intraoperative aspect inverted T abdominoplasty.
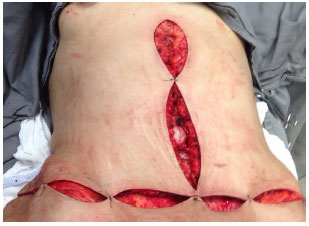
Figure 4. Intraoperative aspect inverted T abdominoplasty.
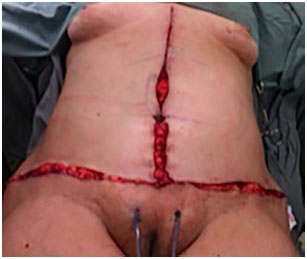
Figure 5. Intraoperative aspect inverted T abdominoplasty.
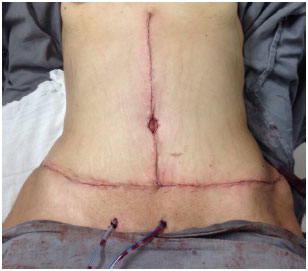
Figure 6. Intraoperative aspect inverted T abdominoplasty.
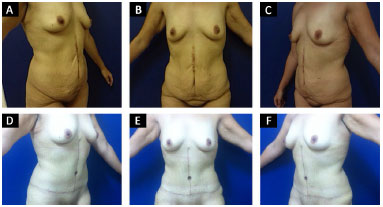
Figure 7. Inverted T abdominoplasty. Above: pre-operative. Below: post-operative period of 6 months.
The piece was excised according to the previous markings that indicated which tissue was to be removed as one block in the supra-aponeurotic plane with electrocautery and minimal detachment of the remaining flaps. Plicature of the diastasis of the rectus abdominis muscle was performed in a single plane using an interrupted and inverted "X" suture made with a nylon 2-0 nonabsorbable suture. The fixation of the umbilical pedicle to the aponeurosis was performed.
The patient was then placed in a semi-flected position. Adhesive sutures (three supraumbilical and four infraumbilical (two on each side)) between the fascia of the flap and the aponeurosis were created. Two 4.8 mm suction drains with pubis outlets were attached and connected to a single reservoir. Suture were made by planes follows: subcutaneous, subdermal and intradermal. The umbilical pedicle was maintained and transposed between the flaps.
Postoperative Care
The patients were maintained in Fowler's upright position overnight, with a bladder catheter, an elastic stocking and pneumatic compression of the calves. Patients were discharged after ambulation and spontaneous urination, while the dressing, the modelling strap, and the suction drain were maintained.
The basic guidelines of postoperative care included always using the compressive modelling strap, increasing water intake, performing stimulating ambulation, laying in Fowler's position, walking slightly bent, avoiding physical exertion, and emptying the drain every 4h. Antibiotic prophylaxis was maintained with cefadroxil 1g/day for 7 days.
The standard consultation visits were performed on the 3rd, 7th, 14th and 30th postoperative days, or earlier, if deemed necessary.
The drains were removed on the 7th day, regardless of the flow rate.
The clinical evaluation consisted of an inspection, percussion, and palpation for signs of infection, necrosis, dehiscence, and seroma. Upon clinical suspicion of seroma, the patient was left in a sitting position, with palpation and percussion being held. If there was bulging or a puddle sign, patients underwent puncture with a 20-mL syringe and 40x12 needle (18G) for verification and possible aspiration.
RESULTS
Data from 30 women, with a mean age 38.6 years (SD** = 10 years; minimum: 20 years; maximum: 64 years) were analyzed. The median age of the patients was 36 years. Half of the women underwent standard surgery and the others, inverted T surgery.
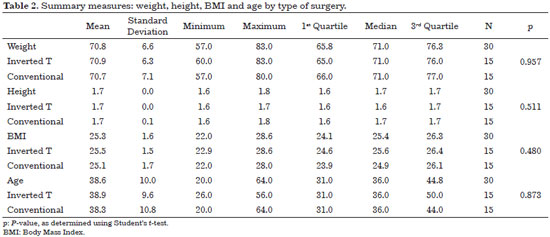
One can observe that the characteristics of the two groups, conventional and inverted T, are similar. According to table 2, there were no statistical differences in relation to the means of weight (p = 0.957), height (p = 0.511), BMI (p = 0,480) and age (p = 0.873) by type of surgery.
