
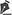
Original Article - Year 2016 - Volume 31 -
Safety and viability of a new format of thoracoepigastric flap for reconstruction of the chest wall in locally advanced breast cancer: a cross-sectional study
Segurança e viabilidade de um novo formato de retalho toracoepigástrico na reconstrução da parede torácica em câncer de mama localmente avançado: um estudo transversal
ABSTRACT
INTRODUCTION: Patients who undergo radical mastectomy with extensive tissue loss require a surgical procedure for rapid and simple closure of the lesion, with good skin coverage and minimal morbidity, to make them eligible for early complementary treatments. We evaluated the efficacy and safety of a new format of thoracoepigastric flap with patients in the Semi-Fowler position during surgery. We hypothesized that this procedure would achieve proper closure of large lesions and ensure the survival of the flap.
METHODS: All consecutive patients who underwent radical mastectomy between 2009 and 2014 and had chest wall reconstruction were evaluated. The main outcomes evaluated were the viability of the flap and effectiveness of the surgical closure.
RESULTS: During the study period, we operated on 29 patients with locally advanced (90%) or recurrent tumor (10%), and one patient was operated on bilaterally (total of 30 flaps). Of the study sample, 23 patients (79%) were at stage III and 6 (21%), at stage IV. The dimensions of the resected areas varied from 20 x 15 cm to 13 x 9 cm (average 15.5 x 11.6 cm). The dimensions of the thoracoepigastric flaps varied from 25 x 12 to 18 x 8 cm (average 21.3 x 10.4 cm). There were only 2 cases of dehiscence (7%), which resolved without surgical intervention, and one case of hematoma, which was drained surgically. One patient died on the eleventh postoperative day.
CONCLUSION: Thoracoepigastric flaps were effective and safe, did not require the use of other flaps or skin grafting, and adequately closed the donor areas in all cases. All patients, except the patient who died, were eligible for complementary treatment one month after surgery.
Keywords: Chest; Chest wall; Mastectomy; Reconstructive surgical procedures; Surgical flaps.
RESUMO
INTRODUÇÃO: Pacientes submetidas à mastectomia radical, com extensa perda tecidual, necessitam de procedimento cirúrgico de fechamento rápido e simples da lesão, com boa cobertura cutânea e mínima morbidade, para que possam receber precocemente tratamentos complementares. Estudamos a eficácia e a segurança de um novo formato do retalho toracoepigástrico com o posicionamento semissentado (Fowler) da paciente durante a cirurgia. A hipótese é de que o procedimento, além de obter adequado fechamento de grandes lesões, permita garantir a sobrevivência do retalho.
MÉTODOS: Foram analisadas todas as pacientes consecutivamente operadas com mastectomias radicais entre 2009 e 2014 submetidas a reconstruções torácicas. Os principais desfechos analisados foram a viabilidade do retalho e a eficácia no fechamento cirúrgico.
RESULTADOS: No período do estudo, foram operadas 29 pacientes com tumor localmente avançado (90%) ou recidivado (10%), uma operada bilateralmente (30 retalhos); vinte e três (79%) com estadiamento III e seis (21%), estadiamento IV. A extensão das áreas ressecadas variou de 20 x 15 cm a 13 x 9 cm (média 15,5 x 11,6 cm). Retalho toracoepigástrico foi utilizado com dimensões variando de 25 x 12 cm a 18 x 8 cm (média de 21,3 x 10,4 cm). Houve apenas duas deiscências (7%), que cicatrizaram sem necessidade de intervenção cirúrgica, e um hematoma, drenado cirurgicamente. Uma paciente faleceu no 11º dia pós-operatório.
CONCLUSÃO: O retalho toracoepigástrico foi eficaz e seguro, sem necessidade do uso de outros retalhos ou enxertos cutâneos, fechando a área doadora adequadamente em todos os casos. Todas as pacientes, excluindo o óbito, estavam aptas para o tratamento complementar após um mês.
Palavras-chave: Tórax; Parede torácica; Mastectomia; Procedimentos cirúrgicos reconstrutivos; Retalhos cirúrgicos.
