
Original Article - Year 2013 - Volume 28 -
Breast reconstruction using a definitive expander implant: an account of a personal experience
Reconstrução mamária com implante expansor definitivo: experiência pessoal
ABSTRACT
INTRODUCTION: With the impossibility of prosthetic implantation with a definitive final volume due to dehiscence and posterior extrusion risks, the development of skin-sparing mastectomy provides an ideal condition for the use of a definitive expander implant. Therefore, this study aimed to demonstrate the use of a definitive expander implant and discuss its indications, cutaneous incision, and safety, as well as its advantages and complications.
METHODS: Thirty 150 definitive expander implants were used in 27 women who underwent mastectomy between March 1998 and March 2012.
RESULTS: Twenty-nine reconstructions were performed immediately after skin-sparing mastectomy and only 1 was performed after a late Halstead mastectomy. The complication rate was low, with seroma being the most frequent (20%), followed by valve dislocation (13.3%), pain in valve location (10%), post-radiotherapy capsular contracture (3.3%), infection (3.3%), and late extrusion (3.3%). No complications such as hematomas, cutaneous incision, and early extrusion were encountered, and none of the cases required surgical repositioning of the expander implant.
CONCLUSIONS: Despite its high cost, the use of a definitive expander implant may be considered as a potential breast reconstruction modality because it is associated with low complication rates and is easy to use. In our study, the appropriate indications and systematized cutaneous incisions, combined with the various definitive expander implant shapes and volumes, led to the satisfactory aesthetic results of the breast reconstruction in a single surgical stage.
Keywords: Breast neoplasms. Mastectomy. Mammaplasty. Tissue expansion devices. Reconstructive surgical procedures/methods.
RESUMO
INTRODUÇÃO: Com o advento da técnica de mastectomia conservadora de pele (skin-sparing mastectomy), em que muitas vezes há impossibilidade de implante de prótese com volume final definitivo, sob risco de deiscência e extrusão posterior da mesma, surge a situação ideal para se optar pela introdução de um implante expansor definitivo. Este artigo demonstra a utilização do implante expansor definitivo, suas indicações, incisão cutânea, segurança, vantagens e complicações.
MÉTODO: Trinta implantes expansores definitivos (estilo 150) foram utilizados em 27 mulheres submetidas a mastectomia, no período de março de 1998 a março de 2012.
RESULTADOS: Vinte e nove reconstruções foram imediatas pós-mastectomia com economia de pele e apenas uma foi tardia pós-mastectomia tipo Halstead. Os índices de complicação encontrados foram baixos: seromas (20%), deslocamento da válvula (13,3%), dor no local da válvula (10%), contratura capsular pós-radioterapia (3,3%), infecção (3,3%) e extrusão tardia (3,3%). Não houve complicações como hematomas, necroses cutâneas e extrusões precoces, bem como necessidade de cirurgias para reposicionar o expansor.
CONCLUSÕES: O baixo índice de complicações e a facilidade de realização da técnica são fatores importantes para a decisão de sua utilização, apesar do custo ainda elevado. A adequada indicação e a incisão cutânea sistematizada, combinadas a uma variedade de formatos e volumes dos expansores definitivos, permitiram resultado estético satisfatório, num único estágio cirúrgico.
Palavras-chave: Neoplasias da mama. Mastectomia. Mamoplastia. Dispositivos para expansão de tecidos. Procedimentos cirúrgicos reconstrutivos/métodos.
Breast reconstruction is offered to the majority of patients who undergo mastectomy, and it is performed immediately or later after mastectomy. With the improvement of diagnostic methods, surgical techniques for breast cancer treatment have become less invasive and more economical in terms of breast skin preservation (e.g., with the skin-sparing mastectomy [SSM]).
In particular, prophylactic mastectomy has greatly increased in popularity and is similarly economical for skin removal as SSM. However, this type of approach, even as an "economic" initiative for skin preservation, can leave the breast skin very thin and with poor blood circulation. When cutaneous damage becomes an obstacle to establishing the final volume of the definitive prosthesis, posing risks of dehiscence and posterior extrusion, the use of a definitive expander implant is recommended.