In total, the occurrence of seroma was observed in seven (23.3%) of the 30 patients (Figure 8). Among those who underwent conventional abdominoplasty, six (40%) presented with clinically detectable seroma. With regard to patients covered by the inverted T technique, only one (6.7%) presented with a seroma. This difference was statistically significant (p = 0.040).
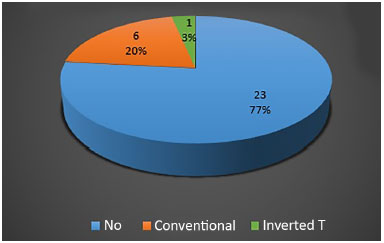
Figure 8. Global frequency of seroma in the study.
We also analyzed the presence of dehiscence after patients underwent the different techniques (Figure 9). Dehiscence was documented in four of 30 (13.3%) patients. There was a higher frequency of dehiscence in the conventional group, three patients (20%), compared to in the inverted T group, one patient (6.7%); however, this difference was not significant (p = 0.299).
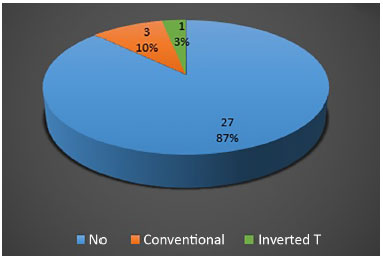
Figure 9. Global frequency of dehiscence in the study.
Table 3 and figure 10 illustrate the distribution of patients, according to the frequency of seroma formation and dehiscence.
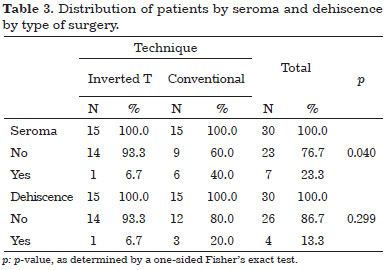
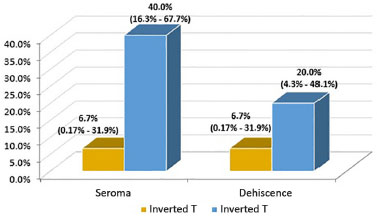
Figure 10. Percentage of seroma and dehiscence and corresponding 95% confidence intervals by type of surgery.
All patients who presented with seroma were subjected to percutaneous drainage, with no presence of fluid detected after the 30th postoperative day.
There were no cases of infection, hematoma, venous thromboembolism, or other complications in this series.
DISCUSSION
Seroma is the most common complication that is observed during the postoperative period following abdominoplasties. Its reported incidence is quite varied, ranging from 4% to 80%8. One factor that contributes to this discrepancy is the concept of seroma itself. Some authors characterize seroma as a collection of fluid that is clinically relevant13 (as shown in the present study), while others characterize it as the serous fluid which needs repetitive punctures14,15. Moreover, some authors consider the detection of fluid collection by ultrasonography during the postoperative period16 as being indicative of seroma formation.
Another factor that may influence the incidence of seroma is the surgical technique used. Many studies have postulated that the use of adhesive sutures, as initially described by Baroudi and Ferreira11, or that the use of progressive tension sutures, as described by Pollock and Pollock12, can drastically reduce the incidence of seromas. Baroudi described 10 cases of abdominoplasty with adhesive sutures and without drains, with no cases of seroma.
This decrease in its incidence was reproduced in other studies and in clinical practice.7-9,17 Pollock published a series of cases using their technique in 597 patients, in which only one case presented with seroma. In the present study, adhesive sutures were also used in seven cases, including three supraumbilical sutures and four sutures placed in the iliac fossa. We also observed a large reduction in the number of seroma cases, mainly in the supraumbilical region.
The preservation of the fascia of Scarpa was also frequently described in previous reports after the work of Saldanha showed lipoabdominoplasty can be successfully performed with a drastic reduction in the rate of seroma formation (from 60% to 0.4%, p < 0.00001)18. Other studies by Costa-Ferreira et al.19, Koller and Hinthinger20, Wulkan and Hurwitz21, also showed the results with decreased drain output and the formation of seroma.
According to the study by Martino et al.16, which analyzed the natural evolution of seroma with ultrasonography in the follow-up after abdominoplasty, the peak incidence (38.1% of cases) of seroma occurred on the 11th postoperative day, and progressively decreased to 19% by the 32nd day. It was also observed that seromas were significantly more frequently located in the right iliac fossa. In our study, we also observed a higher incidence until the second postoperative week, and no seromas were diagnosed in any other patient after 30 days of surgery.