We still encounter cases of extensive tumors due to late diagnosis as well as cases of local recurrence with aggressive behavior1. Locally advanced breast cancer includes T3 and T4 tumors (clinical stages IIb, IIIa, and IIIb) and inflammatory carcinoma2,3. It comprises 10%-25% of all cases of breast cancer in developed countries and 40%-50% in undeveloped countries4,5.
Radical surgical resection in these patients leads to extensive skin loss with major chest wall defects, which cannot be repaired by primary closure6,7. These patients often have a poor clinical prognosis and extensive necrotizing wounds that cause pain, bleeding, and infection7. Due to the high morbidity and severity of these cases, a rapid and simple procedure for skin closure with adequate coverage should be performed to make these patients eligible for early chemotherapy and postoperative radiation8.
The use of elaborate flaps, such as myocutaneous flaps, provides effective coverage for large defects; however, they require a longer duration of surgery, which can increase morbidity and delay the implementation of additional treatments9,10. There are precise indications for myocutaneous flaps in chest reconstruction after mastectomy11-13, but importance of locoregional fasciocutaneous flaps14,15, which were developed by examining the vasculature of the fascial territory of the abdominal wall, has been demonstrated16-18.
A retrospective study of 315 patients with advanced or recurrent tumors compared the use of fasciocutaneous flaps with myocutaneous flaps in 40 patients who required surgery for closure of the chest wall; the study demonstrated that fasciocutaneous flap surgeries can be performed rapidly, and the flaps cause low morbidity, and have a low rate of necrosis, similar to that of myocutaneous flaps, although use of these flaps is limited by the amount of skin that can be mobilized and the previous use of radiotherapy. Therefore, this strategy represents a good option for the treatment of chest wall injuries19.
Although they were not used in a study by Deo et al.19, thoracoepigastric (or transverse abdominal) flaps are similar to fasciocutaneous flaps, and cause little morbidity in the reconstruction of chest defects after mastectomy. Since the 1970s, studies have indicated that this method is useful for the closure of large defects of the chest wall after mastectomy20. It was first described by Tai and Hasegawa as an delayed transposition flap in 3 cases and as non-delayed in 2 cases for the treatment of recurrent breast cancer20. In the non-delayed cases, the lateral limit of the flap considered safe was the posterior axillary line.
Seven years later, Davis et al.21 reported a clinical series and anatomical study based on the concept of vascular territories of the deep superior epigastric artery perforators developed by Brown et al.22 and Bohmert23, and defined the pedicle of the thoracoepigastric flap as axial, establishing its anatomical limits. According to this description21, the superior border of the thoracoepigastric flap should include the region of the mammary fold, which contains a lateral branch of the superior epigastric artery with a caliber similar to that of the internal mammary artery23. The base of the flap is positioned medially, from the xiphoid process to the midpoint between this process and the umbilical region. The inferior margin of the flap is a line parallel to the superior margin and is positioned according to bidigital clamping (which can reach up to 15 cm) of excess skin in the thoracoabdominal region24.
The thoracoepigastric flap is axial from the lateral border of the rectus abdominis to the anterior axillary line; beyond this line, it has a random pattern (subdermal plexus) and loses its vascular safety24, especially if it exceeds the posterior axillary line21. The extended thoracoepigastric flap has a segment with a random pattern attached to its axial portion, and requires greater care during its dissection; its limit should be the lateral border of the rectus abdominis.
The flaps described by Davis et al.21 in 5 patients presented no complications and could reach a length of up to 35 cm and a width of 15 cm, provided that the recommendation to narrow the end was observed, in order to improve the subdermal supply and facilitate closure by approximation with the donor area. The total number of cases of chest reconstruction reported to date is 16 but only 5 were individually described and detailed.
McCraw et al.25, in a study without case descriptions, reported that the thoracoepigastric flap could extend up to 5 cm beyond the posterior axillary line and that the rate of loss of the randomly patterned distal end was 10%.
Woods et al.26 reported 2 cases of thoracoepigastric flaps that were extended in length, in a case series that included both fasciocutaneous and myocutaneous flaps. The donor area of these flaps was grafted, but complications were not individually detailed.
