
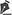
Original Article - Year 2015 - Volume 30 -
Use of 3D geometrical models to improve efficacy and safety of Laser-assisted liposuction: a prospective study
Uso de modelos geométricos tridimensionais para melhorar a eficácia e segurança da lipoaspiração a laser: estudo prospectivo
ABSTRACT
INTRODUCTION: On the basis of the available information, it is difficult to establish the appropriate dose of laser energy with which to obtain predictable results in laser-assisted liposuction. The purpose of this study is to evaluate the safety and efficacy of a 980-nm diode laser by using geometrical formulas. These formulas allow a precise quantification of tissue volume and, as a result, an estimation of the required laser dose.
METHODS: This prospective study was conducted to evaluate 39 consecutive patients who underwent 980-nm diode laser-assisted liposuction (LAL) between November 2011 and November 2013. Four geometric patterns were used to determine the volume of fat before laser application. Ultrasonography was used to determine fat depth. Biopsies were conducted to determine immediate laser tissue reaction relative to laser dose. The aesthetic results and complications were recorded. Pearson's correlation coefficient was used to determine the relationship between the applied energy and tissue volume.
RESULTS: 163 anatomic regions were treated with 980-nm LAL. The applied energy was relative to the volume in each area (R = 0.8786). 8 to 14 J/cm3 was the dose needed to produce effective hemostasis and minimal lipolysis. The results were very satisfactory in most cases. Biopsy results revealed lipolysis, ballooning, membrane rupture, and collagen band breakage; these changes varied with the radiation dose. The only complications were edema and transient bruising.
CONCLUSION: The use of 3D geometrical models improved safety and efficacy of laser-assisted liposuction by permitting accurate determination of the tissue volume.
Keywords: Surgery, Plastic; Lipectomy; Mathematical models; Laser-therapy.
RESUMO
INTRODUÇÃO: Baseada na informação disponível encontram-se dificuldades em estabelecer a dose apropriada de energia a laser para alcançar resultados previsíveis na lipoaspiração a laser. Este estudo avaliou a segurança e eficácia do laser diodo 980-nm com uso de fórmulas geométricas. Essas fórmulas permitem uma qualificação precisa do volume do tecido, e como consequência, uma estimativa da dose de laser necessária.
MÉTODOS: Tratase de estudo prospectivo que avaliou consecutivamente 39 pacientes submetidos a lipoaspiração a laser diodo (LLD) 980-nm entre Novembro de 2011 e Novembro de 2013. Quatro padrões geométricos foram adotados para determinar o volume de gordura antes da aplicação do laser. A ultrassonografia foi utilizada para determinar a profundidade da gordura. Foram realizadas biópsias para estabelecer a reação imediata do tecido ao laser relativo à dose do laser. Os resultados estéticos e as complicações foram documentadas. Utilizou-se o coeficiente de correlação de Pearson para determinar a relação entre a energia aplicada e o volume do tecido.
RESULTADOS: Um total de 163 áreas anatômicas foram tratadas com LLD 980-nm. A energia aplicada foi baseada no volume de cada área (R = 0,8786). Foi necessário dose de 8 a 14 J/cm3 para produzir dose de hemostase efetiva, e lipectomia mínima. Os resultados foram muito satisfatórios na maioria dos casos. A biópsia relevou lipectomia, balonamento, ruptura de membrana, e rompimento de banda de colágeno; essas mudanças variaram com a dose de radiação. As complicações foram somente edema e hematoma transitório.
CONCLUSÃO: O uso de modelos geométricos tridimensionais melhoraram a segurança e eficácia da lipoaspiração a laser, pois permitiram determinar o volume do tecido.
Palavras-chave: Cirurgia plástica; Lipectomia; Modelos matemáticos; Terapia a laser.
Laser-assisted liposuction (LAL) allows hemostasis, lipolysis, and good skin retraction with low morbidity in the hands of experienced surgeons. However, there are difficulties in establishing the dose of energy to be applied on the tissues to obtain predictable results1,2. Different methods to quantify the fat volume reduction have been proposed to determine optimal dosage or to improve dosimetry for laser lipolysis. In 2006, Kim and Geronemus3 reported the evaluation of fat volume reduction using MRI. In 2008, Mordon et al.4 proposed a mathematical model of laser lipolysis and assessed the reduction of volume using a photographic analysis similar to the technique described by Lowe et al.
