
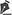
Original Article - Year 2014 - Volume 29 - Issue 3
A report on complications of breast implantation: evaluation of 546 cases in 8 years
Estudo de complicações em próteses mamárias: avaliação de 546 casos em oito anos
ABSTRACT
INTRODUCTION: Breast augmentation implant surgery is one of the most frequently performed plastic surgery procedures; however, it can be challenging because of its associated complications.
METHOD: We conducted a retrospective study of 546 patients operated on in eight years (May 2004 to May 2012). These patients underwent breast augmentation, alone or in association with mastopexy or breast reduction.
RESULTS: In this study, 84.8% textured and 15.2% polyurethane prostheses, with 91.7% deployed in the subglandular plane and 8.24% in the submuscular plane, were used. We investigated the occurrence of contracture (3.3%), seroma (2.7%), ptosis (2.7%), and infection (0.6%). Most contractures occurred 5 years after surgery and only in textured prostheses, which had a longer follow-up (4.2 years for textured implants vs. 1.7 years for polyurethane implants). There was a higher frequency of ptosis in textured implants and of infection in polyurethane implants. Only patients with textured prostheses showed contractures in the observed period. Concerning the deployment plane, seroma was more frequently observed in submuscular implants. More complex procedures showed a higher rate of complications. Polyurethane implants were associated with increased infection rates, whereas textured implants resulted in ptosis and seroma; however, there were no differences in contracture rates. All cases of infection occurred in patients who received reduction mammoplasty with polyurethane prostheses and were caused by common germs, with no cases of mycobacterial infection.
CONCLUSIONS: Contractures and ptosis uniquely occurred in textured prostheses in the shortest follow-up time. Infection occurred only in polyurethane prostheses. Mastopexies and reduction mammoplasties showed a progressively higher rate of complications.
Keywords: Breast implant; Polyurethanes; Capsular contracture of implants; Seroma.
RESUMO
INTRODUÇÃO: O implante de próteses mamárias é uma das cirurgias mais frequentes e desafiadoras da cirurgia plástica, devido às complicações associadas.
MÉTODO: Foi realizado um estudo retrospectivo de 546 pacientes operadas em oito anos (maio de 2004 a maio de 2012), sendo estudadas todas as pacientes submetidas à inclusão de próteses mamárias, isoladamente ou associadas à mastopexia ou mamoplastia redutora.
RESULTADOS: Foram utilizadas próteses texturizadas em 84,8% e poliuretano, em 15,2%, com plano de implantação subglandular em 91,7% e submuscular, em 8,24%. Foram estudados: contratura (3,3%), seroma (2,7%), ptose (2,7%) e infecção (0,6%). A maioria das contraturas surgiu cinco anos após a cirurgia e apenas nas próteses texturizadas, que tiveram tempo de seguimento maior (4,2 anos, nas próteses texturizadas versus 1,7 ano nas de poliuretano). Houve maior frequencia de ptose nas texturizadas e de infecção, nas de poliuretano. Somente apresentaram contraturas pacientes com próteses texturizadas no período observado. Comparando-se o plano de implantação, o seroma foi mais frequente nas submusculares. Considerando-se a complexidade do procedimento, houve aumento do índice de complicações: nas implantadas com poliuretano, aumentou o índice de infecção; nas texturizadas, de ptose e seroma, mas não houve diferenças quanto à contratura. Todos os casos de infecção ocorreram em mamoplastias redutoras com próteses de poliuretano e foram causados por germes comuns, sem casos de micobactérias.
CONCLUSÕES: Contraturas e ptose foram exclusivas em próteses texturizadas, no tempo de seguimento mais curto. Infecção apenas ocorreu em próteses de poliuretano. As mastopexias e mamoplastias redutoras apresentaram um índice progressivamente mais alto de complicações.
Palavras-chave: Implante mamário; Poliuretanos; Contratura capsular de implantes; Seroma.
The breasts, more than any other body part, represent femininity; therefore, their aesthetic improvement is of great importance. Thus, implant breast augmentation is one of the most frequently performed surgeries in Brazil and worldwide.