In the 1980s, Leinster and Webster27 reported 10 cases that involved the use of thoracoepigastric flaps combined with other fasciocutaneous flaps; however, in this study, complications of the thoracoepigastric flaps were not individually detailed26,27.
The number of cases in each of the series involving the thoracoepigastric flaps for chest reconstruction as described by Tai20 and Davis21 varied between 2 and 1620,21,26.
OBJECTIVE
In patients with locally advanced breast cancer, we evaluated the efficacy and safety of a new format of thoracoepigastric flap with the patients in the Semi-Fowler position during surgery. We hypothesized that this procedure can achieve proper closure of large lesions and ensure the survival of the flap.
METHODS
This observational, cross-sectional study was conducted between 2009 and 2014 in the Reconstructive Plastic Surgery Center of the Pérola Byington Hospital in São Paulo, state of São Paulo, Brazil. The study sample included female patients of any age, diagnosed with locally advanced breast cancer, including recurrent cancers (stages III and IV), who underwent radical mastectomy with extensive skin resection and immediate reconstruction of the chest wall with thoracoepigastric flaps. One patient underwent bilateral reconstruction (Figure 1).
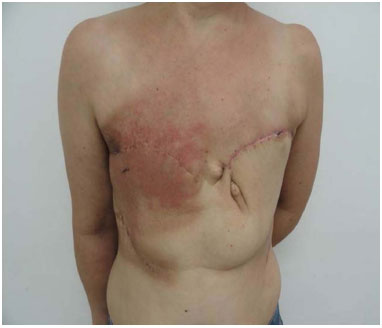
Figure 1. Bilateral thoracoepigastric flap.
This study was based on the analysis of medical records. The data analyzed included demographics, comorbidities, previous neoadjuvant and surgical treatments, histology, tumor size, dimensions and limits of chest wall defects, and dimensions of the flaps used for closure of the chest wall.
The main outcome measures were vascular viability and effectiveness of the flap, postoperative complications, duration of surgery, length of hospital stay, and postoperative follow-up.
The study was approved by the Research Ethics Committee of the Reference Center on Women's Health of the Pérola Byington Hospital under protocol No. 32185614.0.0000.0069. Informed consent was waived because the study was based on the analysis of medical records and the patients were anonymized.
Surgical technique
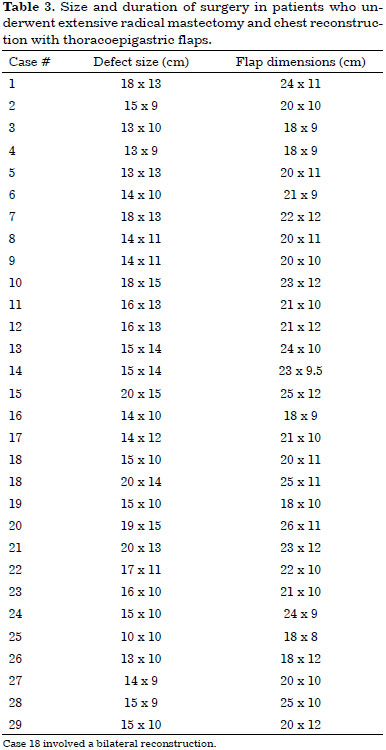
After extended radical mastectomy under general anesthesia and with the patient supine, the limits of the chest defect were determined to mark the extent of the flap. The anatomical extent of the injuries (defects) was measured after maximum approximation of the wound to differentiate the apparent defect from the actual defect. To enable reconstruction using a thoracoepigastric flap, the vertical boundary, as proposed by Davis et al.21, should be the mammary fold and the second intercostal space. Horizontally, the limits of the defect were established as the middle axillary line and the middle sternal line in our service (Figure 2).
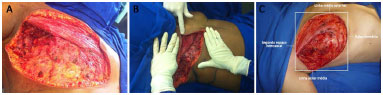
Figure 2. A: Extensive defect after radical mastectomy. B: Extent of the defect after approximation of the wound edges for chest reconstruction using a thoracoepigastric flap. C: Limits of the chest wall defect.
