
Original Article - Year 2005 - Volume 20 -
The use of cyanoacrylate in the cutaneous repair of primary cheiloplasties
Uso do Cianoacrilato no Fechamento Cutâneo das Queiloplastias Primárias
ABSTRACT
This works reports on the experience of the authors with the use of N-Butyl-Cyanoacrylate for the cutaneous closure of primary cheiloplasties in unilateral fissures, comparing the esthetic results with those to 6.0 mononylon sutures. Between April 1999 and December 2003, 62 primary cheiloplasties were performed in the Hospital Municipal Infantil Menino de Jesus utilizing the Millard's rotation-advancement lip repair technique. In Group A, comprised of 35 patients, the skin was sutured using 6.0 mononylon thread. For Group B, comprised of 27 patients, the skin was repaired using N-Butyl- Cyanoacrylate adhesive. The groups were evaluated on the 1st, 7th, 30th and 90th days after surgery. There were no cases of surgical infection. One (3.4%) patient of Group B presented with dehiscence less than one day after surgery requiring conventional suturing. One (2.8%) child of Group A required general anesthesia to remove the suture. The esthetic results of scaring were similar in both the groups studied. The authors stress the advantages of the optimization of this adhesive in the pediatric population. The advantages include the facility and simplicity of its use, the low cost, the time of the surgeon, reduction in the time of surgery and, most importantly, there is no necessity to remove the sutures, thereby reducing the stress of the child and family members in the postoperative return appointment.
Keywords: Tissue adhesives. Cyanoacrylate. Suture techniques. Cleft lip. Cleft palate
RESUMO
Este trabalho mostra a experiência dos autores com o uso do N-Butil- Cianoacrilato no fechamento cutâneo de queiloplastias primárias em fissuras unilaterais, observando os resultados estéticos em relação à sutura de mononylon 6.0. Entre abril de 1999 e dezembro de 2003, 62 queiloplastias primárias foram realizadas no Hospital Municipal Infantil Menino de Jesus, utilizando-se a técnica de rotação e avanço de Millard. No grupo A, composto por 35 pacientes, a pele foi suturada com fio de mononylon 6.0. No grupo B, com 27 pacientes, a pele foi aproximada com o adesivo N-Butil-Cianoacrilato. Os grupos foram avaliados no pós-operatório 1, 7, 30 e 90 dias após a cirurgia. Não houve casos de infecção cirúrgica. Um (3,4%) paciente do grupo B apresentou deiscência no mesmo dia da cirurgia, necessitando de sutura convencional. Uma (2,8%) criança do grupo A necessitou de anestesia geral para a retirada da sutura. Os resultados estéticos das cicatrizes foram semelhantes nos dois grupos estudados. Os autores destacam as vantagens da otimização deste adesivo na população pediátrica, que incluem facilidade e simplicidade no uso, baixo custo, utilização do tempo do profissional, diminuição do tempo cirúrgico e, principalmente, a desnecessidade de remoção das suturas, diminuindo assim o estresse da criança e dos familiares no retorno pós-operatório.
Palavras-chave: Adesivos teciduais. Cianoacrilatos. Técnicas de sutura. Fenda labial. Fissura palatina
Os cianoacrilatos são monômeros que quando em contato com fluidos ou tecidos se polimerizam, levando à adesão tecidual. Estudos comprovam que o N-Butil-Cianoacrilato tem baixa toxicidade tecidual, mantém boa força tênsil e tem propriedades bactericidas e bacteriostáticas1-3. Sua segurança já foi comprovada em mais de vinte anos de uso clínico, sendo a primeira escolha no tratamento de lacerações cutâneas traumáticas, em crianças em diversos centros pediátricos americanos e europeus4-8.
Os resultados estéticos a longo prazo mostraram-se semelhantes à sutura convencional em estudos comparativos prospectivos9,10. Recentemente, seu uso estendeu-se para o fechamento de feridas cirúrgicas eletivas não tensas, com bons resultados e baixa morbidade11-15.
Este estudo tem como objetivo descrever os resultados clínicos obtidos com o fechamento cutâneo da queiloplastia primária unilateral, com o adesivo N-Butil-N-Cianoacrilato e com a sutura convencional com mononylon 6.0.
