
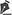
Case Report - Year 2015 - Volume 30 -
Lip reconstruction with cervical platysma muscle randomized flaps
Reconstrução de lábio utilizando o retalho randomizado cervical do músculo platisma
ABSTRACT
INTRODUCTION: Surgical reconstruction of lip deformities requires proper anatomical knowledge and surgical techniques. Factors such as location, extent, depth, and appropriate initial treatment of the lesion are parameters that are simultaneously analyzed to identify the most suitable surgical strategy. The flap described by Tsur is defined as a platysma muscle randomized flap, and can be raised from the neck as a unipedicled or bipedicled tube, depending on the size and location of the loss of substance. This may include the hairy cervical area, and it can be used in defects of the partial or total plane of the lip.
METHOD: Three patients with extensive loss of lip substance underwent surgery. A bipedicled flap was used in two cases, and a unipedicled flap in one case.
RESULTS: In the first patient, one pedicle of the cervical flap was released on the 15th postoperative day. After 30 days, we released the other, after full integration into the upper lip. From this, flaps were randomly made for the reconstruction of the lower lip, columella, and nasal tip. The second patient developed necrosis of the central portion of the flap, and the recipient bed was anchored next to the commissure. The patient showed improved salivary continence. The third patient progressed well, and the tongue flap used to reconstruct the upper lip was released three weeks later.
CONCLUSION: Reconstruction with a Tsur flap was useful in cases of total reconstruction of the upper and lower lip, in addition to being a great alternative in situations in which it was impossible to use microsurgical flaps. This technique also allowed the achievement of satisfactory aesthetic outcomes, and resulted in the recovery of masticatory function and appropriate speech, despite the initial complexity of the cases.
Keywords: Reconstruction; Lip; Surgical flap; Neck.
RESUMO
INTRODUÇÃO: A reconstrução cirúrgica da deformidade labial exige bom conhecimento anatômico e técnica cirúrgica. Fatores como localização da lesão, extensão, profundidade e tratamento inicial adequado constituem variáveis que são analisadas em conjunto para a estratégia cirúrgica mais apropriada. O retalho de Tsur é definido como randomizado do músculo platisma que pode ser elevado do pescoço como tubo unipediculado ou bipediculado, dependendo do tamanho e da localização da perda de substância. Pode incluir área pilosa cervical e ser utilizado em defeitos de plano parcial ou total do lábio.
MÉTODO: Foram operados três pacientes com perda de substância labial extensa. Foi utilizado retalho bipediculado em dois casos e unipediculado em um caso.
RESULTADOS: No primeiro paciente, foi liberado um dos pedículos do retalho cervical no 15º dia do pós-operatório. Após 30 dias, o outro foi liberado após integração completa ao lábio superior. A partir deste, retalhos ao acaso foram confeccionados para reconstrução do lábio inferior, columela e ponta nasal. O segundo paciente evoluiu com necrose da porção central do retalho, sendo realizada confecção de leito de ancoragem próximo à comissura. Apresentou melhora da continência salivar. O terceiro paciente evoluiu bem, sendo liberado o retalho lingual utilizado para reconstruir o lábio superior após 3 semanas.
CONCLUSÃO: A reconstrução com o retalho de Tsur mostrou-se útil nos casos de reconstrução total do lábio superior e inferior, além de ser ótima alternativa na situação de impossibilidade de utilização do retalho microcirúrgico e de permitir um resultado estético aceitável com recuperação da função mastigatória e da fala adequadas, apesar da complexidade inicial dos casos.
Palavras-chave: Reconstrução; Lábio; Retalhos cirúrgicos; Pescoço.
Surgical reconstruction of facial deformities requires proper anatomical knowledge and surgical technique. Owing to their characteristics, labial sequelae in particular are difficult to manage1. Factors such as location, extent, depth, and appropriate initial treatment of the lesion are parameters that are simultaneously analyzed to identify the most suitable surgical strategy2,3. Several variables may influence the final outcome, including retraction and scarring from the initial trauma, infeasibility of local flaps, lip commissure destruction, and orbicularis muscle separation, with degeneration and destruction of muscle fibers3.
A Tsur flap is defined as a platysma muscle randomized flap that can be raised from the neck as a unipedicled or bipedicled tube, depending on the size and location of the loss of substance. This may include the hairy cervical area, and it can be used in defects of the partial or total plane of the lip4.
OBJECTIVES
To describe lip reconstruction using a Tsur flap in three patients, two with loss of substance in the upper and lower lip, and the other with involvement of the upper lip.
PATIENTS AND METHOD
The flap was made wide enough to reconstruct the total thickness of the lip, including the hairy neck region. The detachment began in an area close to the angle of the mandible, where the flap remained pedicled in the skin, subcutaneous tissue, and muscle platysma flap. Once the flap was detached, its transposition into the recipient bed was carried out after debridement.