The flap was drawn transversally in the thoracoabdominal region ipsilateral to the chest defect, parallel to the mammary fold. The base of the flap was positioned medially, from the xiphoid process to the midpoint between the xiphoid and the umbilical region. The lateral limit was the posterior axillary line with the patient supine. The lateral end of the flap was rounded to make better use of the excess skin in this region (Figure 3). This distal rounding with the patient supine would cause the lateral limit of the flap to exceed the posterior axillary line with the patient standing.
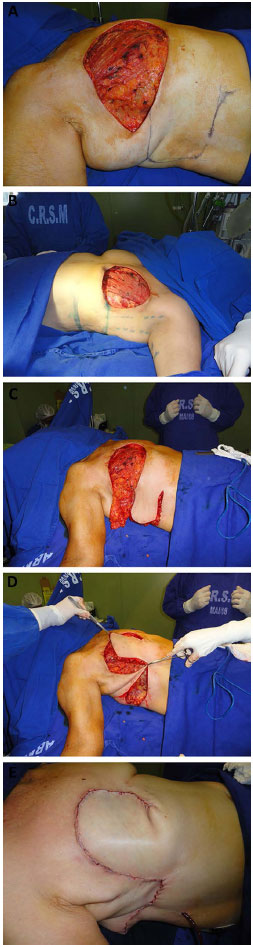
Figure 3. A: Cutaneous marking with rounding of the end of the thoracoepigastric flap. B: Lateral limit at the posterior axillary line with the patient supine. C: Interrupted lower incision. D: Flap rotation after changing the direction of the lower incision towards the umbilical region. E: Closure of the chest defect.
The upper margin of the flap was the mammary fold and should extend medially to the lateral border of the ipsilateral rectus abdominis. The lower margin of the flap was determined by a line parallel to the upper margin, positioned according to the bidigital clamping of excess skin in the thoracoabdominal region, with the patient in the semi-sitted position; these 2 margins defined the width of the flap.
The flap was dissected from its lateral to medial portion, with the patient in the fowler position. The inclusion of the deep fascia under the entire extension of the flap was essential for flap viability. The medial limit of the detachment was the lateral border of the ipsilateral rectus abdominis muscle; however, to increase the vascular base of the flap, reaching the lateral border of this muscle should be avoided by bypassing the lower incision of the flap slightly toward the umbilicus, close to the medial portion of the external oblique muscle, and well before the demarcation of the lateral border of the rectus abdominis muscle (Figure 4). This procedure was used depending on the size of the chest wall defect by testing the closure of the defect with the patient in the Fowler position. As the lesions become medial, the detachment should reach the lateral border of the rectus abdominis muscle to promote a greater arc of rotation.
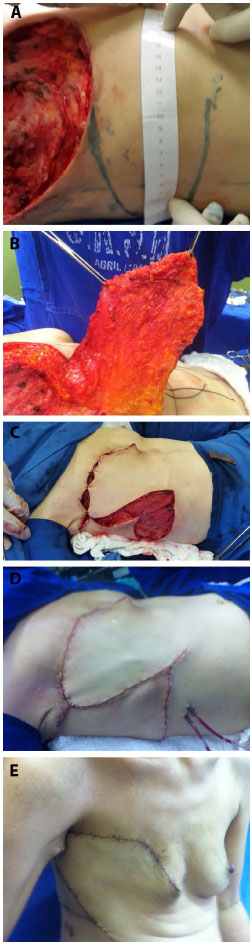
Figure 4. A: Marking of the flap. B: Elevation of the flap. C: Rotation of the flap. D: Postoperative closure. E: Late postoperative - lateral view.
The point of rotation of the flap was defined by the lower incision, whose medial limit was also the lateral border of the ipsilateral rectus abdominal muscle. The degree of detachment of the flap depended on the size of the chest wall defect. The arc of rotation ranged between 45 and 90 degrees.
For the closure of chest wall defects, the patient remained in the Fowler position (Figure 5). The donor area was closed primarily via reverse detachment of the abdomen. Drains were used in the recipient and donor areas of the flap.