MÉTODO
Entre abril de 1999 e novembro de 2003, 62 crianças foram submetidas a queiloplastia primária unilateral pela técnica de rotação e avanço de Millard, no Hospital Municipal Infantil Menino de Jesus - São Paulo. As cirurgias foram realizadas pelo assistente da Disciplina de Cirurgia Plástica e pelos residentes sob sua supervisão.
Os planos da mucosa oral, vermelhão e assoalho nasal foram fechados com poliglactina 910 (vicryl) 5.0 e o plano muscular com mononylon 5.0. Os pacientes foram divididos em grupo A (n=35), em que a pele foi suturada com mononylon 6.0 e grupo B (n=27), no qual a pele foi aproximada com o adesivo N-Butil- Cianoacrilato (Hystoacryl Blue - Laboratório B. Braun). A utilização da cola foi determinada pela disponibilidade do produto no dia da operação, não importando a amplitude da fissura labial ou a presença de fissura palatina associada.
A Figura 1 mostra a distribuição dos pacientes dos grupos A e B quanto ao tipo de fissura. A idade média na época da cirurgia foi de 1 ano e 2 meses (3m a 7a 6m) e 1 ano e 2 meses (3m a 7 a 9m) para os grupos A e B, respectivamente. O seguimento pós-operatório foi de 2 anos para o grupo A e de 2 anos e 7 meses para o grupo B.
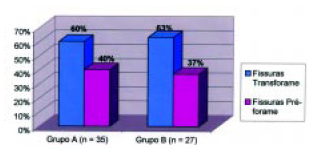
Figura 1 - Incidência das fissuras nos grupos A e B.
No grupo B, após a aproximação das bordas cutâneas com fios de reparo, uma pequena quantidade do adesivo foi colocada sobre a incisão cutânea (Figuras 2 a 5). O produto não deve penetrar na ferida e não há necessidade de aplicação em camadas. Em casos de aplicação inadequada, o adesivo pode ser removido e reaplicado.
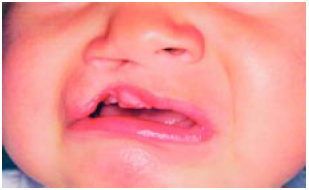
Figura 2 - Caso 1 : Pré-operatório de fissura pré-forame unilateral em criança de 5 meses de idade.
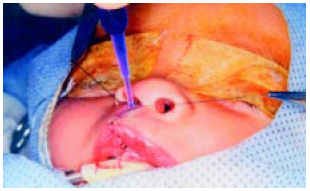
Figura 3 - Caso 1 : Coaptação das bordas cutâneas com fios de reparo e aplicação do N-Butil-Cianoacrilato.
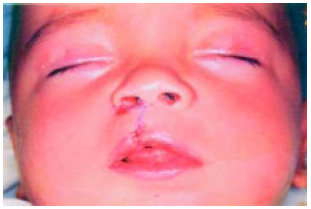
Figura 4 - Caso 1 : pós-operatório imediato.
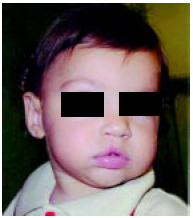
Figura 5 - Caso 1 : Pós-operatório 18 meses.
Em todos os casos, a incisão foi deixada exposta no dia seguinte à cirurgia. A sutura foi retirada com 7 dias e o adesivo descamou naturalmente após 5 a 7 dias.
Nas 62 queiloplastias foram observados os seguintes aspectos no pós-operatório de 1 dia e 7 dias: infecção (secreção purulenta) e deiscência. No pós-operatório de 30 e 90 dias, observamos a qualidade da cicatriz resultante, classificando-as subjetivamente em alargada, avermelhada e aumentada.
RESULTADOS
Nenhum paciente apresentou infecção pós-cirúrgica. Um (3,5%) caso de deiscência de ferida operatória foi verificado no grupo B, no mesmo dia da cirurgia, sendo necessária sutura com mononylon 6.0. A causa foi atribuída à aplicação incorreta do adesivo, aliada à tensão excessiva da pele. No grupo A, uma (2,6%) criança necessitou de anestesia geral para a retirada da sutura. Os resultados estéticos das cicatrizes foram semelhantes nos dois grupos a partir dos critérios observados anteriormente (Figuras 2 a 7).