Since 1889, when the first and unsuccessful breast augmentations with filler substances were performed, many advancements with the procedure have been made. The first silicone implants were introduced in 1962, demonstrating the first challenge: high rates of capsular contracture and rupture that were partially improved by using textured coatings and polyurethane. Rumors of an increased incidence of cancer and autoimmune diseases led to the temporary interruption of their marketing in the United States; however, they were again released after extensive studies have proven their safety.
The implant choices are varied. Moreover, there is much discussion about the best positioning (subglandular or submuscular), and the concomitant performance of mastopexy and prosthesis placement. Yet, reoperation occurs in 24% of patients1-3. Investigating the causes of reoperation is vital in improving results. Contraction is almost always a major cause and has very heterogeneous rates in the literature, between 0.86% and 58%1,3-6. Infection occurs in 1.7% to 2.8%1,4, and is relevant because it usually necessitates the removal of the prostheses, which, in turn, has a large psychological impact on the patient. Seromas have been widely studied in relation to their causes; however, no conclusions have been reached. Moreover, anaplastic large cell lymphoma, a rare cause of late seroma that cannot be overlooked, has also been discussed7-9.
Mastopexy with prosthesis insertion is an old but still very much questioned procedure as it increases the incidence of complications, despite having the advantage of being performed as a single procedure2,10. On the other hand, reduction mammoplasty with prostheses is a more recent technique with fewer supporters because of the paradoxical concept of replacing breast tissue with a prosthesis. However, the poor filling of cleavage in reduction mammoplasty has favored the widespread use of this technique11,12, although the increase in complications is yet to be considered.
In this study, we aim to evaluate the incidence of complications in isolated breast implant surgeries and in implantations associated with mastopexy and breast reduction, through our personal experience of 546 cases operated in 8 years.
METHODS
This is a retrospective study of 546 consecutive patients treated from May 2004 to May 2012, through the analysis of medical records. All patients were operated on by the same surgeon in a private practice.
All patients who underwent breast augmentation, alone or in association with mastopexy or breast reduction, were studied. For reduction mammoplasty with prosthesis insertion, the selected patients were those with predominantly fatty breast tissue, in which the prosthesis would function as a material to improve tissue consistency. The purpose of the implant, in this case, was not to increase the breast volume; therefore, we used an implant volume that is smaller than the resected tissue.
Surgical Technique
The volume of the prosthesis was estimated at preoperative consultation, through the evaluation of samplers.
The subglandular or submuscular position was determined according to the estimated amount of breast tissue to bidigital pinching: for <2 cm thickness in the upper pole, the submuscular plane was used; otherwise, the subglandular position was selected.
All patients were operated on under thoracic epidural anesthesia and sedation. Antisepsis was done with chlorhexidine degerming followed by alcoholic chlorhexidine.
In simple prosthesis insertions, we performed inframammary and periareolar inferior incisions. The inframammary incision was positioned at the level of the future breast groove and had a length of 4 cm. We dissected the subglandular or submuscular space in twin flat. In this case, we performed complete sectioning of the medial insertion of the pectoralis major muscle in the sternal margin until the fourth intercostal space, to decrease the prosthesis superior mobilization promoted by the muscle, preserving the fascial extension that connects the muscle to the rib cage and minimizing the lower displacement of the implant.
In cases of mastopexy, after marking point A and the periareolar and vertical scar, the breast was incised vertically to reach the subglandular or submuscular plane. The prosthesis was inserted and the excess skin was resected vertically, with horizontal compensation.
Breast reduction was performed according to principles of Pitanguy12. After the incision, resection was done in the lower pole and retroareolar keel corresponding to the desired volume to be removed. In case of mammary asymmetry, resection of a greater volume was done on the longest side to attempt to balance the breasts, and to allow the use of the same volume of prostheses, whenever possible.
The gloves were replaced and the prostheses with textured coating or Silimed® polyurethane were inserted. No solution was applied to the prosthesis or to its insertion site. We did not use drains. The breast tissue and skin incision were then closed. We performed antibiotic prophylaxis with cefazolin and prophylactic measures against venous thromboembolism.