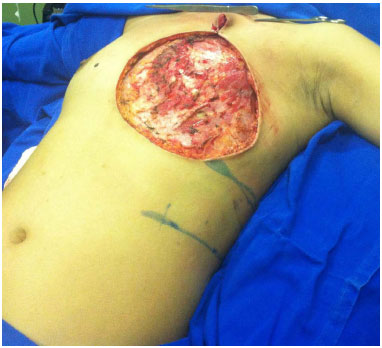
Figure 5. Positioning of the patient on the operating table with elevation of the trunk (Semi-Fowler position) for chest reconstruction.
RESULTS
During the study period, 29 patients underwent radical mastectomy and 1 patient underwent bilateral reconstruction (total of 30 flaps). The patients were operated on according to standard oncologic procedures, including the Halsted technique in 12 patients (40%), Patey technique in 14 (46.6%), and Madden technique in 4 (13.4%).
The patients were aged 26 to 85 years. The postoperative follow-up period varied between 11 days and 5 years, starting from the date of surgery.
Seven patients (24%) had no comorbidities. Twelve patients (41%) had 1 comorbidity and 10 (35%) had 2 or more comorbidities. The comorbidities are described in Table 1.
The most prevalent type of tumor was invasive ductal carcinoma (93.4%). Invasive lobular carcinoma represented 3.3% of the study sample, and carcinosarcoma (3.3%) was diagnosed in one patient.
Of the 29 patients evaluated, 26 (90%) had locally advanced breast tumors and 3 (10%) had relapsed breast tumors. Of the 29 patients, 17 (59%) received neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Radiotherapy was also used in previous treatments in 10% of the study sample (3 patients) (Table 2).
The thoracoepigastric flap was used in the group of 29 patients for whom the chest wall defects could not be repaired via primary closure. The extent of the defects varied from 20 - 15 cm to 13 - 9 cm (average 15.5 - 11.6 cm). For the closure of the defects, the dimensions of the thoracoepigastric flaps varied from 25 - 12 cm to 18 - 8 cm (average 21.3 - 10.4 cm) (Table 3).
The average total duration of surgery (mastectomy and reconstruction) was 3 hours and 52 minutes. The average duration of the reconstruction of the chest wall was 2 hours and 4 minutes (Table 4). The average length of stay was 3 days (range between 1 and 11 days). Four patients (14%) required intensive care.

The thoracoepigastric flap with rounded markings at its end, enlargement of the vascular base, and the maintenance of the patients in the Fowler position during surgery were effective for the closure of the defects after mastectomy in 29 patients, without the need to use other flaps or skin grafts. The donor site was closed properly in all cases using the reverse displacement of the abdominal wall. Chest drainage was performed in all patients for 7 to 10 days.
All patients were instructed to remain in the Fowler position to sleep and to walk bent forward until the seventh postoperative day.
In our series, only 2 (7%) patients developed dehiscence (Figure 6), which resolved without surgery. One case of hematoma (3%) (Figure 7) required surgical drainage in a patient who had pancytopenia due to bone metastases. This patient died on the eleventh postoperative day, but despite the complications, the flap remained viable until the date of death. One month after surgery, 28 (96.5%) patients were eligible for complementary treatments.
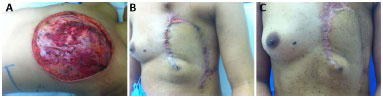
Figure 6. A: Intraoperative aspect of extensive radical mastectomy. B: Dehiscence of the lesion after chest wall reconstruction. C: Resolution of dehiscence without the use of other flaps or skin grafts.
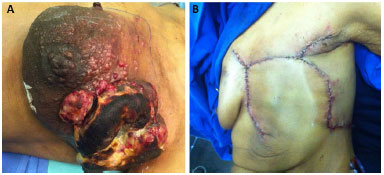
Figure 7. A: Hematoma in the preoperative period. B: Thoracoepigastric flap with the maintenance of flap viability despite the presence of hematoma.
All patients returned to the hospital for follow-up one month after surgery, when the viability of the flap was examined in all cases. Five patients (17.2%) were lost to surgical follow-up after one month, but our service was assisted by other medical specialties, and no further surgical complications were reported in the medical records.