OBJECTIVE
The purpose of the present prospective study was to evaluate the safety and efficacy of a 980-nm diode laser with a new technique that allows quantification of the fat volume and estimation of the required dose of laser energy using three-dimensional geometrical models. In the current report, we describe the three-dimensional laser assisted lipoplasty procedure and review the results of 136 consecutive procedures.
METHODS
Patient Selection
Between November 2011 and November 2013, 980-nm diode LAL was performed in 39 patients (30 women and 9 men) using four geometric patterns.
The series included patients with normal or reduced skin elasticity; a body mass index (BMI) between 18.6 and 29.9; one or more regions to be treated; irregularities in the treatment area (e.g., cellulite); and small regions to be treated, such as the neck, pubis, or knees. Lipoplasty was performed in combination with other surgical procedures in 33 cases (85%).
Patients were excluded if they were younger than 18 years, pregnant, breastfeeding, or smokers. Also excluded were patients with a BMI ≥ 30 (obesity) or < 18.5 (underweight), unrealistic expectations, cardiovascular disease, diabetes, coagulopathy, or other major comorbid diseases.
Preoperative Evaluation
Preoperative evaluation consisted of routine laboratory tests, cardiology evaluation, and standardized photographs. Additionally, all patients signed informed consent in accordance with the basic principles of the Helsinki Declaration of Rights.
On the day before surgery, the following were performed: marking, measurement of the tissue thickness using ultrasonography, and estimation of the fat volume and energy to irradiate the treated regions.
Marking
Surface marking of the treated regions was performed by selecting the three-dimensional geometric shape that was more suitable to the anatomical region and corresponded to a trapezoidal parallelepiped, rectangular parallelepiped, spherical segment, or hemiellipsoid shape. A trapezoidal parallelepiped was used in most cases. Hemiellipsoid or spherical segments were used in the trochanteric area, inner thighs, and breast. One or two patterns were used in each region according to its size. For example, rectus abdominis muscle regions were subdivided into 3 small parts using rectangular and trapezoidal parallelepipeds (Figure 1A).
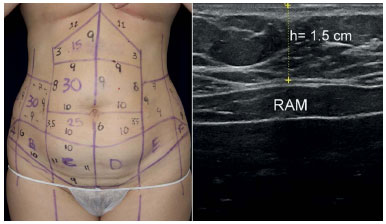
Figure 1. A - Marking before abdominoplasty and 980-nm diode LAL: note the rectus abdominis muscle anatomical region subdivided into three parallelepipeds, and the marked dermolipectomy flap for biopsy (segments A to F) (Left); B - Ultrasonography image showing fat thickness measured in mm over the rectus abdominis muscle (RAM) (Right). In the epigastric region delimited by a trapezoid, the tissue volume calculation without infiltration was as follows: V = (a + a '/2) × (b + b '/2) × h = (11 cm + 9 cm)/2 × (3 cm + 9 cm)/2 × 1.5 cm = 90 ± 0.2 cm3
Ultrasonography
The thickness of the subcutaneous fat was evaluated in all cases using an ultrasound transducer of 7.5 MHz from the subcutaneous fat to the muscle fascia on each region; an average in centimeters was used in the formulas (Figure 1B). The surgeon took all measurements to be sure they were consistent in order to reduce relative and percent error.
Laser Equipment
A 980-nm diode laser device (Lumiia Sonobeam T, Buenos Aires, Argentina) with integrated ultrasound was used to measure and treat all patients. The laser irradiation is applied with a 600-µm fiberoptic that passes through a 1.5- or 3-mm cannula with an opening at the tip, from which the fiber protrudes 2 to 4 mm. The temperature was monitored during the laser application with a non-contact infrared laser-point digital thermometer.