Patients were followed as outpatients for a year, and were advised by the surgeon to return in case of swelling or hardening of the breasts.
RESULTS
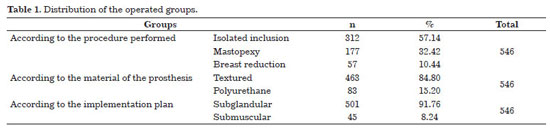
A total of 546 patients were operated on from May 2004 to May 2012. Their ages ranged between 16 and 65 years (mean, 32.4 years; standard deviation, 9.8 years). The mean volume of implant was 310 mL in simple inclusions and 255 mL in mastopexies. In reduction mammoplasties, an average of 309 g breast tissue (160-447 g) was removed and an average implant volume of 225 mL was used (Table 1).
Statistical analysis was done on the most frequent complications: contracture, seroma, and ptosis (Table 2). Ptosis was defined as the downward displacement of the implant. Infection was also investigated given its clinical relevance.
Data were tabulated in software Excel® spreadsheets (2003). The variables were evaluated by using BioEstat® software (version 3.0). We adopted a confidence interval of 95% and a p value of <0.05.
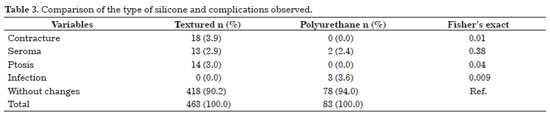
Table 3 shows that among the complications, there was a statistically significant difference for contracture, ptosis, and infection.
Concerning contracture and ptosis, there was a higher incidence in textured than in polyurethane implants in the observed period, with a statistically significant difference.
Concerning seroma, there was no statistical difference between textured and polyurethane implants.
On the other hand, the frequency of infection was higher in polyurethane than in textured implants.
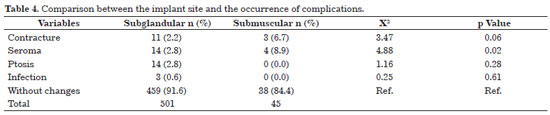
Table 4 shows that the overall incidence of complications was higher in submuscular implants (15.55%) than in subglandular implants (8.38%).
A statistically significant difference was found only in seroma, which showed a higher incidence in submuscular implants.
Concerning infection, there was no statistically significant difference between the two implantation sites although all instances of infection were observed in subglandular implants.
There was no statistical difference between contraction and ptosis in the observed period. However, contraction was almost significant, being more frequent in submuscular implants.
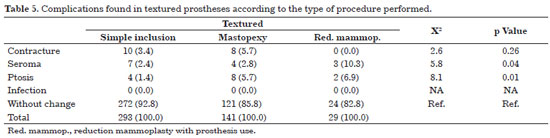
Table 5 shows that in patients with textured implants, ptosis and seroma showed statistically significant differences, being more frequent in those who underwent mammoplasties.
Among patients with seroma, we found similar rates between single inclusion and mastopexy; however, the incidence increased significantly in reduction mammoplasty.
Concerning ptosis, more complex procedures showed an increased statistical frequency of this complication.
Concerning contracture, there was no significant difference among patients with textured implants in various techniques.
No infection was observed in the group with textured implants.
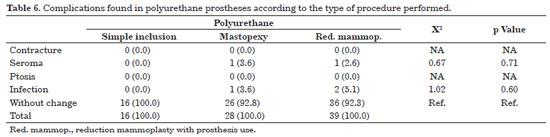
Table 6 shows that in patients implanted with polyurethane prostheses, there was no statistically significant difference between all the complications and the type of inclusion performed. However, it is important to note that all cases of infection appeared in the group with polyurethane prostheses and were progressively more frequent as the complexity of the procedure increased; however, the statistical analysis did not provide evidence for this observation.
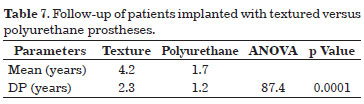
In Table 7, a statistically significant difference was found in the follow-up of each group. Patients who received textured implants had a mean follow-up of 4.2 years, in contrast to 1.7 years in those who received polyurethane implants.