In 1982, the use of temporary breast expander implants, which require later replacement with a definitive prosthesis, was first proposed by Radovan1. In 1984, Becker2 advocated the use of a permanent round expander that combines the benefits of silicone gel, saline, and expander implants in one product and allows performing breast reconstruction in a single stage. Since then, implants have been used based on format and architecture3-6.
This study is a retrospective analysis of a group of patients who underwent breast reconstruction with the definitive expander implant between 1998 and 2012. Herein, the indications, technique, and complications of the procedure are described.
METHODS
Between March 1998 and March 2012, 30 breast reconstructions with a 150 definitive expander implant were performed in 27 patients (Figure 1) with a mean age of 38.7 years (range, 26-55 years). All available reconstruction techniques were presented to the patients for them to choose from, in consideration of expected conditions after mastectomy. Nevertheless, breast reconstruction with the definitive expander implant was specifically recommended for the following patients:

Figure 1 - The definitive expander implant, a biodimensional anatomical implant.
Patients indicated for radiotherapy were directed to decide on another surgical technique.those with small breasts indicated for SSM with papillary-areolar complex (PAC) removal; those with small or medium breasts indicated for SSM, PAC removal, and addition of an elliptical skin section; those indicated for SSM who request for breast augmentation; those indicated for SSM but whose remaining breast skin is in poor condition, making placement of a prosthesis with a proportional volume to the contralateral breast impossible; those indicated for total mastectomy with myocuta-neous flap of the large dorsal muscle, but attaining a final prosthesis volume proportional to the contralateral breast would not be possible.
From an oncological point of view, SSM was recommended to the following patients in the present study:
The decision to remove the PAC was based on the distance between the tumor and the structure, as assessed by nuclear magnetic resonance and additional perioperative retroareolar biopsy.those with small breasts with in situ multifocal carcinoma; those with small breasts with tumors measuring 2 to 5 cm; those indicated for neoadjuvant chemotherapy but with persistent recommendation for mastectomy; young patients with a high family risk of cancer.
The mastologist first discussed the cutaneous mastectomy incision, with consideration of the patient's condition and initial lesion location, for which an oblique incision of the axillary extension is preferential (Figure 2). A second, transverse incision, which is more frequently performed, was made to the inframammary fold. In comparison with the transverse incision, the oblique incision was demonstrated to be safer owing to the underlying pectoral muscles, which provides protection for the expander implant.
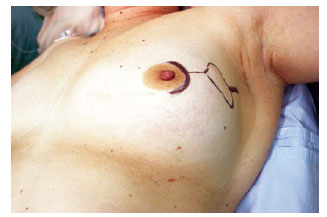
Figure 2 - Surgical marking on the breast skin.
The following types of mastectomy were performed:
SSM with PAC preservation; SSM with PAC removal and removal of a piece of skin; Halstead total mastectomy (Table 1).
Most implant units were placed in 2 cover positions, that is, retropectoral or under the pectoralis major, and subglan-dular. The inferior and lateral margins of the pectoral muscle were removed. The cutaneous section of the inferior breast quadrant was sutured to the inferior margin of the pectoralis major muscle, forming a protective pocket for the expander and, when possible, preserving the inframammary fold limit, which is not always achieved.
In cases of total mastectomy and removal of the PAC associated with a cutaneous segment, the mastologist would prefer to use the large dorsal muscle section to supplement the cutaneous framework, with the myocutaneous section of the large dorsal muscle providing a complete cover of the expander implant, without utilizing the pectoralis major.
Sections of the superior portions of the serratus anterior and rectus abdominis muscles were necessary in patients whose mastectomy incision was transverse to the inframam-mary fold or vertical to the lower pole. Before and during surgery, the height, length, and projection dimensions of the breasts for treatment were measured to provide insight as to the most appropriate expander implant.
A vacuum drain was used in all the patients after surgery. The valve was positioned in a subcutaneous pocket of the lateral thoracic wall and lower to the inframammary fold at approximately 2 to 3 cm from the drain exit. None of the expander implants were filled with physiological serum during the operation. The expansion was started on approximately on the 20th postoperative day or later, when the skin presented a healthy circulatory aspect and the incision had completely healed. Expansion was performed weekly in the clinic, increasing the total implant volume by 10% with each session. Contralateral breast remodeling was completed during the same surgical stage in most of the cases.
The results were presented based on the relative frequency distribution of qualitative variables.
