
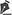
Original Article - Year 2013 - Volume 28 -
Adhesion stitches in rhytidoplasty: a comparative study
Pontos de adesão nas ritidoplastias: estudo comparativo
ABSTRACT
BACKGROUND: Hematomas are one of the most frequent complications in the immediate postoperative period following rhytidoplasty. In the present study, we aimed to assess the efficacy of using adhesion stitches to prevent the development of hematomas following rhytidoplasty.
METHODS: We performed a retrospective assessment of 2 groups of 88 patients who underwent rhytidoplasty. Adhesion stitches were applied to all patients in group 2, but not to those in group 1.
RESULTS: Five patients (5.7%) in group 1 developed massive hematomas that were treated surgically and 12 patients (13.6%) developed small hematomas that were resolved by local puncture. The patients in group 2 did not develop any hematoma that required surgical evacuation. Five patients (5.68%) developed small hematomas that were resolved by local puncture and 4 patients (4.54%) developed seromas.
CONCLUSIONS: During rhytidoplasty, the bilateral application of 12-15 adhesion stitches in the dissected areas prevented the development of hematomas that required surgical evacuation, thus improving postoperative recovery.
Keywords: Rhytidoplasty/methods. Face/surgery. Hematoma/prevention & control.
RESUMO
INTRODUÇÃO: Os hematomas constituem uma das complicações mais frequentes no pós-operatório imediato de ritidoplastias. O objetivo deste estudo é avaliar a eficácia do emprego de pontos de adesão na prevenção de hematomas em ritidoplastias.
MÉTODO: Foram avaliados, retrospectivamente, 2 grupos constituídos por 88 pacientes submetidos a ritidoplastia. Os pacientes do grupo 1 não receberam pontos de adesão, que foram aplicados em todos os pacientes do grupo 2.
RESULTADOS: No grupo 1, foram observados 5 (5,7%) hematomas extensos, que foram tratados cirurgicamente, e 12 (13,6%) hematomas de pequeno porte, solucionados com punção local. No grupo 2, não foi verificado nenhum hematoma que necessitasse limpeza cirúrgica. Foram observados 5 (5,68%) casos com pequenas coleções hemáticas, solucionados com punção local, e 4 (4,54%) seromas.
CONCLUSÕES: Durante ritidoplastias, a aplicação de 12 a 15 pontos de adesão nas áreas dissecadas, bilateralmente, proporcionou melhor recuperação no período pós-operatório, com ausência de hematomas que exigissem limpeza cirúrgica.
Palavras-chave: Ritidoplastia/métodos. Face/cirurgia. Hematoma/prevenção & controle.
Hematomas are one of the most frequent complications in the immediate postoperative period following rhytidoplasty and are caused by a variety of conditions, such as hypertensive crisis, vomiting, agitation, pain, and vesical distention. The surgeon's approach and technical precautions, with regard to hemostasis and extension of the dissected areas, are also important.
The use of medication during the days preceding the procedure, including certain vitamins, Ginkgo biloba, and aspirin can also interfere with the coagulation mechanism.1,2
Vacuum or Penrose drains have been routinely used by surgeons in order to prevent the formation of hematomas; however, this is not always sufficient to avoid these problems.
The use of adhesion stitches applied to the pre- and retroauricular regions has completely reduced the incidence of hematomas requiring urgent surgical drainage.3,4 The number of adhesion stitches applied and the distance between them vary according to the surgeon. Moreover, the use of fibrin glue is also not frequent due to a variety of factors, including its cost.
In the present study, we aimed to assess the efficacy of using adhesion stitches to prevent the development of hematomas following rhytidoplasty.
METHODS
The present study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Hospital Regional de Taubate (Taubate, SP, Brazil).
A retrospective assessment of 2 groups of 88 patients who underwent rhytidoplasty was performed.
Adhesion stitches were not applied to the patients in group 1 because the surgical team was not familiar with adhesion stitches routinely used in abdominoplasty procedures; however, adhesion stitches were applied to all patients in group 2.
The procedures were performed according to the specifications outlined for each case.
Surgical Technique
Patients in groups 1 and 2 underwent the surgical procedure under intravenous sedation and local anesthesia using 0.25% lidocaine and epinephrine (1: 200,000).
Skin dissection was performed according to previously marked limits, and hemostasis was achieved through thermocautery. Thereafter, platysma plication,5,6 excess skin resection, and suturing were performed.