As shown in Graphic 1, half of the patients who presented seroma developed the complication within 45 days after surgery, most within the first 20 days. Of those with late seroma, three patients developed the complication after weaning.
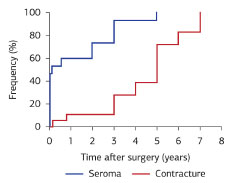
Graphic 1. Time of appearance of contracture and seroma.
There were rare contractures in the first year (0.36%), most of which appeared about 5 years after surgery.
DISCUSSION
Breast implants were introduced in 1962 by Cronin and Gerow, and since then they have been greatly improved. The high initial rate of capsular contracture in smooth implants was reduced by the introduction of textured coating, and subsequently of polyurethane13. Disruptions, usually caused by dissolution of the silicone wrap, have also declined owing to further strengthening of the material.
The polyurethane coating was introduced by Ashley as an alternative that cause less capsular5 contracture; it leads to the occurrence of a cellular response that leads to the formation of a capsule with nonlinear capsule fibrosis pattern, which does not produce a deforming spherical cap, and adheres to the breast tissue. Because its chemical degradation generates toluenediamine (2-4TDA), a carcinogenic product, polyurethane became the target of extensive investigations. Studies that found this by-product in urine were performed in rats and were not reproducible in humans. The Safety Panel of 1991 concluded that polyurethane is a safe material14 and, in 1995, its commercialization was authorized by the Food and Drug Administration.
Together with the general consensus that polyurethane minimizes capsular contracture, some authors showed that its degradation is related to the appearance of late contractures. The largest such study, which analyzed 75 explanted prostheses, concluded that polyurethane was undetectable at 3 years after implantation, especially in cases of contracture and infection15. In the personal experience of the author, there were two cases of polyurethane prostheses exchange; after 5 years, the polyurethane was found intact, with good adhesion to the breast tissue.
In the present study evaluating textured versus polyurethane implants, a higher frequency of contraction and ptosis was observed in the textured implants in the observed period; however, there was no difference in seroma. Importantly, contracture was not observed in polyurethane prostheses; however, the follow-up time was shorter (1.7 years in polyurethane vs. 4.2 years in textured). Considering that most contractures occurred at 5 years after implantation, this follow-up duration may have impaired the evaluation.
Only patients implanted with textured prostheses had ptosis in the observation period. There are several reports about the "Velcro effect" of polyurethane, involving a better attachment of breast tissue to the chest wall; however, this lacks scientific evidence.
When a prosthesis is not used, the results are often compromised by a lack of consistency of the breasts and poor fill of the cleavage; therefore, breast reduction with the use of prostheses has been done to improve the outcome. Moreover, the results are more lasting because the glandular liposubstitution effects are compensated by the presence of the implant, which maintains the round shape of the breast; however, ptosis occurs. The apparent paradox of placing a prosthesis in a surgery for breast reduction should be understood as a sum of the positive factors of each technique11.
This concept was introduced by Gonzalez-Ulloa in 19602. Baroudi, a pioneer of this procedure in Brazil, showed in 1976 that the inclusion of prosthesis in association with mastopexy was a safe surgery with good results, as ptosis correction with simple mastopexy often produces a good positioning of the gland with a lack of volume; on the other hand, the mere inclusion of a prosthesis in a ptotic breast has an unpleasant result of poor complex areolopapilar (CAP)10 positioning. Despite being highly criticized for the increased complication rate, it shows the advantages of being a single intervention, with lower costs and risks, and with faster return to daily activities. A study of 332 cases found a rather higher rate of complications, but only additively because two procedures were involved2.
In the comparison of simple inclusions, mastopexies, and reduction mammoplasties, no statistical difference in ptosis and seroma was found in the group with textured implants. Ptosis gradually increased with increasing complexity of the procedure, probably because patients with previous ptosis have more fragile skin. The rate of seroma was similar between simple inclusions and mastopexies; however, seroma was considerably more common in reduction mammoplasties.