RESULTS
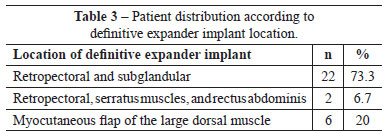
Twenty-six patients (86.7%) were indicated for immediate breast reconstruction; and 3 (10%), for bilateral breast reconstruction. Only 1 reconstruction (3.3%), was performed after Halstead mastectomy, requiring rotation of the myocu-taneous flap of the large dorsal muscle. Unilateral mastectomy (SSM) with PAC preservation was the most frequently used treatment modality in this group of patients (Tables 2 and 3).
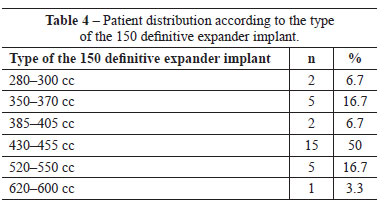
The definitive expander implant used was anatomically textured and biodimensional, with a varied silicone gel content according to the size chosen. The expander implant was oval shaped and had a low or full height according to the pre-and post-mastectomy pocket measurements. The expander implant most frequently used had a volume ranging from 430 to 455 cc (15 cases) with a 215-mL silicone gel content. The final expander implant volume, at the end of expansion, varied from 300 to 500 mL (mean, 371.47 mL; Table 4).
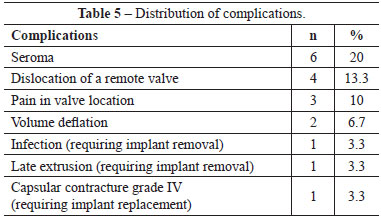
The postoperative follow-up duration varied from 6 months to 10 years. Complications included 6 immediate postoperative cases (20%) of seroma, which were treated with puncture aspiration. The start of expansion accelerated residual seroma reabsorption (Table 5). Valve dislocation was encountered in 4 patients (13.3%), requiring minor surgery under local anesthesia for localization and expansion. In the immediate postoperative period, no adverse events such as hematomas or cutaneous necrosis were observed.
One patient (3. 3 %) presented with expander implant contamination on the third postoperative month after chemotherapy, which required removal of the expander implant. Three patients (10%) reported pain in the valve location, with local anesthesia intervention required for a later deeper placement after expansion completion. Two patients (6.7%) requested an expander implant replacement with a larger definitive prosthesis and therefore an increase in the contralateral breast. Another 2 patients (6.7%) reported a spontaneous long-term reduction in expander volume, requesting late expansion for an adjustment of the final volume. Only 1 patient (3.3%) presented with extrusion, which occurred 1 year after the operation. Another patient (3.3%) had intense capsular contracture occurring 1 year after the procedure and radiotherapy, requiring expander implant removal. All the patients opted for a concomitant approach, with prosthesis placement in the contralateral breast (Figures 3 to 6).
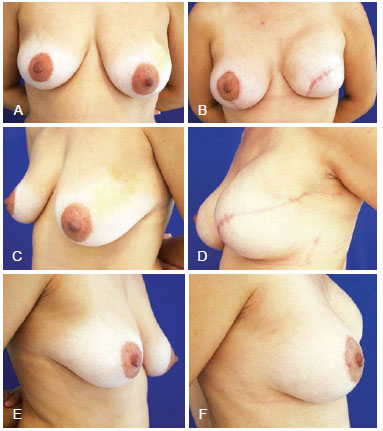
Figure 3 - Mastectomy in the left breast and breast reconstruction with expander prosthesis, mastopexy, and prosthesis placement in the opposite breast. In A, C, and E, Pre-surgical aspect from the front, left oblique, and right oblique views, respectively. In B, D, and F, Postoperative aspect from the front, left oblique, and right oblique views, respectively.
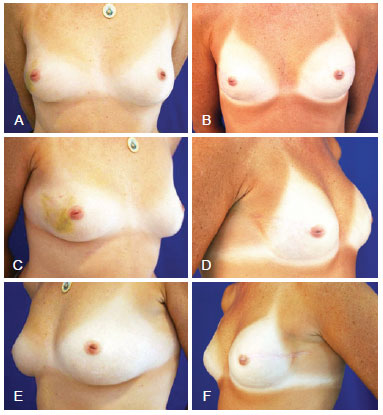
Figure 4 - Mastectomy in the right breast (skin-sparing mastectomy), and breast reconstruction with definitive expander prosthesis and prosthesis implant in the contralateral breast. In A, and E, Preoperative aspect from the front, right oblique, and left oblique views, respectively. In B, D, and F, Postoperative aspect from the front, right oblique, and left oblique views, respectively.