The patients in group 2 underwent the same dissection steps, hemostasis, and excess skin resection. However, unlike in group 1, the skin flap was adjusted around the ear in group 2 patients and sutured at 2 reference points: an anterior point at the root of the helix and a second point at the apex of the retroauricular incision (Figure 1). To mark both the skin and the dissected tissue underneath, the skin was marked and transfixed at 12-15 points in the pre- and retroauricular regions using a needle with methylene blue applied at the distal end (Figure 2). The flap was reopened and adhesion stitches were applied using 3-0 or 4-0 monocryl absorbable thread at each marking (Figure 3). Thereafter, the edges were sutured with isolated stitches using 6-0 nylon thread in the preauricular region and 4-0 nylon thread in the retroauricular region.
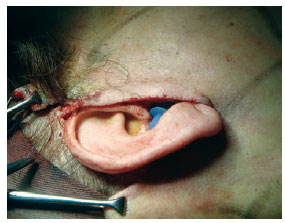
Figure 1 - Detailed view of the cervicofacial skin flap dissected according to the marked limits and pulled with 1 temporary fixing stitch at the root of the helix and 1 fixing stitch at the apex of the retroauricular incision.
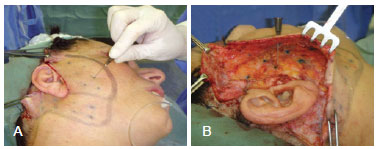
Figure 2 - In A, a needle with methylene blue applied at the distal end externally transfixes and marks the skin 12 to 15 times. In B, dissected tissue exhibiting the markings made with methylene blue.
Figure 3 - In A and B, isolated adhesion stitches using 4-0 monocryl thread are applied for better adjustment of the skin flap on the dissected tissue underneath.
In both groups, occlusive dressings and Penrose drains were used and maintained for 24 hours.
RESULTS
In group 1, 5 patients (5.7%) had massive hematomas that were treated surgically. One of the patients was taking Ginkgo biloba and was not excluded from the sample. Twelve patients (13.6%) had small hematomas that were resolved by puncture (6 in the retroauricular region, 5 in the preauricular region, and 1 in the cervical region). Two patients (2.3%) who were smokers developed minimal skin necrosis in the retroauricular region, with a necrotic area of approximately 2 cm2.
The patients in group 2 did not develop any hematoma that required surgical evacuation. Five patients (5.68%) developed small hematomas and 4 patients (4.54%) developed seromas (3 were located in the pre- and retroauricular regions and 1 in the zygomatic region) that were treated by puncture.
DISCUSSION
Vasoconstrictor administration combined with extensive dissections are routinely performed by plastic surgeons during rhytidoplasty procedures, despite the associated complications such as hematoma formation.5-7
Skin markings performed using a hypodermic needle applied with methylene blue following skin dissection, excess skin resection, and temporary repositioning of the skin at 2 reference points (1 at the root of the helix and 1 at the apex of the retroauricular incision) are simple procedures that can be used to guide the application of adhesion stitches. Moreover, the application of these stitches is guided by 12-15 perforations in order to better adjust the skin flap suture around the ear with a high degree of adhesion, thereby reducing the risk of hematoma development to a great extent (Figures 4 to 7).
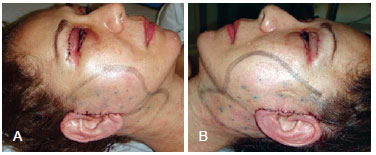
Figure 4 - In A and B, final appearance (absence of ecchymoses or hematomas).
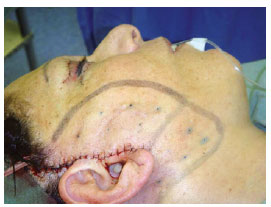
Figure 5 - Postoperative image of the sutured skin flap. Small skin depressions, if present, disappear within a few days postoperatively.
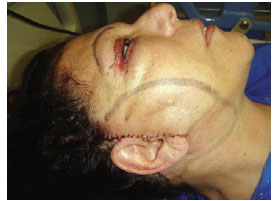
Figure 6 - Appearance on the first postoperative day (absence of ecchymoses and hematomas).