Anatomic pathology
The areas for biopsy sampling were defined and the tissue volume was measured using the described geometric models. Biopsy specimens were obtained approximately 1 hour after laser application in dermolipectomy flaps to assess the immediate tissue reaction related to the dose. The samples were examined by two pathologists. Twenty-seven irradiated surgical specimens with different values (7, 10, 15, 20, 30, and 50 J/cm3) of applied energy were analyzed.
Geometric Models and Mathematical Formulas
We considered that a succinct definition was necessary for the geometric patterns applied: a two-dimensional figure is formed by surfaces, areas, or sides that could be a circle, an ellipse, or a parallelogram, each corresponding to a surface of a three-dimensional figure.
The three-dimensional figures used were as follows: rectangular parallelepiped, trapezoidal parallelepiped, segment of a sphere and hemiellipsoid5 (Figure 2 A-D). The mathematical formulas of these four geometric models were as follows:
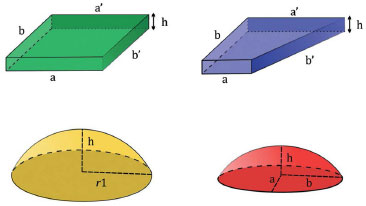
Figure 2. A - Rectangular parallelepiped (Above, left); B - Trapezoidal parallelepiped (Above, right); C - Spherical segment (Below, left); D - Hemiellipsoid (Below, right).
1) Rectangular parallelepiped
A parallelepiped is a polyhedron with six faces, which is limited by three pairs of planes. A rectangular parallelepiped is a figure formed by three pairs of parallel planes in which all angles are right angles (Figure 2A). The simplified mathematical formula to calculate the tissue volume of this figure is as follows: V = (a × b × h) + S, where V = volume; a, b = lengths of the sides of the figure measured in cm. h = depth of fat in cm, and S = volume of infiltrated tumescent solution in cm3.
2) Trapezoidal parallelepiped
The trapezoidal parallelepiped is a three-dimensional figure in which two faces are trapezoids and four faces are parallelograms (Figure 2B). The simplified mathematical formula to calculate the tissue volume of this figure is as follows: V = [(a + a '/2) × (b + b '/2) × h] + S, where V = volume; a, a ', b, b' = lengths of the sides of the figure in cm; h = height or depth in cm; and S = cm3 of infiltrated tumescent solution.
3) Spherical segment
The spherical segment is defined as a portion of a sphere cut out of the center plane (Figure 2C). The formula for the volume of a spherical segment is as follows: V = π/6 × (3 × r12 + h2) × h, where V = volume, π = 3.14159, r1 = radius, and h = height. The simplified formula to calculate the tissue volume of this figure is as follows: V = [0.5233 × (3 × r12 + h2) × h] + S, where V = volume, r1 = radius of the segment in cm, h = height of the segment in cm, and S = volume of infiltrated tumescent solution in cm3.
4) Hemiellipsoid
An ellipsoid is a three-dimensional figure in which all plane sections are ellipses. A hemiellipsoid is either of the halves into which an ellipsoid is divided by a plane of symmetry. To calculate the volume, the semiaxes a, b, and h must be measured. Each semiaxis is equal to half the length of the axis (expressed in cm) and corresponds to the radius of a sphere; semiaxis h is represented by the height or greatest depth from the skin to the muscular fascia (Figure 2D). The simplified formula to calculate the tissue volume of the hemiellipsoid is as follows: V = [4.186 × 0.5 × (a × b × h)] + S = [2.093 × (a × b × h)] + S, where V = volume; a, b, and h = length of semiaxes in cm; and S = volume of infiltrated tumescent solution in cm3.
Operative Technique
Prior to the procedure, 1 g cefazolin was administered intravenously as antibiotic prophylaxis. The infiltration of the tumescence saline solution was performed at room temperature (74.3ºF or 23.5ºC on average) with 0.05% to 0.1% lidocaine and epinephrine 1:1,000,000. The infiltrated volume was added to the estimated volume in the corresponding formula6.
In most cases (139 of 163 [85%]), each region was irradiated before liposuction until the estimated dose for effective hemostasis was reached.