The duration of follow-up was 5 years. Because of its severity, the underlying disease caused the deaths of 13 patients (44.8%) during the study period.
DISCUSSION
The locally advanced stage of primary tumors, the quality of the tissue adjacent to the irradiated breast in tumor recurrence, and the clinical status of patients are critical when choosing the most suitable method of chest wall reconstruction7,9,19,14. Fasciocutaneous flaps are a good option for treating these lesions7,19.
The number of cases in series involving fasciocutaneous and thoracoepigastric flaps for chest reconstruction varied between 2 and 1620,21,26,27. These reports adequately described the technique, vascular pattern, anatomical limits of the flap, and the closure of chest defects; however, they did not properly describe individual complications; these flaps were presented as fragile from the vascular point of view because of the randomly patterned segment attached to their axial region. The anterior axillary line defined the end of the axial pattern of the flap, and the more it extended toward the posterior axillary line, the less reliable was the vascularization at its end on the basis of the structure of the subdermal plexus alone. For this reason, this end should have a narrower marking21.
Davis et al.21 described 16 surgeries, 4 of which involved a thoracoepigastric flap that exceeded 5 cm from the posterior axillary line, with a narrower marking at the distal end for closure of the chest, but they did not observe necrosis in these cases.
Woods et al.26 reported 2 cases involving the use of thoracoepigastric flaps with the donor area grafted between the flaps. Leinster and Webster27 reported 10 cases involving the use of this flap combined with other fasciocutaneous flaps. These authors also exceeded the posterior axillary line and narrowed the ends of the flaps. The complications from thoracoepigastric flaps in these studies were not individually described and were included in the total number of complications for all fasciocutaneous flap surgeries performed26,27.
Despite the vascular fragility of these flaps, none of these authors devised surgical strategies that would minimize the loss of the randomly patterned distal end of the thoracoepigastric flap, with a loss rate of 10% according to McCraw et al.25.
This study involved 29 patients, 1 of whom was operated on twice and 3 who underwent previous radiotherapy in the operated region; this is the first report with a sample size larger than 16 cases that individually described the complications. Herein we proposed a new format for the randomly patterned distal end of the thoracoepigastric flap, which was rounded to ensure the closure of larger defects horizontally and took advantage of the excess tissue from the lateral region of the chest.
We predicted the vascular fragility of this distal flap and consequently limited its detachment toward the lateral border of the rectus abdominis by maintaining the patient in the Fowler position during surgery. This position decreased the distance between the flap and the defect and allowed the coverage of an area up to the second intercostal space using a flap that was smaller and had a larger vascular base, making the procedure safer.
The decrease in the length of the lower incision of the flap may limit its arc of rotation, which may then limit the closure of higher and medial lesions; this limitation should be evaluated at the time of elevation of the flap by testing the closure of the chest defect with the patient in the Fowler position. As the defects become located medially, the detachment should be performed closer to the lateral border of the rectus abdominis muscle to promote a greater arc of rotation.
To maintain the broader base of the flap, even for closure of major defects (20 - 15 cm) in the study sample, we diverted the lower incision of the flap slightly toward the umbilical region, close to the medial region of the external oblique muscle and well before the demarcation of the lateral border of the rectus abdominis. The change in the end of the lower incision enabled a larger cranial arc of rotation. We performed a 25 - 12 cm flap to close a 20 - 15 cm thoracic injury; this flap was identical to the largest flap described by Davis et al.21, who performed a larger detachment and obtained a flap with a longer length and a smaller base (35 - 11 cm), consequently exposing the patient to more risks, although the authors did not observe necrosis in that case.
The decrease in the level of detachment of the flap with patients in the Fowler position allowed us to safely round its randomly patterned end (a round flap fits better in a circular defect) and to close large defects without the risk of distal necrosis. In fact, no cases of distal necrosis were observed, although we observed 2 cases of dehiscence in 30 flaps, which resolved without further surgery.
Therefore, future clinical studies should evaluate whether a possible increase in the size of the flap could avoid dehiscence.
Due to the development of a tumor in the contralateral breast, one patient in the study sample underwent 2 reconstructions at different periods using thoracoepigastric flaps, because this flap uses the circulation of the rectus abdominis muscle ipsilateral to the chest defect, leaving the circulatory supply of the contralateral rectus abdominis muscle for future procedures.