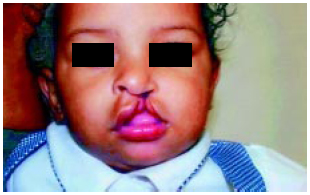
Figura 6 - Caso 2 : Pré-operatório de fissura transforame unilateral em criança com 11 meses de idade.
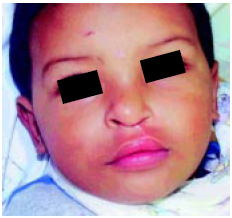
Figura 7 - Caso 2 : Pós-operatório 12 meses com o uso do cianoacrilato.
DISCUSSÃO
A fissura lábio-palatina é uma afecção complexa e multidisciplinar. É muito importante a compreensão da interferência dos procedimentos cirúrgicos no desenvolvimento psicológico do paciente. Na retirada da sutura, a contenção da criança muitas vezes é necessária e, não raro, uma nova anestesia geral. A maior vantagem do uso do adesivo cutâneo é a possibilidade de evitar esse trauma, uma das razões que faz com que seja a primeira opção na reparação de lacerações cutâneas em grandes centros pediátricos pelo mundo4-8.
Estudos com o uso do N-Butil-2-Cianoacrilato, no setor de emergência pediátrica, mostram que os familiares percebem um menor sofrimento de seus filhos (aplicação indolor e desnecessidade de retirada de sutura) e recomendariam mais este produto para outros pais do que a sutura convencional8,10. A maioria dos centros evita o seu uso em áreas de muita mobilidade, juntas, lesões muito tensas e contaminadas, bem como feridas maiores que 4 ou 5 cm4,6,7,9. Além das restrições anteriores, Bruns et al.8 não utilizam adesivos em áreas como lábios, nariz, orelhas, mãos, pés e períneo.
Bowen e Selinger13 realizaram um estudo comparativo do uso do N-Butil-2-Cianoacrilato e suturas com vicryl no fechamento de episiotomias e demonstraram que com o uso do adesivo houve uma diminuição significativa da dor pós-operatória à deambulação e um retorno mais precoce à atividade sexual.
Howell et al.3, em estudos com modelos animais, demonstraram menor crescimento bacteriano nas incisões fechadas com N-Butil-2-Cianoacrilato, quando comparadas à sutura convencional, além de um efeito bacteriostático contra Staphylococcus aureus3. Quinn et al.2 confirmam estas propriedades bacteriostáticas e bactericidas, mostrando também o isolamento da ferida operatória do meio externo, diminuindo sua contaminação no pós-operatório.
Os índices de infecção pós-operatória e deiscência mostram-se baixos nas diversas casuísticas, demonstrando a segurança e baixa morbidade do uso dos adesivos cutâneos4-15. A maioria das complicações relatadas, como a vermelhidão na cicatriz, infecções e deiscências, provavelmente é inerente aos próprios procedimentos cirúrgicos, e não à utilização específica do adesivo12.
Os resultados estéticos a curto e longo prazo são excelentes na maioria dos trabalhos4-8,11,12, dados confirmados em alguns estudos prospectivos comparativos com suturas convencionais9,10.
Na prática clínica, muitos pacientes com fissura lábiopalatina não se beneficiam com o uso da cola devido à presunção do seu alto custo, principalmente porque são os hospitais públicos que mais tratam destes pacientes. Messi et al.5 demonstraram a possibilidade de reutilização do produto por até 12 vezes, desde que a ponta do aplicador seja cortada após cada uso. A adaptação de uma agulha à ponta do aplicador e a troca da mesma após o uso também tornam o reaproveitamento seguro. A durabilidade da cola é longa (dias) se guardada sob refrigeração. Isso faz do N-Butil-2- Cianoacrilato um método mais barato do que a sutura cutânea com fio de nylon convencional5,10,12. Além disso, este produto tem um aplicador com ponta delicada e precisa, razão pela qual foi escolhido para esta pesquisa.
Como conclusão, a utilização do N-Butil-2-Cianoacrilato no fechamento cutâneo de queiloplastias primárias provou ser um método seguro, simples e mais barato que a sutura com mononylon, apresentando resultados estéticos semelhantes aos da sutura convencional, baixa morbidade, possível diminuição na dor pós-operatória e, principalmente, a desnecessidade de retirada, evitando trauma e estresse para a criança, seus familiares e o profissional.