On the other hand, although not statistically significant, all cases of infection occurred in the polyurethane group, and its incidence progressively increased with increasing complexity of the procedure. All cases of CAP necrosis occurred in reduction mammoplasties with polyurethane prostheses. These complications are rare but of great importance. Statistical comparison of these data was difficult owing to the nonoccurrence in all groups and the insufficient sample size.
Capsular contracture is the most common cause of reoperation for prosthesis replacement (Figure 1). It is graded from 1 to 4 according to Baker's criteria16. Its occurrence is heterogeneous in the literature, ranging from 0.86% to 58%1,3-6, attributable mainly to the follow-up criteria: the longer and more rigorous the procedure was, the greater the occurrence of capsular contracture. A study of 812 patients operated on in 15 years showed a contracture index of Baker 3 or 4, of 8.2% in 6 years, with saline and silicone1 prostheses. A prospective study of 5373 women operated on by a group of surgeons in 8 years showed a contracture index of Baker 3 or 4, 1.2% in 3 years, and 1.7% in 5 years; however, follow-up was performed only according to the patients' demand3. Another study of 752 patients, with a follow-up of 27 months, found a contracture rate of 8% that was higher in textured implants. Notably, the occurrence of hematoma doubled the risk of contracture4.
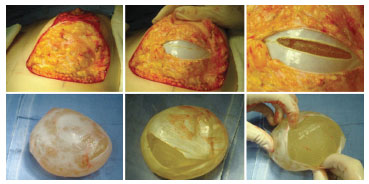
Figure 1. A 33 year-old patient was submitted to insertion of a textured subglandular periareolar prosthesis. The images are at 5 years after the procedure. One year after breast-feeding, she presented Baker 4 contracture on both breasts. During the replacement of the prosthesis, we found a very particular double capsule: within a thin and apparently normal capsule, we found another ball attached to the prosthesis, and this set was found loose in the first capsule. The patient had breast-fed, and she complained of breasts hardening soon after. Unnoticed seroma possibly developed during lactation, which occurred on the second deformed capsule. The patient was submitted to capsulectomy with prosthesis exchange with polyurethane, and showed good postoperative outcome.
The reported rates tended to be lower with polyurethane; however, this is also controversial. Miró found a 0.86% rate of contracture in 350 cases6. In a study of 294 patients implanted with polyurethane and followed for 19 years, there was a progressive incidence of contracture from 28% at 5 years to 58% at 15 years, with patients being systematically monitored. This was attributed to the increased incidence of polyurethane5 biodegradation.
A study of 227 patients with treated contractures in exchange for polyurethane suggests that 90% of patients can expect good breasts consistency up to the second decade. This emphasizes the need for capsulectomy to promote contact of polyurethane with the bloody tissue and cause its adhesion, thus preventing contractures17.
Bozola et al. evaluated 759 patients with polyurethane prostheses in 10 years, and found no contractures that required surgery12.
In the present study, we found a 3.3% frequency of Baker 3 and 4 contractures, with 3.9% occurring in the textured implants and none in the polyurethane implants during the observed period. Only two patients presented contracture in the first year, with most of them reporting such an occurrence after 5 years. Despite reports of an increased incidence after a hematoma, none of the patients in this study showed this phenomenon, even after a follow-up of 3 and 4 years. One possible reason could be because they were immediately reoperated for the removal of clots and washing of the implant site.
Another very common complication in the literature is seroma (Figure 2), the etiology of which remains uncertain. One of the most accepted theories is an infectious etiology; however, not always there are cultivated microorganisms in the liquid. In addition, we discuss the reason why infectious biofilms, although present, manifest late, often >2 years after surgery. In a 27-year study with smooth implants, textured Biocell®, and polyurethane, late seromas and double capsules were seen as an intraoperative incidental finding only with Biocell®; the study also discusses the possible mechanical effect of "shearing" of the capsule already formed in late seroma18.