The flap described by Tsur was planned in the following patients:
Patient 1: The patient was an 18-year-old boy who was the victim of a severe electrical burn 5 months previously He showed an extensive injury with loss of lips and nose wing. A supratrochlear flap was associated with the nasal dorsum, in addition to the bipedicled Tsur flap (Figures 1 to 4).
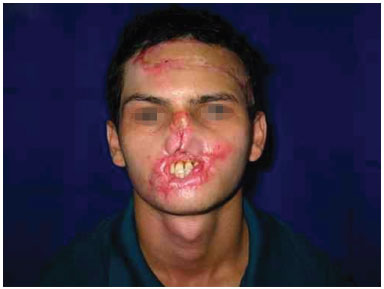
Figure 1. An 18-year-old boy experienced severe electrical burns on the face 5 months previously; he showed loss of the lips and inferior 2/3 of the nose.
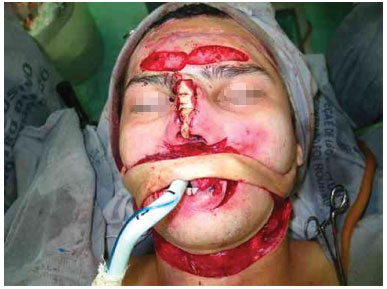
Figure 2. A bipedicled cervical flap was used.
Figure 3. Release of one of the pedicles when the lower lip was already reconstructed.
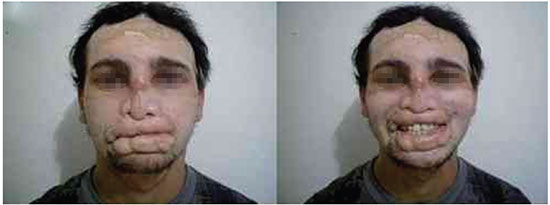
Figure 4. Sphincter function of the mouth was restored in the late postoperative period.
Patient 2: A 36-year-old presented with 50% loss of substance of the upper lip and nose wing after a motorcycle accident. We used a bipedicled flap (Figures 5 to 7).
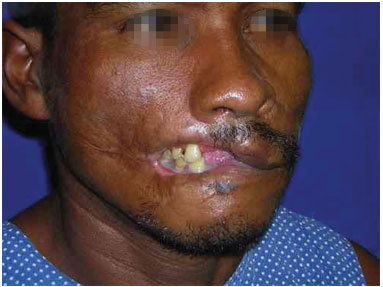
Figure 5. A 35-year-old man showed loss of substance in the lower right and upper lips in a car accident.
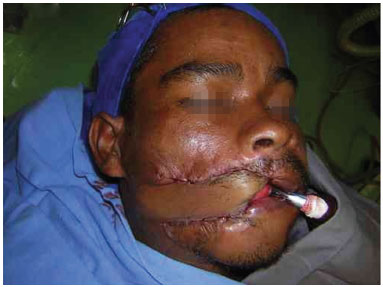
Figure 6. A unipedicled flap in the immediate postoperative period.
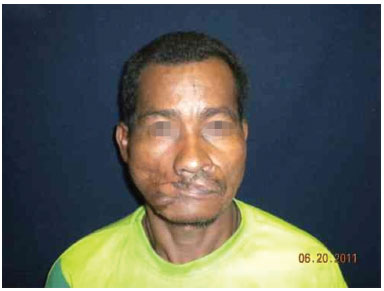
Figure 7. Improved labial occlusion in the late postoperative period.
Patient 3: A 35-year-old man presented with a loss of substance in the upper right and lower lip after a car accident. A tongue flap was associated with the reconstruction of the upper lip, besides the unipedicled Tsur flap (Figures 8 to 11).
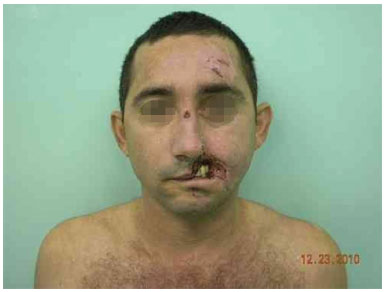
Figure 8. A 36-year-old man showed 50% loss of substance of the upper lip and nose wing in a car accident.
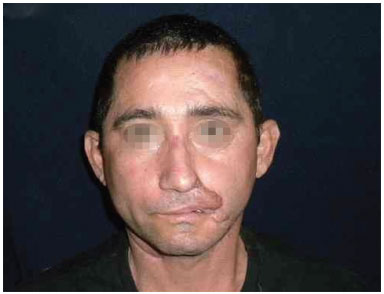
Figure 9. Improved labial occlusion in the late postoperative period.
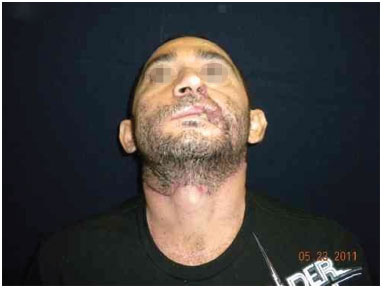
Figure 10. Good appearance of the scar in the donor area.