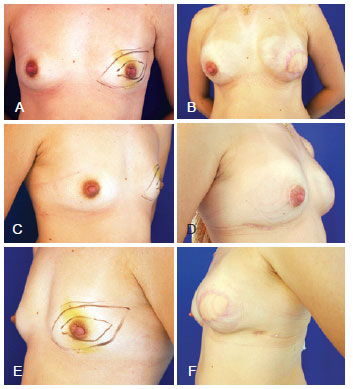
Figure 5 - Mastectomy in the left breast (skin-sparing mastectomy with removal of the papillary-areola complex and skin section), and breast reconstruction with the large dorsal muscle and definitive expander prosthesis and prosthesis implantation in the contralateral breast. In A, C, and E, Preoperative aspect from the front, right oblique, and left oblique views, respectively. In B, D, and F, Postoperative aspect from the front, right oblique, and left oblique views, respectively.
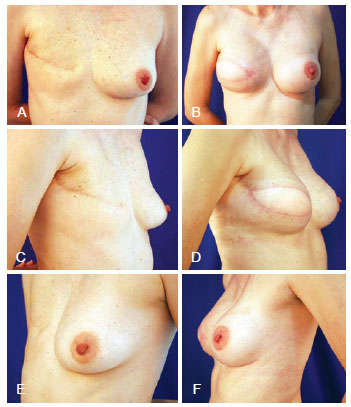
Figure 6 - Halstead mastectomy, and breast reconstruction with large dorsal muscle definitive expander prosthesis and prosthesis implantation in the contralateral breast. In A, C, and E, Preoperative aspect from the front, right oblique, and left oblique views, respectively. In B, D, and F, Postoperative aspect from the front, right oblique, and left oblique views, respectively.
DISCUSSION
Our institution began using the definitive expander implant in 1998, when breast reconstruction was not yet covered by all health insurance plans. In comparison with other available techniques, the use of a definitive expander implant was restricted due to its high cost. In recent years, with the change in health insurance policies to cover breast reconstruction and the increase in the use of skin-sparing mastectomy, the definitive expander implant has been increasingly recommended for breast reconstruction.
One of the advantages of the technique is the cost reduction of surgery for adjusting definitive prosthesis volume, flap remodeling, or replacement of provisional expander implants with definitive permanent implants. Aside from allowing any desired increases in volume, the technique allows skin healing after mastectomy, preserving the breast skin without tension. Therefore, this results in lower risks of dehiscence and implant contamination.
In contrast with patients in the studies of Guimarães et al.7 and Manfredini8, the patients in our study did not use the transpectoral route with combined elevation of the pectoral muscles, serratus anterior, and abdominis rectus. Instead, the preferred route for expander implant introduction was the lateral edge of the pectoral muscle with superior, medial, and inferior displacements combined with the cutaneous flap of the inferior breast quadrant. Other than being fast and safe to perform, it does not require inferior pole breast rectification. For patients who underwent extensive skin removal, the myocutaneous flap of the great dorsal muscle was used to provide total protection for the expander implant.
Immediate breast reconstruction did not significantly delay, reduce, or interfere with administration of adjuvant chemotherapy and was not associated with late diagnosis9-13. In addition, the emotional benefits of immediate breast reconstruction have been widely discussed.
In 2001, Vandeweyer et al.14 discussed the oncological risks of immediate reconstruction with saline implants, concluding that the technique is safe and does not alter the biological behavior of the tumor. Nevertheless, radiotherapy was considered a limiting factor to expander implant placement, as the local post-radiotherapy reaction is highly intense and provokes severe capsular contracture. In their study, they observed only 1 case of Baker class IV capsular contracture, secondary to postoperative radiotherapy, which required expander implant removal.
Scuderi et al.15 verified that in the assessment of 204 patients indicated for reconstruction with Becker expander implants, 34.2% of complications were associated with healing, bleeding, and seromas aside from valve obstruction (2%), dislocation (1.6%), class III and IV capsular contracture (2.4%), and poor implant positioning (1.6%). Despite these complications, the authors concluded that breast reconstruction with a permanent expander implant is a useful technique for patients indicated for simple or modified radical mastectomy.