Laser liposuction cannulas of 1.5 mm were used in the face and neck, and cannulas of 3 mm were used in the body, depending on the tissue thickness. The doses of radiation ranged from 5 to 15 J/cm3, depending on the region being treated (Table 1). The range of power used in each region was as follows: 10-15 watts (W) in the face; 10-20 W in the neck; 15-25 W in the arms, thighs, and knees; and 20-35 W in the abdomen. The hand movement speed was practically the same, 40.1 cm/sec average for each area treated by the same surgeon to achieve an even distribution inside each area.
All patients were discharged from the hospital on the day of surgery1. We left some liposuction incisions open to facilitate drainage. For abdominoplasties and neck lifts, we used Jackson Pratt drains, which were removed between 2 and 5 days postoperatively.
Postoperative Instructions
Postoperative instructions included the following: early mobilization, adequate hydration, normocaloric diet, cephalexin and ketorolac regimen for 4 days, diclofenac for 10 to 14 days, return to usual activities between 7 and 14 days, and compressive elastic garment(s) for 6 to 10 weeks.
RESULTS
The average age of the patients in this series was 41 years (range, 19-63 years). The average length of follow-up was 15 months (range, 3-27 months).
There was a strong positive correlation between the applied energy and the volume of infiltrated tissue evaluated by Pearson's correlation coefficient (R = 0.8786) (Figure 3).
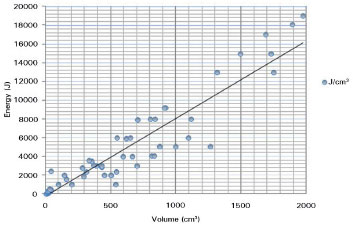
Figure 3. Pearson's correlation coefficient was used to determine the relationship between the applied energy and tissue volume. The applied energy was relative to the volume in each area (R = 0.8786).
Table 1 summarizes the 163 anatomic regions treated with 980-nm LAL, the average volume before and after infiltration with tumescent solution, the aspirated volume, and the dose of laser irradiation.
A 5-point global aesthetic improvement scale (GAIS) was used to assess the opinion of the patients, whereas two surgeons reviewed the pre- and postoperative photographs showing each patient's result using the same scale7. Most patients (25 of 39 [64%]) reported very good improvement (4 points). The surgeons noted very good improvement (4 points) in 56% of patients (Figures 4, 5, 6, 7, and 8).
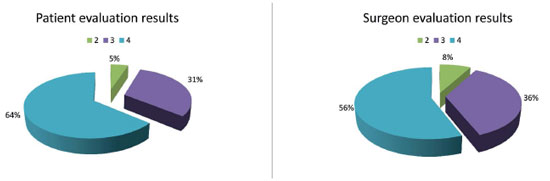
Figure 4. A - Patient evaluation results (Left); B - Surgeon evaluation results (Right). 5-point scale: very much improved (4 points); much improved (3 points); improved (2 points); no change (1 point); worse (0 point).
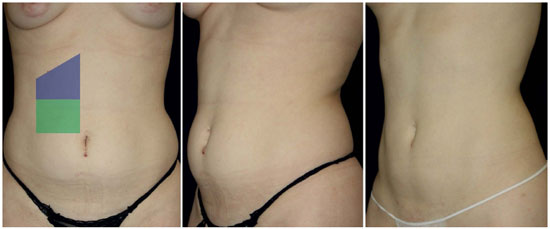
Figure 5. Case 1. A 21-year-old woman with abdominal fat deposition and good skin elasticity; A - Trapezoidal and rectangular parallelepipeds patterns used (Left); B - Preoperative oblique view (Center); C - Nine months after abdominal LAL with a 980-nm diode laser (Right). In the epigastric region delimited by a trapezoid, the tissue volume calculation was as follows: V = [(a + a '/2) × (b + b '/2) × h] + S = (11 cm + 9 cm)/2 × (8 cm + 2 cm)/2 × 0.8 cm + 250 cm3 = 290 ± 0.2 cm3. 2900 J was irradiated in a volume of 290 cm3-i.e., 10 J/cm3.