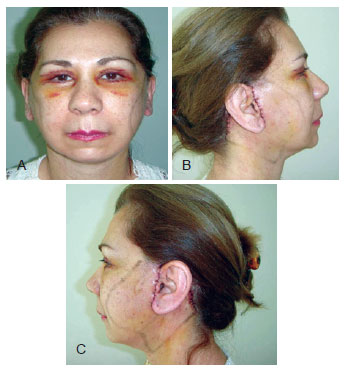
Figure 7 - Facial appearance on the third postoperative day (minimal ecchymosis).
In the present study, the benefit of using adhesion stitches was confirmed by the absence of hematoma development and minimal ecchymosis in the patients in group 2. Prior transfixion of skin using a needle applied with methylene blue facilitates the easy application of adhesion stitches.
In addition to the use of adhesion stitches, less-extensive dissections combined with selective tunneling using doublesided underminers8-10 can reduce the incidence of hematoma formation.
CONCLUSIONS
During rhytidoplasty, the bilateral application of 12-15 adhesion stitches in the dissected areas prevented the development of hematomas that required surgical evacuation, thus improving postoperative recovery.
REFERENCES
1. Baroudi R, Ferreira CA. Contouring the hip and the abdomen. Clin Plast Surg. 1996;23(4):551-72.
2. Baroudi R, Ferreira CA. Seroma: how to avoid it and how to treat it. Aesthet Surg J. 1998;18(6):439-41.
3. Destro MW, Speranzini MB, Cavalheiro Filho C, Destro T, Destro C. Bilateral haematoma after rhytidoplasty and blepharoplasty following chronic use of Ginkgo biloba. Brit J Plast Surg. 2005;58(1):100-1.
4. Destro MWB, Speranzini MB, Destro C, Guerra C, Recco GC, Romagnolo LGC. Estudo da utilização no pré-operatório de medicamentos ou drogas fitoterápicas que alteram a coagulação sanguínea. Rev Col Bras Cir. 2006;33(2):107-11.
5. Baker DC. Complications of cervicofacial rhytidectomy. Clin Plast Surg. 1983;10(3):543-62.
6. Baker CD, Stefani WA, Chiu ES. Reducing the incidence of hematoma requiring surgical evacuation following male rhytidectomy: a 30-year review of 985 cases. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2005;116(7):1973-85.
7. Barton EF Jr. Aesthetic surgery of the face and neck. Aesthet Surg J. 2009;29(6):449-63.
8. Luz DF, Wolfenson M, Figueiredo J, Didier JC. Full-face undermining using progressive dilators. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2005;29(2):95-9.
9. Menezes MVA, Abla LEF, Dutra LB, Junqueira AE, Ferreira LM. Avaliação dos resultados do mini-lifting modificado: estudo prospectivo. Rev Bras Cir Plást. 2010;25(2):285-90.
10. Saldanha OR. Ritidoplastia com descolamento seletivo. In: Luz D, ed. Técnica Dílson Luz. Tunelizações progressivas: princípios, aplicações e procedimentos complementares. Rio de Janeiro: Dilivros; 2010. p. 99-108.
1. Plastic Surgeon, Doctor in Surgery, Full Member of the Sociedade Brasileira de Cirurgia Plástica (Brazilian Society of Plastic Surgery - SBCP), Head of the Plastic Surgery Department at the Hospital Regional do Vale do Paraíba, Taubaté, SP, Brazil
2. Plastic Surgeon, Associate Member of the SBCP, Member of the Clinical Staff at the Hospital Regional de Taubaté, Taubaté, SP, Brazil
3. Plastic Surgeon, Full Member of the SBCP, Editor-in-chief of the Revista Brasileira de Cirurgia Plástica, Campinas, SP, Brazil
Correspondence to:
Marco Willians Baena Destro
Rua Joaquim Tavares, 50
Taubaté, SP, Brazil - CEP 12020-280
E-mail: marcodestro@uol.com.br
Submitted to SGP (Sistema de Gestão de Publicações/Manager Publications System) of RBCP (Revista Brasileira de Cirurgia Plástica/Brazilian Journal of Plastic Surgery).
Article received: July 5, 2012
Article accepted: September 29, 2012
This study was performed at the Hospital Regional do Vale do Paraíba, Taubaté, SP, Brazil.


 Read in Portuguese
Read in Portuguese
 Read in English
Read in English
 PDF PT
PDF PT
 Print
Print
 Send this article by email
Send this article by email
 How to Cite
How to Cite
 Mendeley
Mendeley
 Pocket
Pocket
 Twitter
Twitter