In the present study, we did not have the opportunity to enroll any male patients due to the exclusion criteria; however, this resulted in a greater uniformity of the compared groups. According to the study by Canan Junior7, men more frequently developed complications associated with seroma and hematoma. This is due to a higher tendency to bleed, greater weight loss, greater weight at the time of surgery, and hormonal issues affecting coagulation.
In the only series found in the literature comparing the two abdominoplasty techniques, conventional and inverted T, Canan Junior7 found no significant difference in the incidence of seroma formation (p = 0.146), hematoma development (p = 0.702), or infection (p = 1). In this same work, the evolution of the surgical technique was shown to follow a natural learning curve. According to the author, this included the increasing use of adhesive sutures, which culminated in ending the use of drains.
In a series of 39 patients, Cortes et al.22 reported an incidence of 53% of cases of seroma in patients who were treated with inverted T abdominoplasties in ex-obese patients. This incidence was even greater in patients with high BMI. Cavalcante23 also found an association between the number of complications after weight loss and BMI at surgery in 23 patients who were treated with abdominoplasties. Similarly, this was more significant in patients with a pre-abdominoplasty BMI that was higher than 35. The rate of seroma was 30%. Tardelli et al.24 reported a new surgical standardization for inverted T abdominoplasty in post-gastroplasty, which included 67 patients, with a rate of seroma of 26.9%.
Studies on the prevention of seroma with a high statistical power (i.e., multicenter, randomized and double-blind studies with good sampling) or those with a level of evidence that helps dictate the rules in surgical standardization are still scare. However, with the help of technology and globalization, plastic surgery and abdominoplasty can still experience significant advances.
CONCLUSION
The incidence of seroma was higher in patients undergoing conventional abdominoplasty compared to inverted T abdominoplasty.
COLLABORATIONS
LSS Analysis and/or interpretation of data; final approval of the manuscript; conception and design of the study; completion of operations and/or experiments; drafting the manuscript or critical review of its contents.
MNH Analysis and/or interpretation of data; final approval of the manuscript; drafting the manuscript or critical review of its contents.
EMCB Final approval of the manuscript; drafting the manuscript or critical review of its contents.
REFERENCES
1. Sociedade Brasileira de Cirurgia Bariátrica e Metabólica. Obesidade - prevenção e tratamento. [acesso 2015 Jul 21]. Disponível em: http://www.sbcbm.org.br/wordpress/obesidade/prevencao
2. Cortes JES, Oliveira DPO, Sperli A. Abdominoplastias em âncora em pacientes ex-obesos. Rev Bras Cir Plast. 2009;24(1):57-63.
3. Aly A. Abdominoplastia e contorno corporal circunferencial do tronco inferior. In: Thorne CE, ed. Grabb e Smith Cirurgia Plástica. 6ª ed. Rio de Janeiro; Guanabara Koogan; 2009. p. 528-36.
4. Saldanha O, Federico R, Doi M. Lipoabdominoplastia: Técnica de Saldanha. In: Aston SJ, Steinbrech DS, Walden JL. Cirurgia Plástica estética. Rio de Janeiro: Elsevier; 2011. p. 757-64. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S1983-51752011000200014
5. Sociedade Brasileira de Cirurgia Plástica. Entenda Melhor a Cirurgia Pós-bariátrica. [acesso 2015 Jul 21]. Disponível em: http://www2.cirurgiaplastica.org.br/blog/entenda-melhor-a-cirurgia-plastica-pos-bariatrica/
6. International Society of Aesthetic Plastic Surgery (ISAPS). ISAPS International Survey on Aesthetic/Cosmetic - Procedures Performed in 2014. [acesso 2015 Jul 21]. Disponível em: http://www.isaps.org/Media/Default/global-statistics/2015 ISAPS Results.pdf
7. Canan Junior LW. Abdominoplastia após grandes perdas ponderais: análise crítica de complicações em 130 casos consecutivos. Rev Bras Cir Plást. 2013;28(3):381-8.