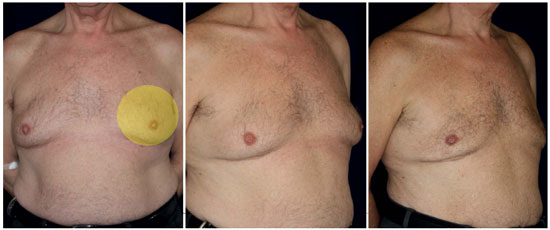
Figure 6. Case 2. A 60-year-old man with gynecomastia and moderate to severe skin laxity. A - Preoperative anteroposterior view; spherical segment pattern used (Left); B - Preoperative oblique view (Center); C - Twelve months after undergoing LAL with a 980-nm diode laser (Right). The tissue volume calculation was as follows: V = [0.5233 × (3 × r12 + h2) × h] + S = [0.5233 × (3 cm × 62 cm + 12 cm) × 1 cm] + 200 cm3 = 257 ± 0.3 cm3. The dose applied to each breast was therefore 2000 J/257 cm3 = 7.78 J/cm3.
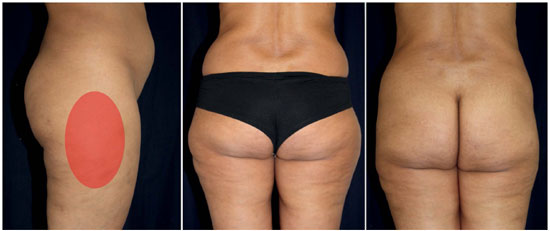
Figure 7. Case 3: Example of hemiellipsoid model use. A 49-year-old woman with fat deposition in the thighs and abdominal flanks, with pronounced irregularities (cellulite); A - Preoperative lateral view. Here, we chose a hemiellipsoid pattern (Left); B - Preoperative anteroposterior view (Center); C - Thirteen months after 980-nm diode LAL (Right). The tissue volume calculation was as follows: V = [4.186 × 0.5 × (a × b × h)] + S = [2.093 × (7.5 cm × 10 cm × 2.6 cm)] + 300 cm3 = 708 ± 0.1 cm3. The total dose applied in this area was 5000 J (7.06 J/cm3).
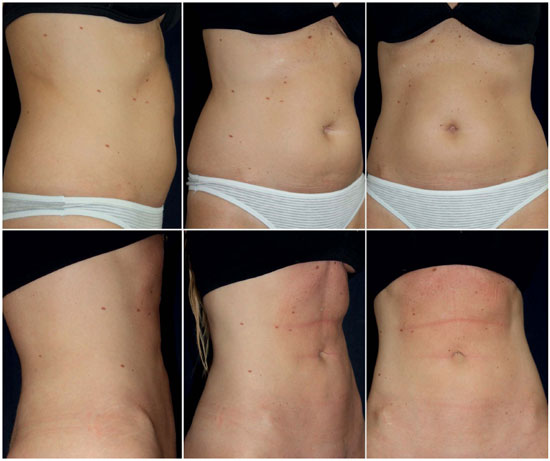
Figure 8. A 34-year-old woman presented abdominal fat deposition and slight skin laxity; ABC - Preoperative views (Above); DEF - Twelve months after undergoing 980-nm diode LAL (Below).
There were no major or relevant complications, such as hematomas, seromas, wound dehiscence, infections, burns, skin necrosis, or irregularities.
Mild to moderate edema and mild transient ecchymosis were observed in most cases, but these effects subsided within 4 weeks with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Mild to moderate pain was observed in the first 15 days, but this effect likewise subsided with NSAIDs. A 60-year-old male patient (2.56%) who underwent extensive liposuction with 10 J/cm3 irradiation in the abdomen and no irradiation in the pubic area had significant bruising in the scrotal region and edema for 4 weeks, as well as moderate infraumbilical edema up to 8 weeks. These effects also subsided with NSAIDs.
The surgery time slightly increased in the initial cases because of the measurements made during surgery.
The anatomic pathological reports showed the following in samples irradiated with 10 or more J/cm3: lipolysis, adipocyte ballooning, and focal or diffuse adipocyte membrane rupture. No bleeding foci were observed in these samples. In samples irradiated with 15 or more J/cm3, the following were noted: extensive lipolysis and more adipocyte membrane rupture than ballooning, broken collagen bands (due to thermal effects) were observed, but no epidermal detachment was noted (Figure 9).