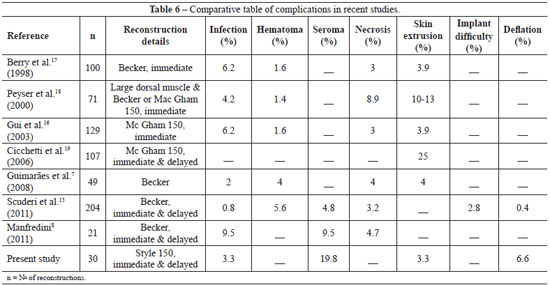
In 2003, Gui et al.16 reported incidence rates of 6.2%, 1.6%, and 3.9% for infection, hematoma, and implant loss in 129 breast reconstructions. Meanwhile, in the 30 reconstructions presented in this study, minor complications occurred, such as seromas (20%), valve dislocation (13.3%), pain in valve location (10%), and expander implant volume reduction (6.7%). In addition, we encountered 1 case (3.3%) of late infection related with a chemotherapy session and 1 late extrusion (3.3%; Table 6).
In their study published in 2004, Di Benedetto et al.20 discussed the advantages of breast expander implants in the lateral valve position in comparison with the medial position. The former has more advantages, although these are initially less obvious to patients. In the present study, the valve was positioned in the lateral thorax of all the patients.
Cicchetti et al.20 defined definitive expander implants as a revolution in reconstructive surgery. In 107 reconstructed breasts with McGhan 150 expander implants, the authors identified grade III or IV capsular contracture in 26% of cases, with a high rate of extrusion due to local metastasis of the disease. Chew et al.21 performed a study of patients indicated for definitive expander implant reconstruction, with a mean follow-up period of 12.5 years. They indicated that during a 10-year period, only 9.5% of expander implants were not removed.
In accordance with the report by Gui et al.16, reconstruction with the definitive expander implant presents a high level of satisfaction for physicians and patients. In the present study, only 2 patients (6.6%) requested replacement of the prosthesis with a larger one to provide an increase in volume, along with prosthesis replacement for the contralateral breast.
Expander implants with a greater volume also allow the new breast to reach variable sizes according to the patient's preference in contralateral volume. The positioning of the inframammary fold in relation to the contralateral breast has been one of the most difficult situations presented. Nevertheless, no request for expander implant repositioning has been made thus far.
The preferential incision for SSM was the external lateral oblique incision of the nipple toward the axilla (armpit), providing cover of the inferior pole of the implant with intact and better vascularized skin, considering that the large pectoral muscle does not always cover the whole inferior portion of an implant. Furthermore, this incision allows for the mastologist to address the axilla.
CONCLUSIONS
Breast reconstruction using the definitive expander implant improved the safety of SSM reconstructions, which in many cases would otherwise increase the risk of vascular compromise. The most frequent complication was seroma. The need for implant removal due to infection was low, as was the need for removal of the expander implant due to post-radiotherapy contracture, as confirmed by contraindication of the definitive expander implant in patients indicated for follow-up radiotherapy.
The expander implants with larger volumes allowed for the new breast to reach various sizes, according to the volume of the contralateral breast. In our study, the appropriate indications and systematized cutaneous incisions, combined with the various definitive expander implant shapes and volumes, led to the satisfactory aesthetic results of the breast reconstruction in a single surgical stage.
REFERENCES
1. Radovan C. Breast reconstruction after mastectomy using the temporary expander. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1982;69(2):195-208.
2. Becker H. Breast reconstruction using an inflatable breast implant with detachable reservoir. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1984;73(4):678-83.
3. Mansel RE, Horgan K, Webster DJ, Shrotria S, Hughes LE. Cosmetic results of immediate breast reconstruction post-mastectomy: a follow-up study. Br J Surg. 1986;73(10):813-6.
4. Becker H. The expandable mammary implant. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1987;79(4):631-7.
5. Becker H. The permanent tissue expander. Clin Plast Surg. 1987;14(3):519-27.
6. Becker H. Breast augmentation using the expander mammary prosthesis. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1987;79(2):192-9.