8. Boggio RF, Almeida FR, Baroudi R. Pontos de adesão na cirurgia do contorno corporal. Rev Bras Cir Plást. 2011;26(1):121-6. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S1983-51752011000100022
9. Rangaswamy M. Minimising complications in abdominoplasty: An approach based on the root cause analysis and focused preventive steps. Indian J Plast Surg. 2013;46(2):365-76. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.4103/0970-0358.118615
10. Andrades P, Prado A. Composition of postabdominoplasty seroma. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2007;31(5):514-8. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00266-007-0078-3
11. Baroudi R, Ferreira CA. Seroma: How to avoid it and how to treat it. Aesthetic Surg J. 1998;18(6):439-41. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S1090-820X(98)70073-1
12. Pollock TA, Pollock H. No-drain abdominoplasty with progressive tension suture. Clin Plast Surg. 2010;37(3):515-24. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cps.2010.03.004
13. Quaba AA, Conlin S, Quaba O. The no-drain, no-quilt abdominoplasty: a single-surgeon series of 271 patients. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2015;135(3):751-60. PMID: 25719694 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0000000000001031
14. Hunstad JP, Repta R. Complications. In: Hunstad JP, Repta R. Atlas of Abdominoplasty. Philadelphia: Saunders Elsevier; 2009. p. 229-42.
15. Kim J, Stevenson TR. Abdominoplasty, liposuction of the flanks and obesity: analyzing risk factors for seroma formation. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2006;117(3):773-9. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/01.prs.0000200056.57357.3f
16. Di Martino M, Nahas FX, Kimura AK, Sallum N, Ferreira LM. Natural evolution of seroma in abdominoplasty. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2015;135(4):691e-8e. PMID: 25811581 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0000000000001122
17. Hurvitz KA, Olaya WA, Nguyen A, Wells JH. Evidence-based medicine: Abdominoplasty. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2014;133(5):1214-21. PMID: 24776552
18. Saldanha O, Azevedo SFD, Kuroyanagi FM, Saldanha Filho OR, Saldanha CB. Lipoabdominoplastias. In: Carrerão S. Cirurgia Plástica para a formação do especialista. São Paulo: Atheneu; 2011. p. 951-964. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S1983-51752011000200014
19. Costa-Ferreira A, Rebelo M, Silva A, Vásconez LO, Amarante J. Scarpa fascia preservation during abdominoplasty: randomized clinical study of efficacy and safety. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2013;131(3):644-51. PMID: 23446574 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0b013e31827c704b
20. Koller M, Hinthinger T. Scarpa fascia or rectus fascia in abdominoplasty flap elevation: a prospective clinical trial. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2012;36(2):241-3. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00266-011-9795-8
21. Wulkan M, Hurwitz D. Preservação e suspensão da fáscia de Scarpa na abdominoplastia. Rev Bras Cir Plast. 2010; 25(3):490-8. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S1983-51752010000300016
22. Cortes JES, Oliveira DPO, Sperli A. Abdominoplastias em âncora em pacientes ex-obesos. Rev Bras Cir Plast. 2009; 24(1):57-63.
23. Cavalcante HA. Abdominoplastia após perda de peso maciça: abordagens, técnicas e complicações. Rev Bras Cir Plast. 2010; 25(1):92-9.
24. Tardelli HC, Vilela DB, Schwartzmann GLE, Azevedo M, Mello Júnior AM, Farina Júnior JA. Padronização cirúrgica das abdominoplastias em âncora pós-gastroplastia. Rev Bras Cir Plast. 2010;26(2):266-74. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S1983-51752011000200013
1. Sociedade Brasileira de Cirurgia Plástica, São Paulo, SP, Brazil
2. Hospital da Cruz Vermelha Brasileira, São Paulo, SP, Brazil
Institution: Hospital da Cruz Vermelha Brasileira, São Paulo, SP, Brazil.
Corresponding author:
Luciano Sales de Souza
Avenida Moreira Guimarães, 699 - Indianópolis
São Paulo, SP, Brazil Zip Code 04074-031
E-mail: sales.souza@uol.com.br
Article received: August 12, 2015.
Article accepted: November 11, 2015.
Conflicts of interest: none.
* More than 20% of cells of a contingency table with expected values below 5 cases.
** Standard Deviation.


 Read in Portuguese
Read in Portuguese
 Read in English
Read in English
 PDF PT
PDF PT
 Print
Print
 Send this article by email
Send this article by email
 How to Cite
How to Cite
 Mendeley
Mendeley
 Pocket
Pocket
 Twitter
Twitter