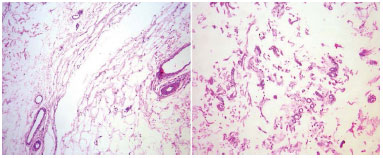
Figure 9. Biopsy samples stained with hematoxylin-eosin, viewed under optic microscopy at 100x magnification. A - Tissue irradiated with 10 J/cm3: note the adipocyte ballooning, rupture of membranes, and vascular preservation (Left); B - Sample of biopsy irradiated with 15 J/cm3: note the extensive lipolysis with ruptured adipocyte membranes (Right).
Case Examples
The following three cases exemplify the use of geometric patterns in different regions.
Case 1
A 21-year-old woman presented with abdominal fat deposits and good skin elasticity. Here, we used trapezoidal and rectangular parallelepipeds in the subdivisions of the abdomen: 2900 J was irradiated in a volume of 290 cm3-i.e., 10 J/cm3, whereby liposuction was conducted with minimal bleeding. In the epigastric region delimited by a trapezoid, the tissue volume calculation was as follows: V = [(a + a '/2) × (b + b '/2) × h] + S = (11 cm + 9 cm)/2 × (8 cm + 2 cm)/2 × 0.8 cm + 250 cm3 = 290 ± 0.2 cm3. The shape and degree of skin retraction in the postoperative period were very satisfactory (Figure 5).
Case 2
A 60-year-old man presented with gynecomastia with moderate to severe skin flaccidity. Here, we used a spherical segment that corresponded approximately to the shape of the irradiated tissue, with the patient in supine position. The 6-cm radius included the entire breast region. The dose used to remove almost pure fat, with minimal blood loss, was 7.78 J/cm3. The tissue volume calculation was as follows: V = [0.5233 × (3 × r12 + h2) × h] + S = [0.5233 × (3 × 62 cm+ 12 cm) × 1] + 200 cm3 = 257 ± 0.3 cm3. The dose applied to each breast was therefore 2000 J/257 cm3 = 7.78 J/cm3. As shown in Figure 6, the shape and skin retraction improved after surgery.
Case 3
A 49-year-old woman had fat deposits in the thighs and abdominal flanks, with pronounced irregularities (cellulite). Here, we chose a hemiellipsoid pattern, which better fit these regions. The total dose applied in this area was 5000 J (7.06 J/cm3). The procedures were conducted with minimal bleeding. The tissue volume calculation was as follows: V = [4.186 × 0.5 × (a × b × h)] + S = [2.093 × (7.5 cm × 10 cm × 2.6 cm)] + 300 cm3 = 708 ± 0.1 cm3. Figure 7 shows these regions before and 13 months after the procedure.
DISCUSSION
LAL is an increasingly used alternative to conventional lipoplasty. Previous reports on LAL and laser lipolysis refer to the partial or total energy measured in J applied to certain regions and refer to volume reduction of fat by lipolysis, but volume measurements before surgery were not reported1-4,8-18.
Before comparing our results with previous reports we would like to clarify some points to avoid semantic confusions:
First, we refer to laser-assisted liposuction instead of laser lipolysis, which is fat removed by liposuction. This means we don't pursue to reduce fat by extensive laser lipolysis. On the contrary, we believe that very high doses must be avoided, particularly when several large areas are treated. Fat reduction by laser lipolysis with high doses should be limited only to small areas. Our goal was to avoid extensive burning of tissue and to minimize complications, reducing the dose to the minimal effective for an optimal hemostasis19.
Second, to the best of our knowledge, 3-D geometrical patterns have never been proposed for fat volumetry. The use of these patterns permits us to define tissue volume in every area for any possible treatment.
In the submental zone, Kim and Geronemus3 reported that approximately 3000 J needs to be applied to get a mean volume reduction of 5.2 ± 2.8 cm3 evaluated by MRI. Similarly, Mordon et al.4 quantified the fat volume reduction in the submental zone using 3D photography. They found a similar reduction: 10 cm3 ± 1 cm3 for a total energy of 6600 J. Consequently, the volumetric dosage is approximately 660 J/cm3 for lipolysis.