7. Guimarães GS, Daher JC, Cammarota MC. Reconstrução mamária com expansor permanente: uma outra alternativa. Rev Bras Cir Plást. 2008;23(2):75-81.
8. Manfredini RL. Reconstrução mamária com expansor definitivo: enfoque diferenciado. Rev Bras Cir Plást. 2011;26(3):472-80.
9. Rowland JH, Holland JC, Chaglassian T, Kinne D. Psychological response to breast reconstruction. Expectations for and impact on post-mastectomy functioning. Psychosomatics. 1993;34(3):241-50.
10. Atabek U, Barot L, Matthews M, Brown AS, Spence RK, Mossberg L, et al. Immediate breast reconstruction after mastectomy. N Engl J Med. 1993;90(5):379-82.
11. Rosenqvist S, Sandelin K, Wickman M. Patients' psychological and cosmetic experience after immediate breast reconstruction. Eur J Surg Oncol. 1996;22(3):262-6.
12. Ramon Y, Ullmann Y, Moscona R, Ofiram E, Tamir A, Har-Shai Y, et al. Aesthetic results and patient satisfaction with immediate breast reconstruction using tissue expansion: a follow-up study. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1997;99(3):686-91.
13. Spear SL, Majidian A. Immediate breast reconstruction in two stages using textured, integrated-valve tissue expanders and breast implants: a retrospective review or 171 consecutive breast reconstructions from 1989 to 1996. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1998;101(1):53-63.
14. Vandeweyer E, Hertens D, Nogaret JM, Deraemaecker R. Immediate breast reconstruction with saline-filled implants: no interference with the oncologic outcome? Plast Reconstr Surg. 2001;107(6):1409-12.
15. Scuderi N,Alfano C, Campus GV, Rubino C, Chiummariello S, PudduA, et al. Multicenter study on breast reconstruction outcome using Becker implants. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2011;35(1):66-72.
16. Gui GP, Tan SM, Faliakou EC, Choy C, A'Hern R, Ward A. Immediate breast reconstruction using biodimensional anatomical permanent expander implants: a prospective analysis of outcome and patient satisfaction. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2003;111(1):125-38.
17. Berry MG, al-Mufti RA, Jenkinson AD, Denton S, Sullivan M, Vaus A, et al. An audit of outcome including patient satisfaction with immediate breast reconstruction performed by breast surgeons. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 1998;80(3):173-7.
18. Peyser PM, Abel JA, Straker VF, Hall VL, Rainsbury RM. Ultra-conservative skin-sparing "keyhole" mastectomy and immediate breast and areola reconstruction. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2000;82(4):227-35.
19. Cicchetti S, Leone MS, Franchelli S, Santi PL. One-stage breast reconstruction using McGhan Style 150 biodimensional expanders: a review of 107 implants with six years experience. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2006;59(10):1037-42.
20. Di Benedetto G, Aquinati A, Santoli M, Bertani A. Which is the best position for the remote injection dome using the adjustable expander/prosthesis in breast reconstruction? A comparative study. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2004;113(6):1629-33.
21. Chew BK, Yip C, Maylon AD. Becker expander implants: truly a long term single stage reconstruction? J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2010;63(8):1300-4.
Plastic surgeon, full member of the Sociedade Brasileira de Cirurgia Plástica (Brazilian Society of Plastic Surgery), director and owner of the Clínica Vanité, São José dos Campos, SP, Brazil
Correspondence to:
Claudia Francisco Oliveira
Av. Barão do Rio Branco, 508 - Jardim Esplanada
São José dos Campos, SP, Brazil - CEP 12242-800
E-mail: clinicavanite@terra.com.br
Submitted to SGP (Sistema de Gestão de Publicações/Manager Publications System) of RBCP (Revista Brasileira de Cirurgia Plástica/Brazilian Journal of Plastic Surgery).
Article received: November 18, 2012
Article accepted: March 10, 2013
This study was performed at the Clínica Vanité, São José dos Campos, SP, Brazil.


 Read in Portuguese
Read in Portuguese
 Read in English
Read in English
 PDF PT
PDF PT
 Print
Print
 Send this article by email
Send this article by email
 How to Cite
How to Cite
 Mendeley
Mendeley
 Pocket
Pocket
 Twitter
Twitter