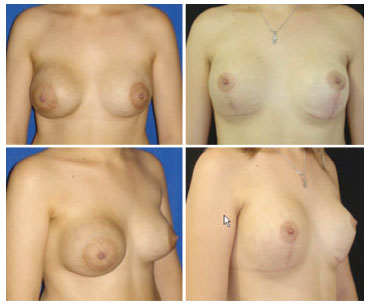
Figure 2. Photographs of a 22-year-old patient at 3 years after insertion of a subglandular textured prosthesis. She was nursing when she presented with a seroma. Ultrasound-guided puncture obtained 320 mL of citrine fluid with negative culture. She was treated with betamethasone. After a month, a new seroma was found with a positive culture for Staphylococcus aureus that was sensitive to ciprofloxacin. She was treated for 21 days with improvement. After 2 months, relapse occurred and she was indicated for surgery. A very thick, crispy, calcified capsule, with gelatinous content and adhered fibrin was found, which caused great doubt about the redeployment of the prosthesis. As the patient had no clinical infectious test and had negative inflammatory activity test, capsulectomy and replacement with a submuscular prosthesis was decided, with good progress after 1.5 years.
In this study, 2.4% of patients had seroma. There were no differences between textured and polyurethane implants; however, seroma was more frequent in submuscular implants. Concerning the complexity of the procedure, the highest incidence was found in reduction mammoplasty with textured implants; no incidence was observed with polyurethane. In addition, there were two intraoperative incidental findings of double capsules, both with textured implants.
A recent study investigated the relation between breast implants and the emergence of an anaplastic large cell lymphoma, a rare tumor associated with the occurrence of late seroma. Many authors have consistently recommended cytological testing of the oncotic liquid7-9. Tebbets proposed an algorithm for late seroma, emphasizing the need to perform puncture and cytological and bacteriological analysis. Extending the time of observation of the culture medium, considering low virulence and slow-growing bacteria, is also important. Capsule thickening, nodules, and/or a positive cytology indicate the need for capsulectomy with implant removal, to clarify the clinical state.
Infection in the implant site almost always requires removal of the prosthesis in a surgery with such great expectations. We found infection rates of around 1.7% to 2.8%1,4. The endogenous flora of the breast include staphylococci, diphtheroids, streptococci, and enterococci, with staphylococci being the most frequent cause of infection. Studies suggest an increased incidence of infection with polyurethane prosthesis, and with textured prosthesis in relation to the smooth type, due to the greater surface roughness and microporosity of polyurethane that facilitate bacterial adhesion. The presence of foreign bodies enhances infections: in the absence of a biomaterial, 1 ' 106 microorganisms are needed to cause infection; in its presence, 100 bacteria is enough19.
In the present study, we found an incidence of infection below what is found in the literature when considering the total number of patients (0.54%); however, the incidence with polyurethane (3.61%) was well above the reported rates, as infection only occurred with this material. This is a particularly relevant finding that could support the above theory; however, the sample size precludes a definitive conclusion. Agents were common and the AFB research negative. In an infection case after 7 months (Figure 3), a false-negative result was obtained for mycobacteria; however, the patient recovered well after conventional antibiotic therapy.
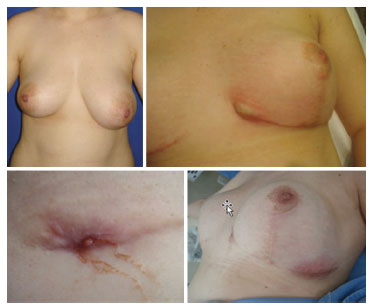
Figure 3. Photographs of a 25-year-old patient who underwent breast reduction, with insertion of advanced polyurethane prostheses. She developed seroma in the immediate postoperative period, which was treated clinically. After 7 months, she presented an abscess in the medial scar of the left breast. Ultrasonography showed a collection in contact with the prosthesis without periprosthesis liquid. Drained pus and bloody material were obtained, with a positive culture for Klebsiella pneumoniae that was sensitive to ciprofloxacin and negative for AFB. Clinical treatment attempts for 3 weeks were not successful and the prosthesis was removed, with good outcome.