Our results show that only 8 to 14 J/cm3 is needed to produce hemostasis and minimal lipolysis, without producing complications, when 980-nm diode LAL is performed19.
Quantitative measurement of fat volume from noninvasive imaging modalities such as photography and MRI is feasible, has been used for assessment of fat volume reduction, and might play a role in research3 . However, these methods might be impractical to quantify fat and volume variations due to tumescent infiltration or liposuction during surgery.
The problem arises when dose is not correlated to volume in the treated region. The volume can vary significantly in each region and even more with tumescent infiltration. Therefore, for a given dose, the heating effect will have significant variations. In accordance with previous reports, the thermal effect of lasers vary with laser wavelength, the dose and the irradiated volume of tissue, which was confirmed by anatomic pathological biopsies9-11,15-18.
Consequently, it is essential for accurate dosimetry to relate the energy applied to the volume of infiltrated tissue, making the LAL technique predictable, safe, and reproducible, permitting comparisons of results, and establishing standard treatments1,3,12,18.
In accordance with previous reports, we propose the unit J/cm3 to relate energy (J) to tissue volume (cm3), which allows minimizing the applied energy to obtain sufficient coagulation, vascular and nerve preservation, and minimal lipolysis. As a result we obtain low morbidity and maximum efficiency; compared with previous reports, we irradiate with relatively low doses at the point of hemostasis, avoiding unnecessary lipolysis of fat that will be removed by liposuction.
We believe that it is important to use adaptive patterns for the treated region. It is preferable to choose symmetrical figures, but each side should be measured separately to avoid errors. There are various factors to be considered because they can alter the estimate of the final volume, leading to a miscalculation. These factors include the volume of anesthetic solution, patient positioning during measurement, modification of the shape and volume redistribution when tissues are compressed by the ultrasound transducer, and the number of measurements per region.
Ultrasonography is an easy-to-use diagnostic tool that permits accurate measurement of the tissue thickness20. It is advisable to calculate an average value of the concerned region thickness based on several measurements. Variation is usually low in small regions; large regions should be subdivided for more accuracy.
The choice of the power used will vary according to the fat thickness, infiltration, and speed considered appropriate by the surgeon. Additionally, laser wavelength and density of tissue absorption must be considered. Therefore, power is a relative value and not the only parameter to be considered3.
The main advantage of the three-dimensional measurement method is that it allows a laser-assisted liposuction performance with minimal bleeding and very low morbidity, mainly due to accurate dosimetry and precise fat volume estimation.
We agree with other authors that the disadvantages of LAL are the cost of equipment and learning curve9.
The small number of cases enrolled is a limitation of this study. However, further research studies will grant the utility of this method.
CONCLUSIONS
The use of three-dimensional geometrical models improved the safety and efficacy of laser-assisted liposuction by permitting accurate determination of the tissue volume.
This approach allows reducing dosage in order to optimize hemostasis in each area, reaching the lipolysis dose when deemed necessary.
REFERENCES
1. Ahmad J, Eaves FF 3rd, Rohrich RJ, Kenkel JM. The American Society for Aesthetic Plastic Surgery (ASAPS) survey: current trends in liposuction. Aesthet Surg J. 2011;31(2):214-24 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/1090820X10395508
2. Leclère FM, Trelles M, Moreno-Moraga J, Servell P, Unglaub F, Mordon SR. 980-nm laser lipolysis (LAL): About 674 procedures in 359 patients. J Cosmet Laser Ther. 2012;14(2):67-73. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.3109/14764172.2012.670704
3. Mordon SR, Wassmer B, Reynaud JP, Zemmouri J. Mathematical modeling of laser lipolysis. BioMedical Engineering OnLine. 2008;7:10. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1475-925X-7-10
4. Kim KH, Geronemus RG: Laser lipolysis using a novel 1,064 nm Nd:YAG Laser Dermatol Surg. 2006;32(2):241-48; discussion 247.