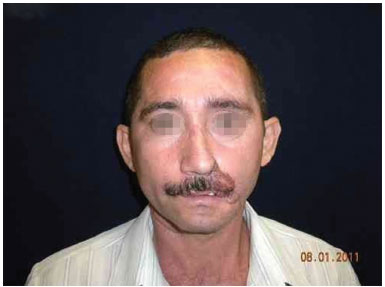
Figure 11. A hairy flap may hide scars resulting from the reconstruction.
RESULTS
In the first patient, one of the cervical flap pedicles was released on the 15th postoperative day. After 30 days, the other pedicle was released, after full integration into the upper lip. Then, random flaps were made every 2 months under local anesthesia for the reconstruction of the lower lip, columella, and nasal tip. The final reconstruction, which occurred 2 years after creation of a Tsur flap, resulted in a structure of limited emotional expression and functionality, but with a satisfactory aesthetic aspect and food continence.
The second patient developed necrosis of the central portion of the flap, and the recipient bed was anchored next to the commissure to ensure its viability. Random flaps were made for wing and lip reconstruction. Several changes were carried out, in addition to commissuroplasty. The patient showed improved salivary continence.
The third patient progressed well, and the tongue flap, used to complement the reconstruction of the upper lip, was released 3 weeks later.
DISCUSSION
Reconstruction of lip defects seeks to ensure proper functional activity, reestablishment of a symmetrical orifice, absence of speech disorders, proper vermillion repair, uniform thickness of the lip to enable complete closure of the mouth, and a satisfactory aesthetic appearance3,5.
Local flaps are described for the reconstruction of loss of substance of upper or lower lips. However, none of these techniques can be used to reconstruct the two structures simultaneously3. While local flaps are used because of their advantages of color and texture, which are similar to the site of injury, their use is difficult or impossible in burn patients2, or with total loss of the upper and lower lip. Microsurgical flaps are a good choice for total head and neck reconstruction1. However, this may be a limited option because of higher cost and the requirement of an experienced microsurgical team. In addition, clinic limitations specific for certain patients contraindicate the use of these procedures in particular cases1.
When it is not possible to perform labial reconstruction microsurgery, the use of a randomized neck bipedicled flap presents the advantages of having two layers, adequate thickness, and mobile and flexible properties. In addition, it may resemble the recipient tissue in terms of color, density, and quality. The scar of the donor area is aesthetically acceptable. Compared to microsurgical reconstruction, this technique also requires multiple minor and complementary surgical procedures, aimed at improving the final outcome4. Despite resulting in a structure with limited emotional expression and speech functionality, we observed improvement in aesthetic appearance and food continence.
CONCLUSION
Reconstruction with a bipedicled neck flap was useful in cases of total reconstruction of the upper and lower lip. In addition to being a great alternative in cases in which it was impossible to use microsurgical flaps, this procedure led to an acceptable aesthetic result, with recovery of masticatory function and adequate speech, despite the initial complexity of the cases.
REFERENCES
1. Carvalho CFAM, Miranda Filho RA, Silva Júnior V, Oliveira VF, Moreira AA. Reconstrução de nariz e lábios em seqüela de queimadura elétrica. Cir Plást Iberolatinoam. 2009;35(3):237-42.
2. Pallua N, Demir E. Postburn head and neck reconstruction in children with the fasciocutaneous supraclavicular artery island flap. Ann Plast Surg. 2008;60(3):276-82. PMID: 18443509 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/SAP.0b013e3180db2775
3. Nabili V, Knott PD. Advanced lip reconstruction: functional and aesthetic considerations. Facial Plast Surg. 2008;24(1):92-104. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1055/s-2007-1021892
4. Tsur H, Shafir R, Orenstein A. Hair-bearing neck flap for upper-lip reconstruction in the male. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1983;71(2):262-5. PMID: 6823490 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/00006534-198302000-00025
5. Aytekin A, Ay A, Aytekin O. Total upper lip reconstruction with bilateral Fujimori gate flaps. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2003;111(2):797-800. PMID: 12560701 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/01.PRS.0000041599.99985.8E
1. Hospital Instituto Dr. José Frota. Fortaleza, CE, Brazil
2. Sociedade Brasileira de Cirurgia Plástica, São Paulo, SP, Brazil
Institution: Hospital Instituto Dr. José Frota, Fortaleza, CE, Brazil.
Corresponding author:
Rodrigo Cesar Pimenta Gomes
Rua Professor Otávio Lobo, 540, Cocó
Fortaleza, CE, Brazil Zip code 60192-290
E-mail: rodrigocesarpimenta@yahoo.com.br
Article received: November 3, 2011.
Article accepted: January 28, 2012.


 Read in Portuguese
Read in Portuguese
 Read in English
Read in English
 PDF PT
PDF PT
 Print
Print
 Send this article by email
Send this article by email
 How to Cite
How to Cite
 Mendeley
Mendeley
 Pocket
Pocket
 Twitter
Twitter