ABSTRACT
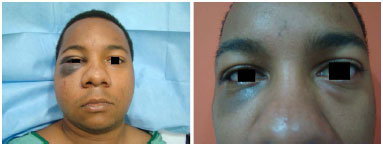
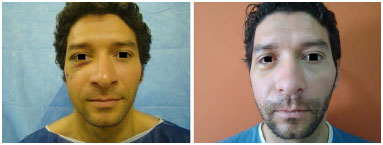
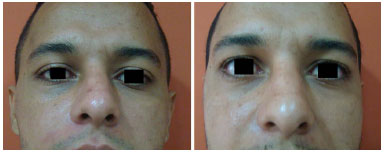
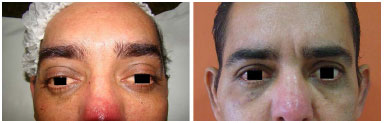
INTRODUCTION: Orbitozygomatic fractures most commonly occur in the midface. The main causes of fractures are traffic accidents, mainly by motorcycles, and interpersonal violence. The basic principles for the treatment of facial fractures are the reduction and fixation of the fracture site. It is fundamental that the surgical access be the most direct and broad as possible. Either the subciliary approach or transconjunctival access with lateral canthotomy can be used. The objective of this study was to evaluate and compare the complications, advantages, and disadvantages of the transconjunctival approach with lateral canthotomy and conventional subciliary access.
METHODS: We selected 15 patients in whom fractures were addressed through a subciliary incision and 15 patients in whom the fractures were addressed by using a transconjunctival incision with lateral canthotomy, and evaluated the incidence of complications with the two methods. The data were statistically analyzed by using the SPSS 20.0 software.
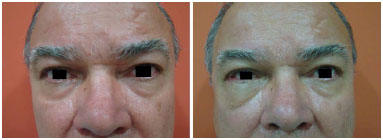
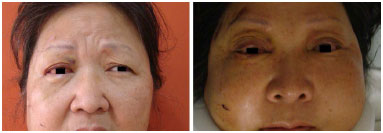
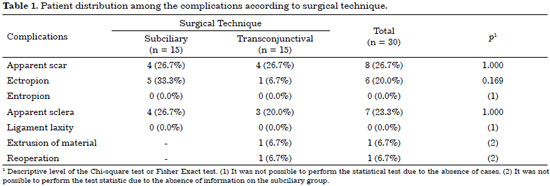
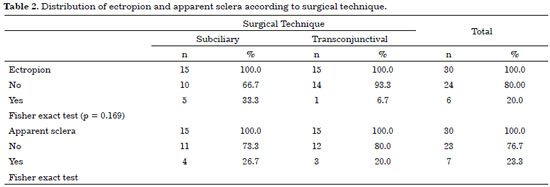
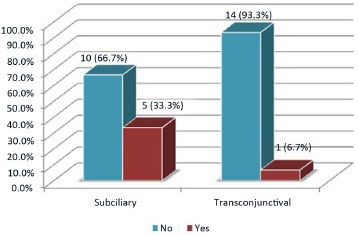
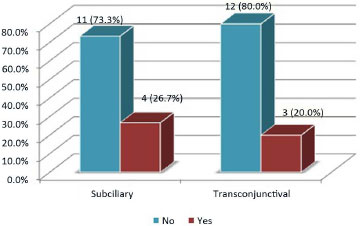
RESULTS: Thirty patients were operated with the subciliary access in 15 patients and the transconjunctival access in the other 15. Trauma occurred more frequently on weekends. The most frequent complications were apparent scar (26%), apparent sclera (23.3%), and ectropion (20%). Ectropion was more common in the > 60-year age group.
CONCLUSION: Both techniques were effective for the correction of fractures of the orbitozygomatic complex. The transconjunctival technique provides more esthetic and less stigmatizing scars. Hence, it is currently the author's first choice of treatment. The global incidence of complications was similar between the two techniques. Ectropion was less frequent with the transconjunctival access.
Keywords: Cranial fractures; Traffic accidents; Reconstructive surgical procedures; Orbit; Zygoma.