5. Beyer, William H. Standard Mathematical Tables. Florida:CRC Press;1987.
6. Klein JA. The tumescent technique. Anesthesia and modified liposuction technique. Dermatol Clin. 1990;8(3):425-37.
7. Narins RS, Brandt F, Leyden J, Lorenc ZP, Rubin M, Smith S: A randomized, double-blind, multicenter comparison of the efficacy and tolerability of Restylane versus Zyplast for the correction of nasolabial folds. Dermatol Surg. 2003;29(6):588.
8. Apfelberg DB. Results of multicenter study of laser-assisted liposuction. Clin Plast Surg. 1996;23(4):713-9. PMID: 8906399
9. Badin AZD, Moraes LM, Gondek L, Chiaratti MG, Canta L. Laser Lipolysis: Flaccidity Under Control. Aesth Plast Surg. 2002;26:335-339. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00266-002-1510-3
10. Badin AZED, Gondek LBE, Garcia MJ, Valle LCD, Flizikowski FBZ, Noronha LD. Analysis of laser lipolysis effects on human tissue samples obtained from liposuction. Aesthetic Plastic Surg. 2005;29(4):281-286. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00266-004-0102-9
11. Brañas EB, Moraga JM. Laser lipolysis using a 924- and 975-nm laser diode in the lower extremities. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2013;37(2):246-53. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00266-012-0027-7
12. Centurión P, Cuba JL, Noriega A. Liposucción con diodo láser 980-nm (LSDL 980-nm): optimización de protocolo seguro en cirugía de contorno corporal. Cir Plást Iberolatinoam. 2011;37(4):355-364. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.4321/S0376-78922011000400007
13. Chia CT, Theodorou SJ. 1,000 consecutive cases of laser-assisted liposuction and suction-assisted lipectomy managed with local anesthesia. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2012;36(4):795-802. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00266-012-9885-2
14. Goldman A, Schavelzon DE, Blugerman GS. Laserlipolysis: Liposuction using Nd-Yag laser. Rev Soc Bras Cir Plast. 2002;17(1):17.
15. Neira R, Arroyave J, Ramirez H, et al. Fat liquefaction: Effect of low-level laser energy on adipose tissue. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2002;110(3):912-922. PMID: 12172159 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/00006534-200209010-00030
16. Reynaud JP, Skibinski M, Wassmer B, Rochon P, Mordon S. Lipolysis Using a 980-nm Diode Laser: A Retrospective analysis of 534 Procedures. Aesth Plast Surg. 2009;33:28-36 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00266-008-9262-3
17. Thomsen S. Pathologic analysis of photothermal and photomechanical effects of laser-tissue interactions. Photochem Photobiol. 1991;53(6):825-835. PMID: 1886941 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1751-1097.1991.tb09897.x
18. Trelles M, Bonanad E, Moreno-Moraga J, Alcolea J, Mordon S, Leclère FM. Lipólisis láser y liposucción en ginecomastia: retracción cutánea eficaz y segura. Rev Col Bras Cir. 2013;40(1):23-31. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S0100-69912013000100005
19. Blum CA, Sasser CG, Kaplan JL. Complications from laser-assisted liposuction performed by noncore practitioners. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2013;37(5):869-75. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00266-013-0153-x
20. Benito-Ruiz J, de Cabo F. Ultrasonography: a useful tool for plastic surgeons. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2014;38(3):561-71. PMID:24643897 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00266-014-0300-z
Sociedade Argentina de Cirurgia Plástica, Estética e Reparadora - Buenos Aires, Argentina
Institution: Sociedade Argentina de Cirurgia Plástica, Estética e Reparadora - Buenos Aires, Argentina.
Corresponding author:
Williams Erik Bukret
1848 Alicia Moreau de Justo Avenue, Floor 2, Suite 6, Puerto Madero
Buenos Aires, Argentina. CEP C1107AFL
E-mail: drbukret@drbukret.com
Article received November 25, 2014.
Article accepted June 07, 2015.


 Read in Portuguese
Read in Portuguese
 Read in English
Read in English
 PDF PT
PDF PT
 Print
Print
 Send this article by email
Send this article by email
 How to Cite
How to Cite
 Mendeley
Mendeley
 Pocket
Pocket
 Twitter
Twitter