CONCLUSION
With the changes proposed in this study, the thoracoepigastric flap was effective in covering extensive areas after mastectomy without the need to use other flaps or skin grafts. Moreover, this flap proved safe, considering that no cases of necrosis and only 2 cases of dehiscence were observed, which resolved without additional surgery.
REFERENCES
1. Buchanan CL, Dorn PL, Fey J, Giron G, Naik A, Mendez J, et al. Locoregional recurrence after mastectomy: incidence and outcomes. J Am Coll Surg. 2006;203(4):469-74. PMID: 17000389 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2006.06.015
2. Kuerer HM, Singletary SE, Buzdar AU, Ames FC, Valero V, Buchholz TA, et al. Surgical conservation planning after neoadjuvant chemotherapy for stage II and operable stage III breast carcinoma. Am J Surg. 2001;182(6):601-8. PMID: 11839324 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0002-9610(01)00793-0
3. Amadori D, Pacini P, Giunchi DC, Maltoni R. Quadro clínico e tratamento do carcinoma de mama localmente avançado e do carcinoma inflamatório. In: Veronesi U. Mastologia oncológica. Rio de Janeiro: Medsi; 2002. p.449-63.
4. Julka PK, Prasad R, Mohanti BK, Shukla NK, Raina V, Lal P, et al. Cancer of the breast. In: Rath GK, Mohanti BK, eds. Textbook of radiation oncology, principles ans practice. New Delhi: Churchill Livingstone; 2000. p.239-83.
5. Rocha FBC, Formigoni MC, Lima BSS, Filassi JR, Baracat ER. Avaliação da incidência do câncer de mama localmente avançado no Instituto do Câncer do Estado de Sao Paulo. Revista Latinoamericana de Mastología. 2012;6(2) [acesso 2 Mar 2016]. Disponível em: http://www.flamastologia.org/rlamastologia/index.php/journal/article/view/27
6. Friedel G, Kuipers T, Dippon J, Al-Kammash F, Walles T, Kyriss T, et al. Full-thickness resection with myocutaneous flap reconstruction for locally recurrent breast cancer. Ann Thorac Surg. 2008;85(6):1894-900. PMID: 18498790 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.athoracsur.2008.02.012
7. Martella S, Caliskan M, Brenelli FP, Rossetto F, Aparecida De Oliveira H, De Brito Lima LN, et al. Surgical closure of chest wall in noninflammatory locally advanced breast carcinoma with ulceration of the skin. Breast J. 2008;14(4):345-52. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1524-4741.2008.00596.x
8. Chin PL, Andersen JS, Somlo G, Chu DZ, Schwarz RE, Ellenhorn JD. Esthetic reconstruction after mastectomy for inflammatory breast cancer: is it worthwhile? J Am Coll Surg. 2000;190(3):304-9. PMID: 10703855
9. Losken A, Thourani VH, Carlson GW, Jones GE, Culbertson JH, Miller JI, et al. A reconstructive algorithm for plastic surgery following extensive chest wall resection. Br J Plast Surg. 2004;57(4):295-302. PMID: 15145731 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.bjps.2004.02.004
10. Chang RR, Mehrara BJ, Hu QY, Disa JJ, Cordeiro PG. Reconstruction of complex oncologic chest wall defects: a 10-year experience. Ann Plast Surg. 2004;52(5):471-9. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/01.sap.0000122653.09641.f8
11. Micali E, Carramaschi FR. Extended V-Y latissimus dorsi musculocutaneous flap for anterior chest wall reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2001;107(6):1382-90. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/00006534-200105000-00010
12. Deo SV, Nootan KS, Niranjan B, Dinesh K. Vertical rectus abdominis myocutaneous flap cover for lower abdomen, chest wall, groin and thigh defects following resection of malignant tumours. Indian J Cancer. 2001;38(1):33-7. PMID: 14758883
13. Howard MA, Polo K, Pusic AL, Cordeiro PG, Hidalgo DA, Mehrara B, et al. Breast cancer local recurrence after mastectomy and TRAM flap reconstruction: incidence and treatment options. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2006;117(5):1381-6. PMID: 16641702 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/01.prs.0000208116.86765.4a