The most widely accepted procedure in the presence of a clear evidence of infection involves implant withdrawal, antibiotics therapy, and a 4-6 months waiting time before the insertion of a new implant. This was performed with good results. There is a report of two successful cases submitted to site washing and immediate exchange of implants associated with antibiotic therapy20.
Another rare complication of significant impact is CAP necrosis (Figure 4), a condition related to blood perfusion deficiencies or excessive compression. In a previous study, partial necrosis was observed in 1.2%, and no cases of total necrosis were found2. In this study, both partial and total necrosis (0.36%) occurred with conical-shape polyurethane implants in reduction mammoplasty with subglandular prostheses. A possible cause is the devascularization of the CAP during the implant site preparation, plus maneuvers to its lift. Polyurethane adheres to the breast tissue, making it difficult to slip the pillars when closing the column. Furthermore, the conical profile fills the skin envelope, which decreases the skin area to be resected. This fact should be carefully considered by surgeons who are planning to use this type of implant, as it may hamper skin closure, leading to retraction, dehiscence, and necrosis. A case of partial necrosis was treated with resuture (Figure 4); however, a case of total necrosis required complete reconstruction, with significant prolongation of the recovery time.
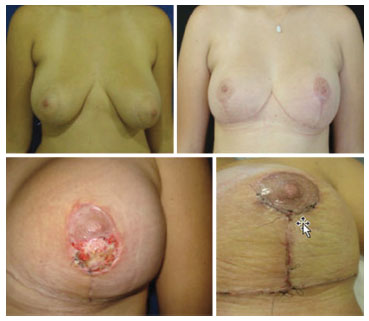
Figure 4. Photographs of a 17-year-old patient who underwent breast reduction, with insertion of an advanced polyurethane prosthesis. She developed partial necrosis of the CAP to the left, which was treated with debridement and resuture after 15 days, with good outcome.
CONCLUSIONS
In conclusion, in this study, a higher frequency of contraction and ptosis was found in textured than in polyurethane prostheses in the observed period. The absence of contracture with polyurethane was possibly related to the shorter follow-up time. A clear and relevant finding was infection, which occurred only with polyurethane prostheses.
The implantation plane adversely affected only the incidence of seroma, which was higher in the submuscular sites.
An increased complexity of the procedure was deleterious in textured prosthesis, as evidenced by the increased incidence of seroma and ptosis in patients who received mastopexy and breast reduction. In polyurethane prostheses, infection was progressively higher in groups with more complex procedures, although no statistical evidence was found. CAP necrosis occurred only in reduction mammoplasties with polyurethane prostheses.
A limitation of this study was the follow-up of patients who were not systematically called but only instructed to return in case of abnormalities. This manner of follow-up may have underestimated the number of complications.
The field of mammoplasty has a long way to go, and it is imperative that patients are strictly followed and that the results of studies are published. In this sum of experiences, we will find the safe guidelines for our procedures.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We thank Dr. José Carlos Ronche for his masterful comments, the couple Drs. Patricia and Vladmir Bermudez for the encouragement and invaluable assistance, and Dr. Nelson Fernandes de Moraes for suggestions and guidance.
REFERENCES
1. Codner MA, Mejia JD, Locke MB, Mahoney A, Thiels C, Nahai FR, et al. A 15-year experience with primary breast augmentation. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2011;127(3):1300-10. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0b013e318205f41b. PMid:21364430
2. Calobrace MB, Herdt DR, Cothron KJ. Simultaneous augmentation/mastopexy: a retrospective 5-year review of 332 consecutive cases. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2013;131(1):145-56. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0b013e318272bf86. PMid:22965238
3. Hvilsom GB, Hölmich LR, Henriksen TF, Lipworth L, McLaughlin JK, Friis S. Local complications after cosmetic breast augmentation: results from the Danish Registry for Plastic Surgery of the breast. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2009;124(3):919-25. PMid:19730312.