REFERÊNCIAS BIBLIOGRÁFICAS
1. Yaron M. Erin MH, Huffer WC, Caims C. Efficacy of tissue glue for laceration repair in an animal model. Acad Emerg Med. 1995;2(4):259-63.
2. Quinn JV, Osmond MH, Yurack JA, Moir PJ. N-2 butylcyanoacrylate: risk of bacterial contamination with an appraisal of its antimicrobial effects. J Emerg Med. 1995;13(4):581-5.
3. Howell JM, Bresnahan KA, Stair TO, Dhindsa HS, Edwards BA. Comparison of effects of suture and cyanoacrylate tissue adhesive on bacterial counts in contaminated lacerations. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1995;39(2):559-60.
4. Mizrahi S, Bickel A, Ben-Layish E. Use of tissue adhesives in the repair of lacerations in children. J Pediatr Surg. 1988;23(4):312-3.
5. Messi G, Canciani G, Marchi AG. Costs and benefits of the use of tissue adhesives in wounds in children. Pediatr Med Chir. 1990;12(2):185-8.
6. Applebaum JS, Zalut T, Applebaum D. The use of tissue adhesion for traumatic laceration repair in the emergency department. Ann Emerg Med. 1993;22(7):1190-2.
7. Quinn JV, Drzewiecki A, Li MM, Stiell IG, Sutcliffe T, Elmslie TJ et al. A randomized, controlled trial comparing a tissue adhesive with suturing in the repair of pediatric lacerations. Ann Emerg Med. 1993;22(7):1130-5.
8. Bruns TB, Simon HK, McLario DJ, Sullivan KM, Wood RJ, Anand KJ. Laceration repair using a tissue adhesive in a children's emergency department. Pediatrics. 1996;98(4 pt 1):673-5.
9. Simon HK, McLario DJ, Bruns TB, Zempsky WT, Wood RJ, Sullivan KM. Long-term appearance of lacerations repaired using a tissue adhesive. Pediatrics. 1997;99(2):193-5.
10. Goktas N, Karcioglu O, Coskun F, Karaduman S, Menderes A. Comparison of tissue adhesive and suturing in the repair of lacerations in the emergency department. Eur J Emerg Med. 2002;9(4):360.
11. Kosko PI. Upper lid blepharoplasty: skin closure achieved with butyl-2-cyanoacrylate. Ophthalmic Surg. 1981;12(6):424-5.
12. Amiel GE, Sukhotnik I, Kawar B, Siplovich L. Use of n-butyl- 2-cyanoacrylate in elective surgical incisions: long term outcomes. J Am Coll Surg. 1999;189(1):21-5.
13. Bowen ML, Selinger M. Episiotomy closure comparing enbucrilate tissue adhesive with conventional sutures. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2002;78(3):201-5.
14. Yavuzer R, Basterzi Y, Tuncer S. Using tissue adhesives for closure of periareolar incisions in breast reduction surgery. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2003;112(1):337.
15. Sinha S, Naik M, Wright V, Timmons J, Campbell AC. A single blind, prospective, randomized trial comparing n-butyl 2-cyanoacrylate tissue adhesive (Indermil) and sutures for skin closure in hand surgery. J Hand Surg. 2001;26(3):264-5.
I. Médica Cirurgiã Plástica; Especialista pela Sociedade Brasileira de Cirurgia Plástica.
II. Médico Cirurgião Plástico; Cirurgião-Dentista Bucomaxilofacial.
Correspondência para:
Tatiana Martins Caloi
Empresarial Burle Marx - Av. Gov. Agamenon Magalhães, 2615, sala 104
Boa Vista, Recife, PE, Brasil - CEP: 50050-290
Tel: 0xx81 3231-6808
E-mail: tatianacaloi@terra.com.br
Trabalho realizado no Hospital Municipal Infantil Menino de Jesus - São Paulo.
Artigo recebido: 02/12/2004
Artigo aprovado: 23/01/2005


 Read in Portuguese
Read in Portuguese
 Read in English
Read in English
 PDF PT
PDF PT
 Print
Print
 Send this article by email
Send this article by email
 How to Cite
How to Cite
 Mendeley
Mendeley
 Pocket
Pocket
 Twitter
Twitter