14. Baroudi R, Pinotti JA, Keppke EM. A transverse thoracoabdominal skin flap for closure after radical mastectomy. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1978;61(4):547-54. PMID: 345306 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/00006534-197804000-00008
15. Tolhurst DE, Haeseker B, Zeeman RJ. The development of the fasciocutaneous flap and its clinical applications. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1983;71(5):597-606. PMID: 6836058 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/00006534-198305000-00001
16. Cormack GC, Lamberty BG. A classification of fascio-cutaneous flaps according to their patterns of vascularisation. Br J Plast Surg. 1984;37(1):80-7. PMID: 6692066 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0007-1226(84)90049-3
17. Boyd JB, Taylor GI, Corlett R. The vascular territories of the superior epigastric and deep inferior epigastric systems. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1984;73(1):1-16. PMID: 6197716 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/00006534-198401000-00001
18. Taylor GI. The angiosomes of the body and their supply to perforator flaps. Clin Plast Surg. 2003;30(3):331-42. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0094-1298(03)00034-8
19. Deo SV, Purkayastha J, Shukla NK, Asthana S. Myocutaneous versus thoraco-abdominal flap cover for soft tissue defects following surgery for locally advanced and recurrent breast cancer. J Surg Oncol. 2003;83(1):31-5. PMID: 12722094 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/jso.10236
20. Tai Y, Hasegawa H. A transverse abdominal flap for reconstruction after radical operations for recurrent breast cancer. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1974;53(1):52-4. PMID: 4272132 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/00006534-197401000-00009
21. Davis WM, McCraw JB, Carraway JH. Use of a direct, transverse, thoracoabdominal flap to close difficult wounds of the thorax and upper extremity. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1977;60(4):526-33. PMID: 333484 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/00006534-197710000-00005
22. Brown RG, Vasconez LO, Jurkiewicz MJ. A transverse abdominal flap and deep epigastric arcade. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1975;55(4):416-21. PMID: 123346
23. Bohmert H. Experience in breast reconstruction with thoraco-epigastric and advancement flaps. Acta Chir Belg. 1980;79(2):105-10. PMID: 7435090
24. Mathes SJ, Nahai F. Thoraco epigastric (Transverse Abdominal) Flap. In: Mathes SJ, Nahai F. Reconstructive surgery: principles, anatomy and technique. New York: Churchill Livingstone; 1997. p.1107-16. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1055/s-2008-1080278
25. McCraw JB, Bostwick J 3rd, Horton CE. Methods of soft tissue coverage for the mastectomy defect. Clin Plast Surg. 1979;6(1):57-69.
26. Woods JE, Arnold PG, Masson JK, Irons GB, Payne WS. Management of radiation necrosis and advanced cancer of the chest wall in patients with breast malignancy. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1979;63(2):235-41. PMID: 419201 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/00006534-197902000-00013
27. Leinster SJ, Webster JT. Thoraco-abdominal and thoracoepigastric flaps: alternatives to skin grafting after mastectomy. Clin Oncol. 1982;8(2):145-8.
1. Centro de Referência da Saúde da Mulher, Hospital Pérola Byington, São Paulo, SP, Brazil
2. Sociedade Brasileira de Cirurgia Plástica, São Paulo, SP, Brazil
Institution: Centro de Referência da Saúde da Mulher - Hospital Pérola Byington.
Corresponding author:
Ana Claudia Benjamim Burattini
Av. Brigadeiro Luís Antônio, 683 - Bela Vista
São Paulo, SP, Brazil, Zip Code 01317-000
E-mail: acburattini@uol.com.br
Article received: August 6, 2014.
Article accepted: February 29, 2016.


 Read in Portuguese
Read in Portuguese
 Read in English
Read in English
 PDF PT
PDF PT
 Print
Print
 Send this article by email
Send this article by email
 How to Cite
How to Cite
 Mendeley
Mendeley
 Pocket
Pocket
 Twitter
Twitter