4. Handel N, Jensen JA, Black Q, Waisman JR, Silverstein MJ. The fate of breast implants: a critical analysis of complications and outcomes. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1995;96(7):1521-33. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/00006534-199512000-00003. PMid:7480271
5. Cohney BC, Cohney TB, Hearne VA. Nineteen years' experience with polyurethane foam-covered mammary prosthesis: a preliminary report. Ann Plast Surg. 1991;27(1):27-30. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/00000637-199107000-00004. PMid:1872550
6. Miró AL. Próteses mamárias revestidas com poliuretano: avaliação de 14 anos de experiência. Rev Bras Cir Plást. 2009;24(3):296-303.
7. Tebbetts JB. Diagnosis and management of seroma following breast augmentation: an update. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2011;128(1):17-25. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0b013e3182134aa3. PMid:21289545
8. Haeck PC, Eaves FF 3rd. Discussion: Diagnosis and management of seroma following breast augmentation: an update. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2011;128(1):29-31. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0b013e31821d2cb1. PMid:21701305
9. Hammond DC. Discussion: Diagnosis and management of seroma following breast augmentation: an update. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2011;128(1):26-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0b013e318217e61c. PMid:21701302
10. Baroudi R, Lewis JR Jr. The augmentation-reduction mammaplasty. Clin Plast Surg. 1976;3(2):301-8. PMid:1261184.
11. Saldanha OR, Maloof RG, Dutra RT, Luz OAL, Saldanha Filho O, Saldanha CB. Mamaplastia redutora com implante de silicone. Rev Bras Cir Plást. 2010;25(2):317-24.
12. Bozola AR, Bozola AC, Carrazzoni RM. Inclusão de próteses mamárias de silicone-poliuretano. Rev Bras Cir Plást. 2006;21(1):18-22.
13. Sperli A, Bersou A Jr, Freitas JOG, Michalany N. Complicações com próteses mamarias. Rev Bras Cir Plást. 2000;15(3):33-46.
14. Safety of polyurethane-covered breast implants. Expert panel on the safety of polyurethane-covered breast implants. CMAJ. 1991;145(9):1125-32. PMid:1751934.
15. Sinclair TM, Kerrigan CL, Buntic R. Biodegradation of the polyurethane foam covering of breast implants. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1993;92(6):1003-13, discussion 1014. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/00006534-199311000-00001. PMid:8234496
16. Baker JL Jr. The effectiveness of alpha-tocopherol (vitamin E) in reducing the incidence of spherical contracture around breast implants. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1981;68(5):696-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/00006534-198111000-00004. PMid:7291341
17. Hester TR Jr, Tebbetts JB, Maxwell GP. The polyurethanecovered mammary prosthesis: facts and fiction (II): a look back and a "peek" ahead. Clin Plast Surg. 2001;28(3):579-86. PMid:11471963.
18. Hall-Findlay EJ. Breast implant complication review: double capsules and late seromas. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2011;127(1):56-66. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0b013e3181fad34d. PMid:21200201
19. Jennings DA, Morykwas MJ, Burns WW, Crook ME, Hudson WP, Argenta LC. In vitro adhesion of endogenous skin microorganisms to breast prostheses. Ann Plast Surg. 1991;27(3):216-20. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/00000637-199109000-00005. PMid:1952748
20. Pitanguy I, Amorim NFG, Ferreira AV, Berger R. Análise das trocas de implantes mamários nos últimos cinco anos na Clínica Ivo Pitanguy. Rev Bras Cir Plást. 2010;25(4):668-74. http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S1983-51752010000400019.
Full Member of Sociedade Brasileira de Cirurgia Plástica (SBCP), Goiânia, GO, Brazil
Institution: Work conducted at Institute of Surgery and Laser, Goiânia, GO, Brazil.
Corresponding author:
Raquel Eckert Montandon
Instituto de Cirurgia e Laser
Avenida T-2, 435, setor bueno
Goiânia, GO, Brazil CEP 74210-010
E-mail : raquel8385@hotmail.com
Article received: June 9, 2013.
Article accepted: February 4, 2014.


 Read in Portuguese
Read in Portuguese
 Read in English
Read in English
 PDF PT
PDF PT
 Print
Print
 Send this article by email
Send this article by email
 How to Cite
How to Cite
 Mendeley
Mendeley
 Pocket
Pocket
 Twitter
Twitter